Abstract
Purpose
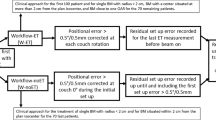
The objective of our study was to explore any significant dosimetric differences between different leaf width (3.0 mm vs. 2.5 mm) micro-multileaf collimator (mMLC)-based treatment systems for intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery using dynamic conformal arcs (DCAs).
Materials and methods
The systems included a 3 mm leaf width mMLC (m3) mounted on a nondedicated linac, and the Novalis Tx system with an integrated 2.5 mm width mMLC (HD120). Thirty plans for brain metastases were replanned for both systems using a uniform method for target definition and treatment planning for baseline comparison.
Results
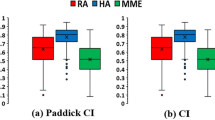
The target coverage values for the 80% isodose surface (IDS) and the D95 values in the HD120 plans were significantly lower than those for the m3 plans. The ratios of lower isodose volumes to the target for the HD120 were smaller than those for the m3. When a 1 mm leaf margin was added to the HD120 plans, these differences were reversed, but statistically significant differences were still observed.
Conclusion
Significant dosimetric differences were observed between these systems. Different planning methods are required for the two systems to attain similar target coverage values with selected IDS, which can be achieved by adjusting the leaf margin with 0.1 mm increments or isocenter dose settings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monk JE, Perks JR, Doughty D, Plowman PN. Comparison of a micro-multileaf collimator with a 5-mm-leaf-width collimator for intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003;57:1443–1449.
Hazard LJ, Wang B, Skidmore TB, Chern SS, Salter BJ, Jensen RL, et al. Conformity of LINAC-based stereotactic radiosurgery using dynamic conformal arcs and micro-multileaf collimator. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;73:562–570.
Wiggenraad RG, Petoukhova AL, Versluis L, van Santvoort JP. Stereotactic radiotherapy of intracranial tumors: a comparison of intensity-modulated radiotherapy and dynamic conformal arc. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;74:1018–1026.
Cosgrove VP, Jahn U, Pfaender M, Bauer S, Budach V, Wurm RE. Commissioning of a micro multi-leaf collimator and planning system for stereotactic radiosurgery. Radiother Oncol 1999;50:325–336.
Chang Z, Wang Z, Wu QJ, Yan H, Bowsher J, Zhang J, et al. Dosimetric characteristics of novalis Tx system with high definition multileaf collimator. Med Phys 2008;35:4460–4463.
Fogliata A, Clivio A, Nicolini G, Vanetti E, Cozzi L. Intensity modulation with photons for benign intracranial tumours: a planning comparison of volumetric single arc, helical arc and fixed gantry techniques. Radiother Oncol 2008;89:254–262.
Tanyi JA, Summers PA, McCracken CL, Chen Y, Ku LC, Fuss M. Implications of a high-definition multileaf collimator (HD-MLC) on treatment planning techniques for stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT): a planning study. Radiat Oncol 2009;10:4:22.
Wu QJ, Wang Z, Kirkpatrick JP, Chang Z, Meyer JJ, Lu M, et al. Impact of collimator leaf width and treatment technique on stereotactic radiosurgery and radiotherapy plans for intra- and extracranial lesions. Radiat Oncol 2009;21:4:3.
Dhabaan A, Elder E, Schreibmann E, Crocker I, Curran WJ, Oyesiku NM, et al. Dosimetric performance of the new highdefinition multileaf collimator for intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery. J Appl Clin Med Phys 2010;11:197–211.
Tanyi JA, Kato CM, Chen Y, Chen Z, Fuss M. Impact of the high-definition multileaf collimator on linear acceleratorbased intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery. Br J Radiol 2011;84:629–638.
Ma J, Chang Z, Wang Z, Wu QJ, Kirkpatrick JP, Yin FF. ExacTrac X-ray 6 degree-of-freedom image-guidance for intracranial non-invasive stereotactic radiotherapy: comparison with kilo-voltage cone-beam CT. Radiother Oncol 2009;93:602–608.
Kubo HD, Wilder RB, Pappas CT. Impact of collimator leaf width on stereotactic radiosurgery and 3D conformal radiotherapy treatment plans. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1999;44:937–945.
Jin JY, Yin FF, Ryu S, Ajlouni M, Kim JH. Dosimetric study using different leaf-width MLCs for treatment planning of dynamic conformal arcs and intensity-modulated radiosurgery. Med Phys 2005;32:405–411.
Clark BG, Teke T, Otto K. Penumbra evaluation of the Varian millennium and Brain LAB m3 multileaf collimators. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;66(suppl):71–75.
Chern SS, Leavitt DD, Jensen RL, Shrieve DC. Is smaller better? Comparison of 3-mm and 5-mm leaf size for stereotactic radiosurgery: a dosimetric study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;66(suppl):76–81.
Ding M, Newman F, Kavanagh BD, Stuhr K, Johnson TK, Gaspar LE. Comparative dosimetric study of three-dimensional conformal, dynamic conformal arc, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for brain tumor treatment using Novalis system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;66(suppl):82–86.
Chang J, Yenice KM, Jiang K, Hunt M, Narayana A. Effect of MLC leaf width and PTV margin on the treatment planning of intensity-modulated stereotactic radiosurgery (IMSRS) or radiotherapy (IMSRT). Med Dosim 2009;34:110–116.
Chen JC, Bugoci DM, Girvigian MR, Miller MJ, Arellano A, Rahimian J. Control of brain metastases using frameless image-guided radiosurgery. Neurosurg Focus 2009;27:E6.
Molenaar R, Wiggenraad R, Verbeek-de Kanter A, Walchenbach R, Vecht C. Relationship between volume, dose and local control in stereotactic radiosurgery of brain metastasis. Br J Neurosurg 2009;23:170–178.
Feuvret L, Noël G, Mazeron JJ, Bey P. Conformity index: a review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;64:333–342.
Nakamura JL, Verhey LJ, Smith V, Petti PL, Lamborn KR, Larson DA, et al. Dose conformity of gamma knife radiosurgery and risk factors for complications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2001;51:1313–1319.
Hwang AB, Bacharach SL, Yom SS, Weinberg VK, Quivey JM, Franc BL, et al. Can positron emission tomography (PET) or PET/computed tomography (CT) acquired in a nontreatment position be accurately registered to a head-and-neck radiotherapy planning CT? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2009;73:578–584.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ohtakara, K., Hayashi, S., Tanaka, H. et al. Dosimetric comparison of 2.5 mm vs. 3.0 mm leaf width micro-multileaf collimator-based treatment systems for intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery using dynamic conformal arcs: implications for treatment planning. Jpn J Radiol 29, 630–638 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-011-0606-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-011-0606-6