Abstract
Objective
Castleman disease (CD) is a rare group of lymphoproliferative disorders, which is easily confused with lymphoma or other solid tumors. Hence, this study aimed to investigate the diagnostic role of 18F-FDG PET/CT and contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) in patients with CD.
Methods
Clinicopathological characteristics, and 18F-FDG PET/CT and CECT findings and parameters were retrospectively reviewed in 32 patients with CD.
Results
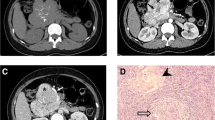
These 32 patients (12 males, 20 females; median age, 41 years) consisted of 17 unicentric CD (UCD) patients and 15 multicentric CD (MCD) patients. Compared with MCD, UCD had a higher prevalence in female (82.4% vs. 40.0%) and hyaline vascular subtype (94.1% vs. 40.0%) (P < 0.05). FDG uptake was avid in all cases, including moderate uptake in 7 cases and intense uptake in 25 cases. The median SUVmax, SUVmean, MLV, and TLG of all cases were 4.4 (range, 1.4–23.6), 2.7 (range, 1.1–15.2), 26.6 (range, 4.8–393.0), and 78.8 (range, 9.4–1545.6), respectively. The lesions of 29 cases showed homogeneous enhancement, and marked enhancement was observed in 27 cases. 18F-FDG PET/CT corrected 6.3% CECT diagnoses, while CECT corrected 37.5% PET/CT diagnosis. The accuracy of combined PET/CT and CECT was superior to PET/CT or CECT alone (78.1%, 31.3%, and 62.5%). Besides, higher SUVmax and SUVmean were found in male subjects, MCD, and plasma cell subtype (P < 0.05), while higher MLV and TLG were observed in larger lesion size and volume (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Castleman disease most commonly appears as marked and homogeneous enhancement meanwhile with moderate or intense FDG uptake. 18F-FDG PET/CT combined with CECT was the effectively diagnostic modality for CD. The glucose metabolism of CD was associated with gender, clinical classification, histopathological classification, and lesion size and volume.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castleman B, Towne VW. Case records of the Massachusetts general hospital: case no 40231. N Engl J Med. 1954;250(23):1001–5.
Simpson D. Epidemiology of Castleman disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2018;32(1):1–10.
Keller AR, Hochholzer L, Castleman B. Hyaline-vascular and plasma-cell types of giant lymph node hyperplasia of the mediastinum and other locations. Cancer. 1972;29(3):670–83.
Dispenzieri A, Fajgenbaum DC. Overview of Castleman disease. Blood. 2020;135(16):1353–64.
Bonekamp D, Horton KM, Hruban RH, Fishman EK. Castleman disease: the great mimic. Radiographics. 2011;31(6):1793–807.
Haap M, Wiefels J, Horger M, Hoyer A, Müssig K. Clinical, laboratory and imaging findings in Castleman’s disease - The subtype decides. Blood Rev. 2018;32(3):225–34.
Ye B, Gao SG, Li W, Yang LH, Zhao SH, Ma K, Zhu XL, Liu XY, Sun KL. A retrospective study of unicentric and multicentric Castleman’s disease: a report of 52 patients. Med Oncol. 2010;27(4):1171–8.
Koa B, Borja AJ, Aly M, Padmanabhan S, Tran J, Zhang V, Rojulpote C, Pierson SK, Tamakloe MA, Khor JS, Werner TJ, Fajgenbaum DC, Alavi A, Revheim ME. Emerging role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Castleman disease: a review. Insights Imaging. 2021;12(1):35.
van Rhee F, Voorhees P, Dispenzieri A, Fosså A, Srkalovic G, Ide M, Munshi N, Schey S, Streetly M, Pierson SK, Partridge HL, Mukherjee S, Shilling D, Stone K, Greenway A, Ruth J, Lechowicz MJ, Chandrakasan S, Jayanthan R, Jaffe ES, Leitch H, Pemmaraju N, Chadburn A, Lim MS, Elenitoba-Johnson KS, Krymskaya V, Goodman A, Hoffmann C, Zinzani PL, Ferrero S, Terriou L, Sato Y, Simpson D, Wong R, Rossi JF, Nasta S, Yoshizaki K, Kurzrock R, Uldrick TS, Casper C, Oksenhendler E, Fajgenbaum DC. International, evidence-based consensus treatment guidelines for idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease. Blood. 2018;132(20):2115–24.
Madan R, Chen JH, Trotman-Dickenson B, Jacobson F, Hunsaker A. The spectrum of Castleman’s disease: mimics, radiologic pathologic correlation and role of imaging in patient management. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81(1):123–31.
Hill AJ, Tirumani SH, Rosenthal MH, Shinagare AB, Carrasco RD, Munshi NC, Ramaiya NH, Howard SA. Multimodality imaging and clinical features in Castleman disease: single institute experience in 30 patients. Br J Radiol. 2015;88(1049):20140670.
