Abstract
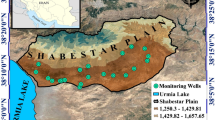
Groundwater level time series is a prime factor for variety of groundwater studies and is of great significance for the management of groundwater resources. Quality control of groundwater level observations is essential for hydrological applications. Artificial Intelligent techniques deal with highly nonlinear interactions and complex hydrological process and hence can be a better alternative for groundwater level prediction. In this research, the performances of Support Vector Regression (SVR) and SVR ensembled with metaheuristic Algorithm of Innovative Gunner (AIG) models were evaluated in simulating the monthly groundwater level of the Shabestar plain during the period 2001–2019. The 80 and 20% of the monthly dataset were used for training and testing the developed models. The efficiency of the developed models was compared using different statistical indices including correlation coefficient (R), Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency (NSE) coefficient, Root-Mean-Square Error (RMSE), RMSE-observation standard deviation ratio (RSR) and Legates & McCabe’s Index (ELM). The results showed that the hybrid model (SVR-AIG) generates accurate estimations in combinatory patterns. Moreover, among the SVR and SVR-AIG models with different input scenarios, the SVR-AIG model showed best results for scenario 6 (M6) in both the training stage (R = 0.995, NSE = 0.99, RMSE = 0.151 (m), RSR = 0.096 and ELM = 0.916) and the testing stage (R = 0.941, NSE = 0.879, RMSE = 0.146 (m), RSR = 0.346 and ELM = 0.660). The hybrid SVR-AIG model is shown to be more accurate and robust than the SVR models, providing a novel capability to capture unknown time-varying dependencies. In general, the results of the proposed model are promising and it provides a reliable insight for water resources planners in conducting future research of groundwater resources.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamowski J, Chan HF (2011) A wavelet neural network conjunction model for groundwater level forecasting. J Hydrol 407:28–40
Almasri MN, Kaluarachchi JJ (2005) Modular neural networks to predict the nitrate distribution in ground water using the on-ground nitrogen loading and recharge data. Environ Model Softw 20(7):851–871
Awad M, Khanna R (2015) Support vector regression. In: Efficient learning machines. Apress, Berkeley, CA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4302-5990-9_4.
Band SS, Heggy E, Bateni SM, Karami H, Rabiee M, Samadianfard S, Chau KW, Mosavi A (2021) Groundwater level prediction in arid areas using wavelet analysis and Gaussian process regression. Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech 15(1):1147–1158. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2021.1944913
Charmahineh AR, Zounemat Kermani M (2017) Evaluation of the efficiency of support vector regression, multi-layer perceptron neural network and multivariate linear regression on groundwater level prediction (case study: Shahrekord plain). J Watershed Manag Res 8(15):1–12. https://www.sid.ir/en/journal/viewpaper.aspx?id=541805.
Chen ST, Yu PS (2007) Real-time probabilistic forecasting of flood stages. J Hydrol 340:63
Coulibaly P, Anctil F, Aravena R, Bobee B (2001) Artificial neural network modeling of water table depth fluctuations. Water Resour Res 37(4):885–896
Daliakopoulos IN, Coulibaly P, Tsanis IK (2005) Groundwater level forecasting using artificial neural networks. J Hydrol 309(1–4):229–240
Dastvareh J, Naserianasl Z, Hasanvand H, Amiri Domari S (2020) Modeling groundwater level and investigating the aquifer status of Minab plain. Geogr Human Relationships 3(2):50–59. https://doi.org/10.22034/gahr.2020.247817.1442.
