Abstract
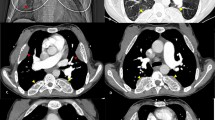
Extramedullary hematopoiesis (EMH) refers to the development of foci of hematopoiesis outside its normal location in the bone marrow. This occurs normally during fetal development but is abnormal postpartum. The most common sites of EMH are the spleen and liver. The phenomenon occurs in a number of disease states, notably in myelofibrosis, thalassemia, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, sickle cell anemia, polycythemia vera, and myelodysplastic syndrome. Affected patients often develop symptoms related to the location of the EMH. Reported treatments include red blood cell transfusions, surgical excision, decompressive laminectomy in cases of cord compression, chemotherapy, and irradiation. Radiation therapy is highly effective for treating hematopoietic tissue because such tissues are extremely radiosensitive. Megavoltage helical tomotherapy is a technical advance in the delivery of radiation therapy, allowing more conformal and precise treatments. The present case report describes a patient with the diagnosis of atypical chronic myeloid leukemia and myelofibrosis who subsequently developed EMH of the pericardium with effusion and tamponade. By utilizing tomotherapy we were able to treat the pericardium while sparing much of the myocardium. The patient tolerated treatment well without acute adverse effects. His symptoms were alleviated, but he died approximately 1 year later.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koch CA, L.C., Mesa RA, Tefferi A. Nonhepatosplenic extramedullary hematopoiesis: associated diseases, pathology, clinical course, and treatment. Mayo Clinic Proc 2003;78:1223–1233.
Steensma DP, Hook CC, Stafford SL, Tefferi A. Low-dose, single-fraction, whole-lung radiotherapy for pulmonary hypertension associated with myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia. Br J Haematol 2002;118:813–816.
Bubley G, Come P, MacDougall D, Thurer R, Goldberg J. Pericardial tamponade associated with myeloid metaplasia. Am J Hematol 1983;14:185–188.
McFarland JT, Kuzma C, Millard FE, Johnstone PA. Palliative irradiation of the spleen. Am J Clin Oncol 2003;26:178–183.
Shih LY, Lin FC, Kuo TT. Cutaneous and pericardial extramedullary hematopoiesis with cardiac tamponade in chronic myeloid leukemia. Am J Clin Pathol 1988;89:693–697.
Haedersdal C, Hasselbalch H, Devantier A, Saunamäki K. Pericardial haematopoiesis with tamponade in myelofibrosis. Scand J Haematol 1985;34:270–273.
Bradford CR, Smith SR, Wallis JP. Pericardial extramedullary haemopoiesis in chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia. J Clin Pathol 1993;46:674–675.
Pipoly GM, Rogers J. Cardiac tamponade resulting from pericardial extramedullary hematopoiesis: a case report and review of the literature. Cancer 1979;44:1504–1506.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Toms, D.R., Cannick, L., Stuart, R.K. et al. Helical tomotherapy for extramedullary hematopoiesis involving the pericardium in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia. Jpn J Radiol 28, 476–478 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-010-0452-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-010-0452-y