Abstract
Background
It has not been reported that ingesting large amounts of strong acid resulted in total gastrointestinal tract necrosis. Here we describe a case of a man with total gastrointestinal tract necrosis after ingestion of a considerable amount of hydrochloric acid.
Discussion
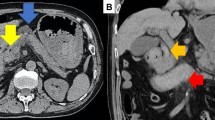
Computed tomography (CT) scan showed significant free air in the neck, lateral esophagus, and abdominal cavity, which indicated perforation of the esophagus and gastrointestinal tract. In addition, the abdominal CT image showed splenic subcapsular hematorna and swollen pancreatic head caused by strong acid causis. We found the entire gastrointestinal tract from stomach to rectum necrosis in the emergency exploratory laparotomy. Our case suggests that ingestion of a considerable amount (e.g., 500 mL) and concentration of strong acid could result in total gastrointestinal tract necrosis. Emergency laparotomy should be performed as early as possible to benefit this kind of patient.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeng LB, Chen HY, Chen SC et al. Upper gastrointestinal tract ablation for patients with extensive injury after ingestion of strong acid. Arch Surg 1994;129:1086–1090.
Muñoz Muñoz E, Bretcha Boix P, Collera Ormazabal P et al. Swallowing of hydrochloric acid: study of 25 cases. Rev Esp Enferm Apar Dig 1998;90:701–707.
Muñoz Muñoz E, Garcia-Domingo MI, Rodriguez Santiago J et al. Massive necrosis of the gastrointestinal tract after ingestion of hydrochloric acid. Eur J Surg 2001;167:195–198.
Tohda G, Sugawa C, Gayer C, et al. Clinical evaluation and management of caustic injury in the upper gastrointestinal tract in 95 adult patients in an urban medical center. Surg Endosc 2008; 22:1119–1125.
Gumaste VV, Dave PB. Ingestion of corrosive substances by adults. Am J Gastroenterol 1992;87:1–5.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the patient’s family members for their kind permission to publish the data and figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Q., Zhou, H., Zheng, X. et al. Total Gastrointestinal Tract Necrosis After Ingesting a Considerable Amount of Hydrochloric Acid. J Gastrointest Surg 13, 578–580 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0524-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0524-9