Dehghani R, Poudeh HT (2021a) Application of novel hybrid artificial intelligence algorithms to groundwater simulation. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03596-5
Dehghani R, Poudeh HT (2021b) Applying hybrid artificial algorithms to the estimation of river flow: a case study of Karkheh catchment area. Arab J Geosci 14:768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07079-2
Ebrahimi H, Rajaee T (2017) Simulation of groundwater level variations using wavelet combined with neural network, linear regression and support vector machine. Global Planet Change 148:181–191
Gholami V, Khaleghi MR, Salimi ET (2020) Groundwater quality modeling using self-organizing map (SOM) and geographic information system (GIS) on the Caspian southern coasts. J Mt Sci 17(7):1724–1734
Gholami V, Khaleghi MR, Pirasteh S, Booij MJ (2022) Comparison of self-organizing map, artificial neural network, and co-active neuro-fuzzy inference system methods in simulating groundwater quality: geospatial artificial. Water Resour Manage 36(2):451–469
Gill MK, Asefa T, Kaheil Y, McKee M (2007) Effect of missing data on performance of learning algorithms for hydrologic prediction: implication to and imputation technique. Water Resour Res 43(7):W07416
Guo XR, Zuo R, Wang JS, Meng L, Teng Y, Shi R, Gao X, Ding F (2019) Hydrogeochemical evolution of interaction between surface water and groundwater affected by exploitation. Groundwater 57:430–442. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12805
Hoque MDA, Adhikary SK (2020) Prediction of groundwater level using artificial neural network and multivariate time series models. In: 5th International conference on civil engineering for sustainable development (ICCESD 2020) at: KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh.
Hsieh PC, Tong WA, Wang YC (2019) A hybrid approach of artificial neural network and multiple regression to forecast typhoon rainfall and groundwater-level change. Hydrol Sci J 64(14):1793–1802. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2019.1677905
Isazadeh M, Biazar SM, Ashrafzadeh A (2017) Support vector machines and feed-forward neural networks for spatial modeling of groundwater qualitative parameters. Environ Earth Sci 76(17):p610
Jalali M, Kamangar M, Razmi R (2019) prediction of the water table surface model using the hyperbolic tangent function of the neural, network case study: Sarkhoon Plain. Hydrogeomorphol Tabriz Univ 6(20):101–119
Jeihouni, E., Eslamian, S., Mohammadi, M., & Zareian, M. J. (2019). Simulation of groundwater level fluctuations in response to main climate parameters using a wavelet–ANN hybrid technique for the Shabestar Plain, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 78(10). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8283-3.
Kayhomayoon Z, Ghordoyee Milan S, Arya Azar N, Moghaddam HK (2021) A new approach for regional groundwater level simulation: clustering, simulation, and optimization. Nat Resour Res 30:4165–4185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-021-09913-6
Kumar D, Roshni T, Singh A, Jha MK, Samui P (2020) Predicting groundwater depth fluctuations using deep learning, extreme learning machine and Gaussian process: a comparative study. Earth Sci Inf 13:1237–1250
Lee S, Lee KK, Yoon H (2019) Using artificial neural network models for groundwater level forecasting and assessment of the relative impacts of influencing factors. Hydrogeol J 27:567–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1866-3
Liu D, Mishra AK, Yu Z, Lu H, Li Y (2021) Support vector machine and data assimilation framework for Groundwater Level Forecasting using GRACE satellite data. J Hydrol 603 (A):126929.
Lorenzo-Lacruz J, Garcia C, Morán-Tejeda E (2017) Groundwater level responses to precipitation variability in Mediterranean insular aquifers. J Hydrol 2017(552):516–531
Malik A, Bhagwat A (2021) Modelling groundwater level fluctuations in urban areas using artificial neural network. Groundw Sustain Dev 12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100484
Milan SG, Roozbahani A, Banihabib ME (2018) Fuzzy optimization model and fuzzy inference system for conjunctive use of surface and groundwater resources. J Hydrol 566:421–434
Mirarabi A, Nassery HR, Nakhaei M, Adamowski J, Akbarzadeh AH, Alijani F (2019) Evaluation of data-driven models (SVR and ANN) for groundwater-level prediction in confined and unconfined systems. Environ Earth Sci 78:489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8474-y
Moghaddam HK, Moghaddam HK, Rahimzadeh Kivi Z, Bahreinimotlagh M, Alizadeh MJ ( 2019) Developing comparative mathematic models, BN and ANN for forecasting of groundwater levels. Groundwater Sustain Dev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100237.
