Abstract
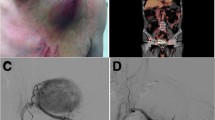
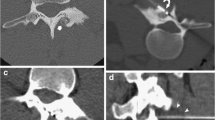
We report three cases of percutaneous osteoplasty for the treatment of hypervascular bone metastasis. Four hypervascular bone metastases were treated in three consecutive patients by percutaneous osteoplasty under fluoroscopic or computed tomographic guidance. Primary malignant tumors included pheochromocytoma and renal cell carcinoma. Pain relief after osteoplasty was achieved in all three patients. There was no major complication. Projectile bleeding and subcutaneous hematoma were noted during or after osteoplasty but were easily controlled conservatively. Percutaneous osteoplasty for hypervascular bone metastases is not only a highly effective but also a minimally invasive technique that provides immediate pain relief without major complication.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Le Gars D. [Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty.] Neurochirurgie 1987;33:166–168.
Hierholzer J, Anselmetti G, Fuchs H, Depriester C, Koch K, Pappert D. Percutaneous osteoplasty as a treatment for painful malignant bone lesions of the pelvis and femur. J Vasc Intervent Radiol 2003;14:773–777.
Hammond A, Riley LH 3rd, Gailloud P, Nussbaum DA, Malhotra A, Watkins M, et al. Treatment considerations for vertebroplasty in men. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25:639–641.
Cotten A, Dewatre F, Cortet B, Assaker R, Leblond D, Duquesnoy B, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteolytic metastases and myeloma: effects of the percentage of lesion filling and the leakage of methyl methacrylate at clinical follow-up. Radiology 1996;200:525–530.
Kelekis A, Lovblad KO, Mehdizade A, Somon T, Yilmaz H, Wetzel SG, et al. Pelvic osteoplasty in osteolytic metastases: technical approach under fluoroscopic guidance and early clinical results. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2005;16:81–88.
Papagelopoulos PJ, Mavrogenis AF, Kelekis AD, Katonis P, Galanis EC, Wenger DE, et al. Percutaneous osteoplasty for pelvic and spine metastases. Orthopedics 2006;29:315–323.
Schirmer CM, Malek AM, Kwan ES, Hoit DA, Weller SJ. Preoperative embolization of hypervascular spinal metastases using percutaneous direct injection with n-butyl cyanoacrylate: technical case report. Neurosurgery 2006;59:E431–432.
Manke C, Bretschneider T, Lenhart M, Strotzer M, Neumann C, Gmeinwieser J, et al. Spinal metastases from renal cell carcinoma: effect of preoperative particle embolization on intraoperative blood loss. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22:997–1003.
Chiras J, Cognard C, Rose M, Dessauge C, Martin N, Pierot L, et al. Percutaneous injection of an alcoholic embolizing emulsion as an alternative preoperative embolization for spine tumor. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1993;14:1113–1117.
Uemura A, Matsusako M, Numaguchi Y, Oka M, Kobayashi N, Niinami C, et al. Percutaneous sacroplasty for hemorrhagic metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005;26:493–495.
Weill A, Chiras J, Simon JM, Rose M, Sola-Martinez T, Enkaoua E. Spinal metastases: indications for and results of percutaneous injection of acrylic surgical cement. Radiology 1996;199:241–247.
Schaefer O, Lohrmann C, Markmiller M, Uhrmeister P, Langer M. Technical innovation: combined treatment of a spinal metastasis with radiofrequency heat ablation and vertebroplasty. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2003;180:1075–1077.
Peh WC, Gilula LA. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: indications, contraindications, and technique. Br J Radiol 2003;76:69–75.
Hartsell WF, Scott CB, Bruner DW, Scarantino CW, Ivker RA, Roach M 3rd, et al. Randomized trial of short-versus long-course radiotherapy for palliation of painful bone metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005;97:798–804.
Purkayastha S, Gupta AK, Kapilamoorthy TR, Kesavadas C, Thomas B, Krishnamoorthy T, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the management of vertebral lesions. Neurol India 2005;53:167–72; discussion 72–3.
Belkoff SM, Molloy S. Temperature measurement during polymerization of polymethylmethacrylate cement used for vertebroplasty. Spine 2003;28:1555–1559.
Bostrom MP, Lane JM. Future directions: augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral bodies. Spine 1997;22:38S–42S.
Dahl OE, Garvik LJ, Lyberg T. Toxic effects of methylmethacrylate monomer on leukocytes and endothelial cells in vitro. Acta Orthop Scand 1994;65:147–153.
King GJ, Kostuik JP, McBroom RJ, Richardson W. Surgical management of metastatic renal carcinoma of the spine. Spine 1991;16:265–271.
Sundaresan N, Choi IS, Hughes JE, Sachdev VP, Berenstein A. Treatment of spinal metastases from kidney cancer by presurgical embolization and resection. J Neurosurg 1990;73:548–554.
Mori K, Nishimura T, Katakami K, Kameda N, Nishimura S, Tanigawa N, et al. Basic experimental study of intraosseous venography using carbon dioxide contrast agent in percutaneous vertebroplasty. Nihon Igaku Houshasen Gakkai Zasshi 2005;62:136–144.
Vasconcelos C, Gailloud P, Beauchamp NJ, Heck DV, Murphy KJ. Is percutaneous vertebroplasty without pretreatment venography safe? Evaluation of 205 consecutive procedures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23:913–917.
Laredo JD, Hamze B. Complications of percutaneous vertebroplasty and their prevention. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 2005;26:65–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Shinoto, M., Hasuo, K., Aibe, H. et al. Percutaneous osteoplasty for hypervascular bone metastasis. Radiat Med 26, 603–608 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-008-0277-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-008-0277-0