Abstract
Introduction
We assessed whether positive microbiological cultures from the islet preparation had any effect on the risk of infectious complications (IC) after total pancreatectomy with islet autotransplantation (TPIAT) in our center.
Methods
We analyzed preservation fluid and final islet product surveillance cultures with reference to clinical data of patients undergoing TPIAT. All patients received routine prophylactic broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Results
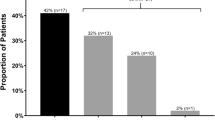
The study involved 10 men and 18 women with a median age of 39 years. Over 30% of surveillance cultures during pancreas processing grew bacterial strains with predominantly polymicrobial contaminations (13 of 22 (59%)). At least one positive culture was identified in almost half of the patients (46%) undergoing TPIAT and a third had both surveillance cultures positive. Infectious complications affected 50% of patients. After excluding cases of PICC line-associated bacteremia/fungemia present on admission, incidence of IC was higher in cases of positive final islet product culture than in those with negative result (57% vs. 21%), which also corresponded with the duration of chronic pancreatitis (p = 0.04). Surgical site infections were the most common IC, followed by fever of unknown origin. There was no concordance between pathogens isolated from the pancreas and those identified during the infection.
Conclusions
While IC was common among TPIAT patients, we found no concordance between pathogens isolated from the pancreas and those identified during infection. Contamination of the final islet product was of clinical importance and could represent a surrogate marker for higher susceptibility to infection.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HbA1c:
-
Hemoglobin A1c
- ERCP:
-
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
- IEQ:
-
Islet equivalent units
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- TPIAT:
-
Total pancreatectomy with islet autotransplantation
References
Okano K, Hirao T, Unno M, Fujii T, Yoshitomi H, Suzuki S, Satoi S, Takahashi S, Kainuma O, Suzuki Y. Postoperative infectious complications after pancreatic resection. Br J Surg. 2015;102:1551–60.
Fisher AV, Sutton JM, Wilson GC, Hanseman DJ, Abbott DE, Smith MT, Schmulewitz N, Choe KA, Wang J, Sussman JJ, Ahmad SA. High readmission rates after surgery for chronic pancreatitis. Surgery.2014;156:787–94.
Shahbazov R, Naziruddin B, Yadav K, Saracino G, Yoshimatsu G, Kanak MA, Beecherl E, Kim PT, Levy MF. Risk factors for early readmission after total pancreatectomy and islet auto transplantation. HPB (Oxford). 2018;20:166–174.
Berger MG, Majumder K, Hodges JS, Bellin MD, Schwarzenberg SJ, Gupta S, Dunn TB, Beilman GJ, Pruett TL, Freeman ML, Wilhelm JJ, Sutherland DE, Chinnakotla S. Microbial contamination of transplant solutions during pancreatic islet autotransplants is not associated with clinical infection in a pediatric population. Pancreatology. 2016;16:555–62.
Witkowski P, Savari O, Matthews JB. Islet autotransplantation and total pancreatectomy. Adv Surg 2014;48:223–33.
Savari O, Golab K, Wang LJ, Schenck L, Grose R,Tibudan M, et al. Preservation of beta cell function after pancreatic islet autotransplantation: University of Chicago experience. Am Surg 2015;81:421–7.
Vantyghem MC, Raverdy V, Balavoine AS et al. Continuous glucose monitoring after islet transplantation in type 1 diabetes: an excellent graft function (β-score greater than 7) Is required to abrogate hyperglycemia, whereas a minimal function is necessary to suppress severe hypoglycemia (β-score greater than 3). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97:E2078–83.
Schneider J, Schenk P, Obermeier A, Fremd J, Feihl S, Forkl S, Wantia N, Römmler F, Neu B, Bajbouj M, von Delius S, Schmid RM, Algül H, Weber A. Microbial colonization of pancreatic duct stents: a prospective analysis. Pancreas. 2015;44:786–90.
Hill SK, Bhalla C, Thomson A. Risk of bacterial colonization of pancreatic stents used in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;46:324–7.
Kozarek R, Hovde O, Attia F, France R. Do pancreatic duct stents cause or prevent pancreatic sepsis?. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:505–9.
Carroll PB, Ricordi C, Fontes P, Rilo HR, Phipps J, Tzakis AG, Fung JJ, Starzl TE. Microbiologic surveillance as part of human islet transplantation: results of the first 26 patients. Transplant Proc. 1992;24:2798–9.
