Abstract
Objective
Lateral internal sphincterotomy is an effective treatment for fissure in ano but carries a definite risk of incontinence. In trial to avoid this complication, segmental lateral internal sphincterotomy was used to treat chronic anal fissures.
Design
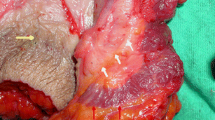
The lateral internal sphincterotomy was done in two parts and at different planes.
Setting
This study was conducted in the General Surgery Department, Zagazig University Hospital, Egypt.
Patients
This study was undertaken on 50 patients (43 men and seven women, with mean age of 37.3 years) with chronic fissure in ano from January 2009 to December 2010.
Interventions
Under general or local anesthesia, lateral internal sphincterotomy was done in two segments under direct vision. Preoperative and postoperative anal manometry study was recorded.
Main Outcome Measures
Postoperative course with early and long-term results were recorded. Mean follow-up was 18.5 months (ranging from 6 to 24 months).
Results
In 31 patients, the technique was done under general anesthesia and the remainder under local anesthesia. The fissures and anal wounds were healed within 4 weeks. Pain was significantly reduced in all patients at day 1 postoperative. Early complications included mild hematoma and urine retention in one male patient (2%). No transient or any persistent degree of incontinence occurred in these patients group.
Conclusion
Segmental lateral internal sphincterotomy is a safe, easy, and effective procedure and not associated with risk of incontinence for the treatment of chronic anal fissure.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dykes SL, Madoff RD. Benign anorectal: anal fissure. In: Wolff BG, Fleshman JW, Beck DE, Pemberton JH, Wexner SD, eds. The ASCRS textbook of colon and rectal surgery. New York: Springer, 2007: 178–191
Brisinda G, Cadeddu F, Brandara F, Brisinda D, Maria G. Treating chronic anal fissure with botulinum neurotoxin. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 1:82–89
Elia Guedea M, Gracia Solanas JA, Royo Dachary P, Ramirez Rodriguez JM, Aguilella Diago V, Martinez Diez M. Prevalence of anal diseases after Scopinaro’s biliopancreatic bypass for super-obese patients. Cir Esp 2008; 84:132–137
Sauper T, Lanthaler M, Biebl M, Weiss H, Nehoda H. Impaired anal sphincter function in professional cyclists. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2007; 119: 170–173
Garg P. Water stream in a bidet-toilet as a cause of anterior fissure-in-ano: a preliminary report. Colorectal Dis 2010; 12:601–602
Aivaz O, Rayhanabad J, Nguyen V, Haigh PI, Abbas M. Botulinum toxin A with Fissurectomy is a viable alternative to lateral internal sphincterotomy for chronic anal fissure. Am Surg 2009; 75: 925–928
Hyman N. Incontinence after lateral internal sphincterotomy: a prospective study and quality of life assessment. Dis Colon Rectum 2004; 47:35–38
Brown CJ, Dubreuil D, Santoro L, Liu M, O’Connor BI, McLeod RS. Lateral internal sphincterotomy is superior to topical nitroglycerin for healing chronic anal fissure and does not compromise long-term fecal continence: six-years follow up of multicenter, randomized, controlled trail. Dis Colon Rectum 2007; 50:442–448.
García-Granero E, Sanahuja A, García-Botello SA, Faiz O, Esclápez P, Espí A, Flor B, Minguez M, Lledó S. The ideal lateral internal sphincterotomy: clinical and endosonographic evaluation following open and closed internal anal sphincterotomy. Colorectal Dis. 2009; 11:502–7
Ayantunde AA, Debrah SA. Current concepts in anal fissures. World J Surg 2006; 30:2246–60.
Eisenhammer S. The evaluation of the internal anal sphincterotomy operation with special reference to anal fissure. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1959; 109:583–90.
Notaras MJ. Lateral subcutaneous sphincterotomy for anal fissure- a new technique. J R Soc Med 1969; 62:713.
Nelson R. Non surgical therapy for anal fissure. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006; 4:CD003431.
Menteş BB, Güner MK, Leventoglu S, Akyürek N. Fine-tuning of the extent of the lateral internal sphincterotomy: spasm-controlled vs. up to the fissure apex. Dis Colon Rectum 2008; 51:128–33.
Wollina U. Pharmacological sphincterotomy for chronic anal fissures by botulinum toxin a. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2008 Jul;1(2):58–63.
Menteş BB, Ege B, Leventoglu S, Oguz M, Karadag A Extent of lateral internal sphincterotomy: up to the dentate line or up to the fissure apex? Dis Colon Rectum. 2005; 48:365–70.
Shafik A. Perianal injection of autologous fat for treatment of sphincteric incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum 1995; 38:583–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lasheen, A.E., Morsy, M.M. & Fiad, A.A. Segmental Internal Sphincterotomy—A New Technique for Treatment of Chronic Anal Fissure. J Gastrointest Surg 15, 2271–2274 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-011-1689-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-011-1689-1