Abstract
Introduction
Alterations in the microbiome contribute to the pathogenesis of many gastrointestinal diseases. However, the composition of the microbiome in gallbladder disease is not well described.
Methods
We aimed to characterize the biliary microbiome in cholecystectomy patients. Bile and biliary stones were collected at cholecystectomy for a variety of surgical indications between 2017 and 2019. DNA was extracted and metagenomic sequencing was performed with subsequent taxonomic classification using Kraken2. The fraction of bacterial to total DNA reads, relative abundance of bacterial species, and overall species diversity were compared between pathologies and demographics.
Results
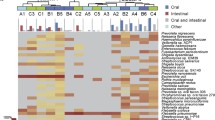
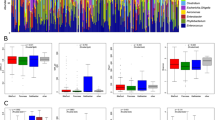
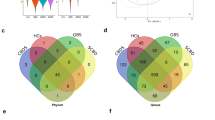
A total of 74 samples were obtained from 49 patients: 46 bile and 28 stones, with matched pairs from 25 patients. The mean age was 48 years, 76% were female, 29% were Hispanic, and 29% of patients had acute cholecystitis. The most abundant species were Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus pasteurianus. The bacterial fraction in bile and stone samples was higher in acute cholecystitis compared to other non-infectious pathologies (p < 0.05). Neither the diversity nor differential prevalence of specific bacterial species varied significantly between infectious and other non-infectious gallbladder pathologies. Multivariate analysis of the non-infectious group revealed that patients over 40 years of age had increased bacterial fractions (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Metagenomic sequencing permits characterization of the gallbladder microbiome in cholecystectomy patients. Although a higher prevalence of bacteria was seen in acute cholecystitis, species and diversity were similar regardless of surgical indication. Additional study is required to determine how the microbiome can contribute to the development of symptomatic gallbladder disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Konturek PC, Koziel J, Dieterich W, Haziri D, Wirtz S, Glowczyk I et al. Successful therapy of Clostridium difficile infection with fecal microbiota transplantation. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;67(6):859-66.
Sokol H, Seksik P, Rigottier-Gois L, Lay C, Lepage P, Podglajen I et al. Specificities of the fecal microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2006;12(2):106-11. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.MIB.0000200323.38139.c6.
Bercik P, Denou E, Collins J, Jackson W, Lu J, Jury J et al. The intestinal microbiota affect central levels of brain-derived neurotropic factor and behavior in mice. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(2):599-609, .e1-3. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.04.052.
Broido PW, Gorbach SL, Condon RE, Nyhus LM. Upper intestinal microfloral control. Effects of gastric acid and vagal denervation on bacterial concentrations. Arch Surg. 1973;106(1):90-3. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1973.01350130088020.
Russo MW, Wei JT, Thiny MT, Gangarosa LM, Brown A, Ringel Y et al. Digestive and liver diseases statistics, 2004. Gastroenterology. 2004;126(5):1448-53. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2004.01.025.
Portincasa P, Moschetta A, Palasciano G. Cholesterol gallstone disease. Lancet. 2006;368(9531):230-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(06)69044-2.
Maki T. Pathogenesis of calcium bilirubinate gallstone: role of E. coli, beta-glucuronidase and coagulation by inorganic ions, polyelectrolytes and agitation. Annals of surgery. 1966;164(1):90–100. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-196607000-00010.
Cetta FM. Bile infection documented as initial event in the pathogenesis of brown pigment biliary stones. Hepatology. 1986;6(3):482-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.1840060327.
Trotman BW. Pigment gallstone disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1991;20(1):111-26.
Ikeda T, Yanaga K, Kusne S, Fung J, Higashi H, Starzl TE. Sterility of bile in multiple-organ donors. Transplantation. 1990;49(3):653-. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007890-199003000-00036.
Begley M, Gahan CG, Hill C. The interaction between bacteria and bile. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005;29(4):625-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsre.2004.09.003.
Molinero N, Ruiz L, Milani C, Gutiérrez-Díaz I, Sánchez B, Mangifesta M et al. The human gallbladder microbiome is related to the physiological state and the biliary metabolic profile. Microbiome. 2019;7(1):100. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-019-0712-8.
Maurer KR, Everhart JE, Ezzati TM, Johannes RS, Knowler WC, Larson DL et al. Prevalence of gallstone disease in Hispanic populations in the United States. Gastroenterology. 1989;96(2 Pt 1):487-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(89)91575-8.
KneadData. https://huttenhower.sph.harvard.edu/kneaddata/.
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England). 2014;30(15):2114-20. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170.
Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nature Methods. 2012;9(4):357-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923.
