Abstract
Background
Radio frequency ablation (RFA) of hepatocellular carcinoma has proved to be useful in local control of tumor. A few data on survival after treatment are available in literature. The aim of the study was to evaluate factors related to survival and to identify different classes of risk after radio frequency ablation.
Methods
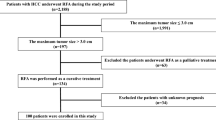
Ninety-eight cirrhotic patients with 145 hepatocellular carcinomas were treated with radio frequency ablation from January 1998 to May 2004. In 55 patients, cirrhosis was in Child-Pugh class A, and in 43, in class B. Tumor was single in 60 and multiple in 38; mean tumor number was 1.5 (range 1–3). Tumor size ranged from 1.5 to 6.0 cm, mean 3.8 cm. Mean follow up period was 24.9 months. Radio frequency ablation was performed with expandable type needle with percutaneous approach under real-time ultrasound guidance. For statistical analysis, univariate and multivariate analysis were performed.
Results
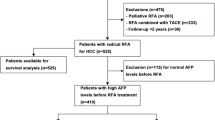
Complete ablation of the tumor was achieved in 85.5% of lesions. Survival, 1 and 3 years, was 76.7 and 36.6%, respectively. Univariate analysis showed that Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) score, tumor growth pattern, α-fetoprotein level, and complete tumor necrosis, were factors significantly related to poor survival. Multivariate analysis identified that factors related to poor survival were α-fetoprotein level >100 ng/ml, Child-Pugh class B, and incomplete tumor necrosis with a hazard ratio of 4.0, 2.7, and 3.8, respectively. After complete ablation, median survival was 38 months in patients with Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis and α-fetoprotein level ≤100 ng/ml, 22 months for patient with Child-Pugh class B cirrhosis and α-fetoprotein ≤100 ng/ml, and 9 months for patient with Child-Pugh class A cirrhosis and α-fetoprotein >100 ng/ml (P < 0.01).
Conclusions
Complete necrosis and absence of residual tumor positively affect survival after RFA. In patients with Child-Pugh A cirrhosis and α-fetoprotein level ≤100 radio frequency, ablation have results, 55% after 3 years, that are comparable to those of surgical resection. Patients with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis and/or α-fetoprotein >100 ng/ml showed less satisfactory results, and in these patients, multimodality treatment or other treatments should be considered.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- (HCC):
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- (RFA):
-
Radio frequency ablation
- (WHO):
-
World Health Organization
- (HRs):
-
Hazard ratio estimates
- (PH):
-
Proportional hazard
- (UICC):
-
International Union Against Cancer
References
Bosch, F. X., Ribes, J., & Borras, J. (1999). Epidemiology of primary liver cancer. Seminars in Liver Disease, 19, 271–285.
Bosch, F. X., Ribes, J., Diaz, M., & Cleries, R. (2004). Primary liver cancer: Worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology, 127(5 Suppl 1), S5–S16, Nov.
Yanaga, K. (2004). Current status of hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Gastroenterology, 39(10), 919–926, Oct.
Carr, B. I. (2004). Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current management and future trends. Gastroenterology, 127(5 Suppl 1), S218–S224, Nov.
Fong, Y., Sun, R. L., Jarnagin, W., & Blumgart, L. H. (1999). An analysis of 412 cases of hepatocellular carcinoma at a Western center. Annals of Surgery, 229, 790–799.
Llovet, J. M., Fuster, J., & Bruix, J. (1999). Intention-to-treat analysis of surgical treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma: Resection versus transplantation. Hepatology, 30, 1434–1440.
Poon, R. T., Fan, S. T., Lo, C. M., Ng, I. O., Liu, C. L., Lam, C. M., et al. (2001). Improving survival results after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective study of 377 patients over 10 years. Annals of Surgery, 234, 63–70.
Bruix, J., & Llovet, J. M. (2002). Prognostic prediction and treatment strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology, 35(3), 519–524, Mar.
Camma, C., Di Marco, V., Orlando, A., Sandonato L., Casaril A., Parisi P., et al. (2005). Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in compensated cirrhosis with radio-frequency thermal ablation (RFTA): A prospective study. Journal of Hepatology, 42(4), 535–540, Apr.
Montorsi, M., Santambrogio, R., Bianchi, P., Donadon, M., Moroni, E., Spinelli, A., et al. (2005). Survival and recurrences after hepatic resection or radiofrequency for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients: A multivariate analysis. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, 9(1), 62–67, Jan.