Wray CJ, Ahmad SA, Lowy AM, D'Alessio DA, Gelrud A, Choe KA, Soldano DA, Matthews JB, Rodriguez-Rilo HL. Clinical significance of bacterial cultures from 28 autologous islet cell transplant solutions. Pancreatology. 2005;5:562–9.
Johnson CN, Morgan KA, Owczarski SM, Wang H, Fried J, Adams DB. Autotransplantation of culture-positive islet product: is dirty always bad?. HPB (Oxford). 2014;16:665–9.
Colling KP, Blondet JJ, Balamurugan AN, Wilhelm JJ, Dunn T, Pruett TL, Sutherland DE, Chinnakotla S, Bellin M, Beilman GJ. Positive sterility cultures of transplant solutions during pancreatic islet autotransplantation are associated infrequently with clinical infection. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2015;16:115–23.
Jolissaint JS, Langman LW, DeBolt CL, Tatum JA, Martin AN, Wang AY, Strand DS, Zaydfudim VM, Adams RB, Brayman KL. The impact of bacterial colonization on graft success after total pancreatectomy with autologous islet transplantation: considerations for early definitive surgical intervention. Clin Transplant. 2016;30:1473–1479.
Meier RPH, Andrey DO, Sun P, Niclauss N, Bédat B, Demuylder-Mischler S, Borot S, Benhamou PY, Wojtusciszyn A, Buron F, Pernin N, Muller YD, Bosco D, van Delden C, Berney T. Pancreas preservation fluid microbial contamination is associated with poor islet isolation outcomes - a multi-centre cohort study. Transpl Int. 2018;31:917–929.
Taylor GD, Kirkland T, Lakey J, Rajotte R, Warnock GL. Bacteremia due to transplantation of contaminated cryopreserved pancreatic islets. Cell Transplant. 1994;3:103–6.
Lakey JR, Rajotte RV, Warnock GL. Microbial surveillance of human islet isolation, in vitro culture, and cryopreservation. Clin Invest Med. 1995;18:168–76.
Bucher P, Oberholzer J, Bosco D, Mathe Z, Toso C, Bühler LH, Berney T, Morel P. Microbial surveillance during human pancreatic islet isolation. Transpl Int. 2005;18:584–9.
Kin T, Rosichuk S, Shapiro AM, Lakey JR. Detection of microbial contamination during human islet isolation. Cell Transplant. 2007;16:9–13.
Gala-Lopez B, Kin T, O'Gorman D, Pepper AR, Senior P, Humar A, Shapiro AM. Microbial contamination of clinical islet transplant preparations is associated with very low risk of infection. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2013;15:323–7.
Murray L, McGowan N, Fleming J, Bailey L. Use of the BacT/alert system for rapid detection of microbial contamination in a pilot study using pancreatic islet cell products. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52:3769–71.
Qi M, Omori K, Mullen Y, McFadden B, Valiente L, Juan J, Bilbao S, Tegtmeier BR, Dafoe D, Kandeel F, Al-Abdullah IH. Prophylactically Decontaminating Human Islet Product for Safe Clinical Application: Effective and Potent Method. Transplant Direct. 2016;2:e63.
Afghani E, Sinha A, Singh VK. An overview of the diagnosis and management of nutrition in chronic pancreatitis. Nutr Clin Pract. 2014;29:295–311.
Bresnahan KA, Tanumihardjo SA. Undernutrition, the acute phase response to infection, and its effects on micronutrient status indicators. Adv Nutr. 2014;5:702–11
Bratzler DW, Dellinger EP, Olsen KM et al. Clinical practice guidelines for antimicrobial prophylaxis in surgery. Am J Health-Syst Pharm. 2013;70:195–283.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the European Society for Organ Transplantation, which supported the training for Justyna Gołębiewska with ESOT Study Scholarship 2017. Martin Tibudan was supported by the University of Chicago Diabetes Research and Training Center, US Public Health Service Grant P30DK020595.
Funding
Justyna Gołębiewska received the ESOT Study Scholarship from the European Society for Organ Transplantation, Martin Tibudan was partially supported by the University of Chicago Diabetes Research and Training Center, US Public Health Service Grant P30DK020595.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Each author has participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content as per the guidelines of the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the University of Chicago Institutional Review Board. All participants provided written informed consent.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 25 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gołębiewska, J.E., Bachul, P.J., Fillman, N. et al. Early Infectious Complications After Total Pancreatectomy with Islet Autotransplantation: a Single Center Experience. J Gastrointest Surg 23, 2201–2210 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-019-04118-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-019-04118-y