Lee ES, Paeng JC, Park CM, Chang W, Lee WW, Kang KW, Chung JK, Lee DS. Metabolic characteristics of Castleman disease on 18F-FDG PET in relation to clinical implication. Clin Nucl Med. 2013;38(5):339–42.
Jiang Y, Hou G, Zhu Z, Huo L, Li F, Cheng W. 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging features of patients with multicentric Castleman disease. Nucl Med Commun. 2021;42(7):833–8.
Barrington SF, Mikhaeel NG, Kostakoglu L, Meignan M, Hutchings M, Müeller SP, Schwartz LH, Zucca E, Fisher RI, Trotman J, Hoekstra OS, Hicks RJ, O’Doherty MJ, Hustinx R, Biggi A, Cheson BD. Role of imaging in the staging and response assessment of lymphoma consensus of the international conference on malignant lymphomas imaging working group. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(27):3048–58.
Salomon T, Nganoa C, Gac AC, Fruchart C, Damaj G, Aide N, Lasnon C. Assessment of alteration in liver (18)F-FDG uptake due to steatosis in lymphoma patients and its impact on the Deauville score. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;45(6):941–50.
Meignan M, Gallamini A, Meignan M, Gallamini A, Haioun C. Report on the first international workshop on interim-PET-scan in lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2009;50(8):1257–60.
Liu ET, Sun TT, Dong HJ, Wang SY, Chen ZR, Liu C, Shao D, Lian ZY, Xie Q, Wang SX. Combined PET/CT with thoracic contrast-enhanced CT in assessment of primary cardiac tumors in adult patients. EJNMMI Res. 2020;10(1):75.
Munshi N, Mehra M, van de Velde H, Desai A, Potluri R, Vermeulen J. Use of a claims database to characterize and estimate the incidence rate for Castleman disease. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56(5):1252–60.
Enomoto K, Nakamichi I, Hamada K, Inoue A, Higuchi I, Sekimoto M, Mizuki M, Hoshida Y, Kubo T, Aozasa K, Hatazawa J. Unicentric and multicentric Castleman’s disease. Br J Radiol. 2007;80(949):e24–6.
Parez N, Bader-Meunier B, Roy CC, Dommergues JP. Paediatric Castleman disease: report of seven cases and review of the literature. Eur J Pediatr. 1999;158(8):631–7.
Waterston A, Bower M. Fifty years of multicentric Castleman’s disease. Acta Oncol. 2004;43(8):698–704.
Dispenzieri A, Armitage JO, Loe MJ, Geyer SM, Allred J, Camoriano JK, Menke DM, Weisenburger DD, Ristow K, Dogan A, Habermann TM. The clinical spectrum of Castleman’s disease. Am J Hematol. 2012;87(11):997–1002.
Barker R, Kazmi F, Stebbing J, Ngan S, Chinn R, Nelson M, O’Doherty M, Bower M. FDG-PET/CT imaging in the management of HIV-associated multicentric Castleman’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009;36(4):648–52.
Han EJ, O JH, Jung SE, Park G, Choi BO, Jeon YW, Min GJ, Cho SG. FDG PET/CT findings of Castleman disease assessed by histologic subtypes and compared with laboratory findings. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10(12):998.
Zhao S, Wan Y, Huang Z, Song B, Yu J. Imaging and clinical features of Castleman disease. Cancer Imaging. 2019;19(1):53.
Talat N, Belgaumkar AP, Schulte KM. Surgery in Castleman’s disease: a systematic review of 404 published cases. Ann Surg. 2012;255(4):677–84.
Guazzaroni M, Bocchinfuso F, Vasili E, Lacchè A, Ranalli T, Garipoli A, Di Tosto F, Floris R. Multicentric Castleman’s disease: report of three cases. Radiol Case Rep. 2019;14(3):328–32.
Kligerman SJ, Auerbach A, Franks TJ, Galvin JR. Castleman disease of the thorax: clinical, radiologic, and pathologic correlation: from the radiologic pathology archives. Radiographics. 2016;36(5):1309–32.
Oksenhendler E, Boutboul D, Fajgenbaum D, Mirouse A, Fieschi C, Malphettes M, Vercellino L, Meignin V, Gérard L, Galicier L. The full spectrum of Castleman disease: 273 patients studied over 20 years. Br J Haematol. 2018;180(2):206–16.
Funding
The work of Lei Jiang was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, 81971645, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, KY0120211130, and Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Image Analysis and Application, No. 2022B1212010011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Chen, Y., Tan, X. et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT and contrast-enhanced CT in the diagnosis of Castleman disease. Jpn J Radiol 41, 98–107 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-022-01318-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-022-01318-6