Vivarelli, M., Guglielmi, A., Ruzzenente, A., Cucchetti, A., Bellusci, R., Cordiano, C., et al. (2004). Surgical resection versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma on cirrhotic liver. Annals of Surgery, 240(1), 102–107, Jul.
Pugh, R. N. H., Murray-Lyon, I. M., & Dawson, J. L. (1973). Transection of oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. British Journal of Surgery, 60, 646–664.
The Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) Investigators. (1998). A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study of 435 patients. Hepatology, 28, 751–755.
Bruix, J., Sherman, M., Llovet, J. M., Beaugrand, M., Lencioni, R., Burroughs, A. K., et al. (2001). EASL Panel of Experts on HCC. Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. European Association for the Study of the Liver. Journal of Hepatology, 35 (3), 421–430, Sep.
Miller, A. B., Hoogstraten, B., Staquet, M., & Winkler, A. (1981). Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer, 47, 207–214.
Rabe-Hesketh, S., & Everitt, B. S. A. (2003). Handbook of Statistical Analyses Using Stata (3rd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: Chapman & Hall/CRC.
Austin, P. C., & Tu, J. V. (2004). Bootstrap methods for developing predictive models. The American Statistician, 58(2), 131–137.
May, S., & Hosmer, D. W. (1998). A simplified method of calculating an overall goodness-of-fit test for the Cox proportional hazards model. Lifetime Data Analysis, 4, 109–120.
Lencioni, R. A., Allgaier, H. P., Cioni, D., Olschewski, M., Deibert, P., Crocetti L., et al. (2003). Small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Randomized comparison of radio-frequency thermal ablation versus percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology, 228, 235–240.
Livraghi, T., Goldberg, S. N., Lazzaroni, S., Meloni, F., Solbiati, L., & Gazelle, G. S. (1999). Small hepatocellular carcinoma: Treatment with radiofrequency ablation versus ethanol injection. Radiology, 210, 655–661.
Guglielmi, A., Ruzzenente, A., Battocchia, A., Tonon, A., Fracastoro, G., & Cordiano, C. (2003). Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients. Hepatogastroenterology, 50, 480–484.
Livraghi, T., Goldberg, S. N., Lazzaroni, S., Meloni F., Ierace T., Solbiati L., et al. (2000). Hepatocellular carcinoma: Radio-frequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology, 214(3), 761–768, Mar.
Poon, R. T., Ng, K. K., Lam, C. M., Ai, V., Yuen, J., & Fan, S. T. (2004). Effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinomas larger than 3 cm in diameter. Archives of Surgery, 139(3), 281–287, Mar.
Rossi, S., Di Stasi, M., Buscarini, E., Quaretti P., Garbagnati F., Squassante L., et al. (1996). Percutaneous RF interstitial thermal ablation in the treatment of hepatic cancer. American Journal of Roentgenology, 167, 759–768.
Sala, M., Llovet, J. M., Vilana, R., Bianchi L., Sole M., Ayuso C., et al. (2004). Initial response to percutaneous ablation predicts survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology, 40(6), 1352–1360, Dec.
Tangkijvanich, P., Anukulkarnkusol, N., Suwangool, P., Lertmaharit S., Hanvivatvong O., Kullavanijaya P., et al. (2000). Clinical characteristics and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis based on serum alpha-fetoprotein levels. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, 31, 302–308.
Wayne, J. D., Lauwers, G. Y., Ikai, I., Doherty, D. A., Belghiti, J., Yamaoka Y., et al. (2002). Preoperative predictors of survival after resection of small hepatocellular carcinomas. Annals of Surgery, 235(5), 722–730, May.
Wildi, S., Pestalozzi, B. C., McCormack, L., & Clavien, P. A. (2004). Critical evaluation of the different staging systems for hepatocellular carcinoma. British Journal of Surgery, 91(4), 400–408, Apr.
The Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) Investigators. (2000). Prospective validation of the CLIP score: A new prognostic system for patients with cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology, 31, 840–845.
Ueno, S., Tanabe, G., Sako, K., Hiwaki T., Hokotate H., Fukukura Y., et al. (2001). Discrimination value of the new western prognostic system (CLIP score) for hepatocellular carcinoma in 662 Japanese patients. Cancer of the Liver Italian Program. Hepatology, 34, 529–534.
Zhao, W. H., Ma, Z. M., Zhou, X. R., Feng, Y. Z., & Fang, B. S. (2002). Prediction of recurrence and prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after resection by use of CLIP score. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 8, 237–242.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guglielmi, A., Ruzzenente, A., Sandri, M. et al. Radio Frequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Patients: Prognostic Factors for Survival. J Gastrointest Surg 11, 143–149 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-006-0082-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-006-0082-y