Wood DE, Lu J, Langmead B. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biology. 2019;20(1):257. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1891-0.
Lu J BF, Thielen P, Salzberg SL. Bracken: estimating species abundance in metagenomics data. PeerJ Computer Science. 2017;3:e104. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.104.
Shen W, Ren H. TaxonKit: A practical and efficient NCBI taxonomy toolkit. Journal of Genetics and Genomics. 2021;48(9):844-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2021.03.006.
16S Illumina Amplicon Protocol. https://earthmicrobiome.org/protocols-and-standards/16s/.
Edgar RC. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(19):2460-1. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461.
Edgar RC. SINTAX: a simple non-Bayesian taxonomy classifier for 16S and ITS sequences. bioRxiv. 2016:074161. https://doi.org/10.1101/074161.
Cole JR, Wang Q, Fish JA, Chai B, McGarrell DM, Sun Y et al. Ribosomal Database Project: data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):D633-42. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1244.
McMurdie PJ, Holmes S. phyloseq: an R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e61217. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061217.
R Development Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2019.
Chung CS, Chang PF, Liao CH, Lee TH, Chen Y, Lee YC et al. Differences of microbiota in small bowel and faeces between irritable bowel syndrome patients and healthy subjects. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2016;51(4):410-9. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2015.1116107.
Dlugosz A, Winckler B, Lundin E, Zakikhany K, Sandström G, Ye W et al. No difference in small bowel microbiota between patients with irritable bowel syndrome and healthy controls. Scientific Reports. 2015;5(1):8508. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08508.
Jovel J, Patterson J, Wang W, Hotte N, O’Keefe S, Mitchel T et al. Characterization of the Gut Microbiome Using 16S or Shotgun Metagenomics. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:459-. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00459.
Brumfield KD, Huq A, Colwell RR, Olds JL, Leddy MB. Microbial resolution of whole genome shotgun and 16S amplicon metagenomic sequencing using publicly available NEON data. PLoS One. 2020;15(2):e0228899. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228899.
Choi SJ, Kim Y, Jeon J, Gwak HJ, Kim M, Kang K et al. Association of Microbial Dysbiosis with Gallbladder Diseases Identified by Bile Microbiome Profiling. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(28):e189. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e189.
Shen H, Ye F, Xie L, Yang J, Li Z, Xu P et al. Metagenomic sequencing of bile from gallstone patients to identify different microbial community patterns and novel biliary bacteria. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17450. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17450.
Natsui M, Honma T, Genda T, Nakadaira H. Effects of endoscopic papillary balloon dilation and endoscopic sphincterotomy on bacterial contamination of the biliary tract. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;23(9):818-24. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0b013e328348c0bf.
Wu T, Zhang Z, Liu B, Hou D, Liang Y, Zhang J et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis and bacterial community assembly associated with cholesterol gallstones in large-scale study. BMC Genomics. 2013;14:669. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-669.
de Martel C, Plummer M, Parsonnet J, van Doorn LJ, Franceschi S. Helicobacter species in cancers of the gallbladder and extrahepatic biliary tract. Br J Cancer. 2009;100(1):194-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6604780.
Barbara L, Sama C, Labate AMM, Taroni F, Rusticali AG, Festi D et al. A population study on the prevalence of gallstone disease: The sirmione study. Hepatology. 1987;7(5):913-7. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.1840070520.
Friedman GD, Kannel WB, Dawber TR. The epidemiology of gallbladder disease: observations in the Framingham Study. Journal of chronic diseases. 1966;19(3):273-92.
Einarsson K, Nilsell K, Leijd B, Angelin B. Influence of age on secretion of cholesterol and synthesis of bile acids by the liver. New England Journal of Medicine. 1985;313(5):277-82.
Sampliner RE, Bennett PH, Comess LJ, Rose FA, Burch TA. Gallbladder disease in Pima Indians: demonstration of high prevalence and early onset by cholecystography. New England Journal of Medicine. 1970;283(25):1358-64.
Maurer KR, Everhart JE, Knowler WC, Shawker TH, Roth HP. Risk factors for gallstone disease in the Hispanic populations of the United States. Am J Epidemiol. 1990;131(5):836-44. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115574.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This abstract was presented virtually at the Scientific Forum of the American College of Surgeons’ Clinical Congress October 2020.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Limberg, J., Egan, C.E., Mora, H.A. et al. Metagenomic Sequencing of the Gallbladder Microbiome: Bacterial Diversity Does Not Vary by Surgical Pathology. J Gastrointest Surg 26, 2282–2291 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-022-05418-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-022-05418-6