Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to engineer the two main components of the esophagus in vitro: (a) esophageal epithelium and (b) smooth muscle tissue. Furthermore, (a) survivability of esophageal epithelial cells (EEC) on basement membrane matrix (BMM)-coated scaffolds and (b) oriented smooth muscle tissue formation on unidirectional BMM-coated collagen scaffolds was investigated.
Methods
Both EEC and smooth muscle cells (SMC) were sourced from Sprague–Dawley rats. The EEC were maintained in vitro and seeded onto BMM-coated 2-D collagen scaffolds. Similarly, smooth muscle cells were obtained using an explants technique and seeded on unidirectional 3-D BMM-coated collagen scaffolds. Cell–polymer constructs for EEC and SMC were maintained in vitro for 8 weeks.
Results
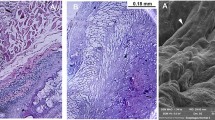
Protocols to obtain higher yield of EEC were established. EEC formed a layer of differentiated epithelium after 14 days. EEC survivability on polymers was observed up to 8 weeks. Unidirectional smooth muscle tissue strands were successfully engineered.
Conclusion
Esophageal epithelium generation, survivability of EEC on BMM-coated scaffolds, and engineering of unidirectional smooth muscle strands were successful in vitro. The hybrid approach of assembling individual tissue components in vitro using BMM-coated scaffolds and later amalgamating them to form composite tissue holds promises in the tissue engineering of complex organ systems.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark DC. Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula. Am Fam Physician. 1999;59:910–916.
Cusick EL, Batchelor AA, Spicer RD. Development of a technique for jejunal interposition in long-gap esophageal atresia. J Pediatr Surg 1993;28:990–994. doi:10.1016/0022-3468(93)90499-B.
Raffensperger JG, Kuck SR, Reynolds M, Schwartz D. Intestinal bypass of the esophagus. J Pediatr Surg 1996;31:38–46. doi:10.1016/S0022-3468(96)90316-4.
Spitz L, Ruangtrakool R. Esophageal substitution. Semin Pediatr Surg 1998;7:130–133.
Cauchi JA, Buick RG, Gornall P, Simms MH, Parikh DH. Oesophageal substitution with free and pedicled jejunum: short- and long-term outcomes. Pediatr Surg Int 2007;23:11–19. doi:10.1007/s00383-006-1770-0.
Arul GS, Parikh D. Oesophageal replacement in children. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2008;90:7–12. doi:10.1308/003588408X242222.
Spitz L. Esophageal atresia—lessons I have learned in a 40-year experience. J Pediatr Surg 2006;41:1635–1640. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2006.07.004.
Saxena AK, Kofler K, Ainoedhofer H, Kuess A, Höllwarth ME. Complexity of approach and demand for esophagus tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A 2008;14:829.
Kajitani M, Wadia Y, Hinds MT, Teach J, Schwartz KR, Gregory KW. Successful repair of esophageal injury using an elastin based biomaterial patch. ASAIO J 2001;47:342–345. doi:10.1097/00002480-200107000-00009.
Badylak S, Meurling S, Chen M, Spievack A, Simmons-Byrd A. Resorbable bioscaffold for esophageal repair in a dog model. J Pediatr Surg 2000;35:1097–1103. doi:10.1053/jpsu.2000.7834.
Takimoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamamoto Y, Kiyotani T, Teramachi M, Shimizu Y. The experimental replacement of a cervical esophageal segment with an artificial prosthesis with the use of collagen matrix and a silicone stent. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1998;116:98–106. doi:10.1016/S0022-5223(98)70247-8.
Isch JA, Engum SA, Ruble CA, Davis MM, Grosfeld JL. Patch esophagoplasty using AlloDerm as a tissue scaffold. J Pediatr Surg 2001;36:266–268. doi:10.1053/jpsu.2001.20685.
Grikscheit T, Ochoa ER, Srinivasan A, Gaissert H, Vacanti JP. Tissue-engineered esophagus: experimental substitution by onlay patch or interposition. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2003;126:537–544. doi:10.1016/S0022-5223(03)00032-1.
Natsume T, Ike O, Okada T, Shimizu Y, Ikada Y, Tamura K. Experimental studies of a hybrid artificial esophagus combined with autologous mucosal cells. ASAIO Trans 1990;36:M435–437.
Sato M, Ando N, Ozawa S, Miki H, Kitajima M. An artificial esophagus consisting of cultured human esophageal epithelial cells, polyglycolic acid mesh, and collagen. ASAIO J 1994;40:M389–392. doi:10.1097/00002480-199407000-00028.
