Abstract
Introduction
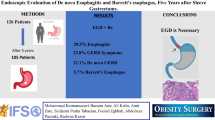
The relationship between the Los Angeles (LA) grade of esophagitis and acid exposure by pH monitoring is unclear. The aim of this study was to correlate the results of pH testing in patients with esophagitis to determine at what LA grade of esophagitis a pH test is not necessary.
Methods
A retrospective review was performed of the records of all patients who underwent upper endoscopy and were found to have esophagitis graded using the LA system and who had pH monitoring from 2014 to 2016. An abnormal pH test was determined based on the DeMeester score.
Results
There were 56 patients with a median age of 57 years. Esophagitis was LA grade A in 19, B in 20, C in 15 and D in 2 patients. An abnormal pH score was present in 47 patients (84%). All patients with C or D esophagitis had an abnormal pH score compared to 79% and 75% of patients with A and B esophagitis, respectively.
Conclusions
The presence of LA C or D esophagitis was always associated with increased esophageal acid exposure on pH testing and is proof of reflux disease. However, pH testing is recommended prior to antireflux surgery in patients with LA A or B esophagitis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Serag HB, Sweet S, Winchester CC, Dent J: Update on the epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut 2014, 63:871–880.
Sutton FM, Graham DY, Goodgame RW: Infectious esophagitis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 1994, 4:713–729.
Zografos GN, Georgiadou D, Thomas D, Kaltsas G, Digalakis M: Drug-induced esophagitis. Dis Esophagus 2009, 22:633–637.
Bredenoord AJ, Hemmink GJ, Smout AJ: Relationship between gastro-oesophageal reflux pattern and severity of mucosal damage. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2009, 21:807–812.
Bremner RM, Crookes PF, DeMeester TR, Peters JH, Stein HJ: Concentration of refluxed acid and esophageal mucosal injury. Am J Surg 1992, 164:522–526; discussion 526-527.
Armstrong D: Endoscopic evaluation of gastro-esophageal reflux disease. Yale J Biol Med 1999, 72:93–100.
Armstrong D, Bennett JR, Blum AL, Dent J, De Dombal FT, Galmiche JP, Lundell L, Margulies M, Richter JE, Spechler SJ, et al: The endoscopic assessment of esophagitis: a progress report on observer agreement. Gastroenterology 1996, 111:85–92.
Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, Blum AL, Armstrong D, Galmiche JP, Johnson F, Hongo M, Richter JE, Spechler SJ, et al: Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut 1999, 45:172–180.
Campos GM, Peters JH, DeMeester TR, Oberg S, Crookes PF, Tan S, DeMeester SR, Hagen JA, Bremner CG: Multivariate analysis of factors predicting outcome after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 1999, 3:292–300.
Ayazi S, Lipham JC, Portale G, Peyre CG, Streets CG, Leers JM, Demeester SR, Banki F, Chan LS, Hagen JA, Demeester TR: Bravo catheter-free pH monitoring: normal values, concordance, optimal diagnostic thresholds, and accuracy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009, 7:60–67.
Boys J AB, Martinez M, Lin B, Oh D, Hagen J, DeMeester S: Is EGD Reporting Adequate: A Review of Reports in 100 Referred Patients (Manuscript in preparation). 2017.
Acknowledgements
No grant support or other assistance
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors listed above contributed substantially to the conception or design of the work and the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; and all authors contributed to the drafting of the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content and the final approval of the version to be published; and all authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Southern California.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwameis, K., Lin, B., Roman, J. et al. Is pH Testing Necessary Before Antireflux Surgery in Patients with Endoscopic Erosive Esophagitis?. J Gastrointest Surg 22, 8–12 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-017-3554-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-017-3554-3