Abstract
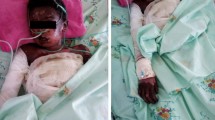
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are two of the most severe, rare, and life-threatening adverse reactions to medications. Their incidence is approximately two patients per million population per year. Several cases have been reported in the literature in which SJS and TEN have occurred in patients with a neoplasm undergoing radiation therapy and who are taking an anticonvulsant. We report a case of SJS-TEN that developed in a 51-year-old woman with nonresectable non-small-cell lung cancer during treatment with phenobarbital plus radiation therapy for bone metastases but in whom the irradiated areas did not exhibit the SJS skin reaction. To our knowledge, no similar cases have been reported in the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pereira A, Adarsh Vijay M, Rosmarin DM. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2007;56:181–200.
Aguiar D, Pazo R, Duràn I, Terrasa J, Arrivi A, Manzano H, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in patients receiving anticonvulsants and cranial irradiation: a risk to consider. J Neurooncol 2004;66:345–350.
Sommers RK, Kong MK, Bui TD, Fruehauf JP, Holcombe RF. Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis in a patient receiving concurrent radiation and gemcitabine. Anticancer Drugs 2003;14:659–662.
French EL. Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Steven Johnson syndrome: our current understanding. Allergol Int 2006;55:9–16.
Bastuji-Garin S, Fouchard N, Bertocchi M, Roujeau JC, Revuz J, Wolkenstein P. SCORTEN: a severity-of-illness score for toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Invest Dermatol 2000;115:149–153.
Mockenhaupt M, Messenheimer J, Tennis P, Schlingmann J. Risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in new users of antiepileptics. Neurology 2005;64:1134–1138.
Devi K, George S, Criton S, Suja V, Sridevi PK. Carbamazepine: the commonest cause of toxic epidermal necrolysis and Steven-Jonhson syndrome: a study of 7 years. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2005;71:325–328.
Rzany B, Correia O, Kelly JP, Naldi L, Auquier A, Stern R. Risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis during first weeks of antiepileptic therapy: a casecontrol study?Study Group of the International Case Control Study on Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions. Lancet 1999;354:1033–1034.
Paul C, Wolkenstein P, Adle H, Wechsler J, Garchon HJ, Revuz J, et al. Apoptosis as a mechanism of keratinocyte death in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Br J Dermatol 1996;134:710–714.
Belka C, Ottinger H, Kreuzfelder E, Weinmann M, Lindemann M, Lepple-Wienhues A, et al. Impact of localized radiotherapy on blood immune cells counts and function in humans. Radiother Oncol 1999;50:199–204.
Mitra S, Simcock R. Erlotinib induced skin rash spares skin in previously radiotherapy field. J Clin Oncol 2006;24:e28–e29.
Sanz A, Del Valle ML. A man whose scapula was spared a drug-associated rash. CMAJ 2005;15:745.
Lacouture EM, Hwang C, Marymont MH, Patel J. Temporal dependence of the effect of radiation on erlotinib-induced skin rash J Clin Oncol 2007;25:2140.
Vincenzi B, Santini D, Grilli C, La Cesa A, Dianzani C, Tonini G. Toxic epidermal necrolysis induced by oral phenobarbital and whole-brain radiotherapy in a breast cancer patient. J Clin Oncol 2004;15:4649–4651.
Duncan KO, Tigelaar RE, Bolognia JL. Stevens-Johnson syndrome limited to multiple sites of radiation therapy in a patient receiving phenobarbital. J Am Acad Dermatol 1999;40:493–496.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Musio, D., Parisi, E., Dionisi, F. et al. Irradiated fields spared Stevens-Johnson syndrome in a patient undergoing radiotherapy for bone metastases. Jap J Radiol 27, 103–106 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-008-0297-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-008-0297-9