Miki H, Ando N, Ozawa S, Sato M, Hayashi K, Kitajima M. An artificial esophagus constructed of cultured human esophageal epithelial cells, fibroblasts, polyglycolic acid mesh, and collagen. ASAIO J 1999;45:502–508. doi:10.1097/00002480-199909000-00025.
Oda D, Savard CE, Eng L, Sekijima J, Haigh G, Lee SP. Reconstituted human oral and esophageal mucosa in culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 1998;34:46–52. doi:10.1007/s11626-998-0052-7.
Saxena AK, Ainoedhofer H, Höllwarth ME. Esophagus tissue engineering: In-vitro generation of esophageal epithelial cell sheets and viabilty on scaffold. J Pediatr Surg. In press.
Debnath J, Muthuswamy SK, Brugge JS. Morphogenesis and oncogenesis of MCF-10A mammary epithelial acini grown in three-dimensional basement membrane cultures. Methods 2003;30:256–268. doi:10.1016/S1046-2023(03)00032-X.
Biederer T, Scheiffele P. Mixed-culture assays for analyzing neuronal synapse formation. Nat Protocols 2007;2:670–676. doi:10.1038/nprot.2007.92.
McGuire PG, Orkin RW. Isolation of rat aortic endothelial cells by primary explant techniques and their phenotypic modulation by defined substrata. Lab Invest 1987;57:94–105.
Maeshima Y, Manfredi M, Reimer C, Holthaus KA, Hopfer H, Chandamuri BR, Kharbanda S, Kalluri R. Identification of the anti-angiogenic site within vascular basement membrane-derived tumstatin. J Biol Chem 2001;276:15240–15248. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007764200.
Kisucka J, Butterfield CE, Duda DG, Eichenberger SC, Saffaripour S, Ware J, Ruggeri ZM, Jain RK, Folkman J, Wagner DD. Platelets and platelet adhesion support angiogenesis while preventing excessive hemorrhage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006;103:855–860. doi:10.1073/pnas.0510412103.
Saxena AK, Ainoedhofer H, Baumann P, Kristler M, Höllwarth ME. In-vitro investigation of esophageal cell organization and collagen scaffold interaction. Tissue Eng Part A 2008;14:747.
Beckstead BL, Pan S, Bhrany AD, Bratt-Leal AM, Ratner BD, Giachelli CM. Esophageal epithelial cell interaction with synthetic and natural scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005;26:6217–6228. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.04.010.
Pattison MA, Wurster S, Webster TJ, Haberstroh KM. Three-dimensional, nano-structured PLGA scaffolds for bladder tissue replacement applications. Biomaterials 2005;26:2491–2500. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.07.011.
Schnell AM, Hoerstrup SP, Zund G, Kolb S, Sodian R, Visjager JF, Grunenfelder J, Suter A, Turina M. Optimal cell source for cardiovascular tissue engineering: venous vs. aortic human myofibroblasts. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2001;49:221–225. doi:10.1055/s-2001-16113.
Lim JI, Yu B, Lee YK. Fabrication of collagen hybridized elastic PLCL for tissue engineering. Biotechnol Lett 2008;30:2085–2090. doi:10.1007/s10529-008-9808-0.
Sell SA, McClure MJ, Barnes CP, Knapp DC, Walpoth BH, Simpson DG, Bowlin GL. Electrospun polydioxanone-elastin blends: potential for bioresorbable vascular grafts. Biomed Mater 2006;1:72–80. doi:10.1088/1748-6041/1/2/004.
Duling RR, Dupaix RB, Katsube N, Lannutti J. Mechanical characterization of electrospun polycaprolactone (PCL): a potential scaffold for tissue engineering. J Biomech Eng 2008;130:011006. doi:10.1115/1.2838033.
Acknowledgment
We thank Prof. Wout Feitz (Radboud University Medical Centre, Nijmegen, The Netherlands), Dr. Ingo Heschel (Matricel GmbH, Herzoganrath, Germany) along with Mrs. Anna Kuess (Medical University of Graz, Austria) for the valuable contributions toward this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research is funded by the European Union within the 6th Framework Program (EuroSTEC; LSHC-CT-2006–037409).
XXIst International Symposium on Pediatric Surgical Research, 2–4 October 2008, Leipzig, Germany
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saxena, A.K., Kofler, K., Ainödhofer, H. et al. Esophagus Tissue Engineering: Hybrid Approach with Esophageal Epithelium and Unidirectional Smooth Muscle Tissue Component Generation In Vitro . J Gastrointest Surg 13, 1037–1043 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-009-0836-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-009-0836-4