Moosavi V, Mahjoobi J, Hayatzadeh M (2021) Combining group method of data handling with signal processing approaches to improve accuracy of groundwater level modeling. Natural Resources Res 30(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-020-09799-w.
Moravej M, Amani P, Hosseini-Moghari SM (2020) Groundwater level simulation and forecasting using interior search algorithm-least square support vector regression (ISA-LSSVR). Groundw Sustain Dev 11:100447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100447
Nadiri AA, Naderi K, Khatibi R, Gharekhani M (2019) Modelling groundwater level variations by learning from multiple models using fuzzy logic. Hydrol Sci J 64(2):210–226. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2018.1554940
Nadiri AA, Razzagh S, Khatibi R, Sedghi Z (2021) Predictive groundwater levels modelling by Inclusive Multiple Modelling (IMM) at multiple levels. Earth Sci Inf 14(14):749–763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-021-00572-y
Natarajan N, Sudheer Ch (2019) Groundwater level forecasting using soft computing techniques. Neural Comput Appl 32(12):7691–7708.
Nourani V, Mogaddam AA, Nadiri AO (2008) An ANN-based model for spatiotemporal groundwater level forecasting. Hydrol Process 22:5054–5066. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7129
Nourani V, Alami MT, Vousoughi FD (2015) Wavelet-entropy data pre-processing approach for ANN-based groundwater level modeling. J Hydrol 524:255–269
Di Nunno F, Granata F (2020) Groundwater level prediction in Apulia region (Southern Italy) using NARX neural network. Environ Res 190:110062. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110062.
Osman AAI, Ahmed AN, Fai Chow M, Feng Huang Y, El-Shafie (2021) Extreme gradient boosting (Xgboost) model to predict the groundwater levels in Selangor Malaysia. Ain Shams Eng J 12(2):1545–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2020.11.011
Panahi M, Misaqi F, Qanbari F (2017) Determining of trend variation in quality parameters of Shabestar plain underground water. Environ Sci 15(3):19–38
Pijarski P, Kacejko P (2019) A new metaheuristic optimization method: the algorithm of the innovative gunner (AIG). Eng Optim 51(12):2049–2068.
Raghavendra N, Deka PC (2015) Forecasting monthly groundwater level fluctuations in coastal aquifers using hybrid Wavelet packet-support vector regression. Cogent Eng 2(1):p999414
Rajaee T, Ebrahimi H, Nourani V (2019) A reviewof the artificial intelligencemethods in groundwater level modeling. J Hydrol 572:336–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.12.037
Ranjpisheh M, Karimpour Reihan M, Zehtabian GhR, Khosravi H (2018) Assessment of drought and landuse changes: impacts on groundwater quality in Shabestar basin. North of Lake Urmia Desert 23(1):9–19
Reinecke R, Wachholz A, Mehl S, Foglia L, Niemann C, Döll P (2020) (2020) Importance of spatial resolution in global groundwater modeling. Groundwater 58:363–376
Roshni T, Jha MK, Deo RC, Vandana A (2019) Development and evaluation of hybrid artificial neural network architectures for modeling spatio-temporal groundwater fluctuations in a complex aquifer system. Water Resour Manage 33:2381–2397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02253-4
Roshni T, Jha MK, Drisya J (2020) Neural network modeling for groundwater-level forecasting in coastal aquifers. Neural Comput & Appl 32:12737–12754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04722-z
Roshni T, Jha MK, Kamii Y (2008) Modeling groundwater fluctuations in unconfined aquifers by Artificial Neural Networks. In: Conference: second international junior researcher and engineer workshop on hydraulic structures at: Pisa, Italy.
Roy DK, Biswas SK, Mattar MA, El-Shafei AA, Murad KFI, Saha KK, Datta B, Dewidar AZ (2021) Groundwater level prediction using a multiple objective genetic algorithm-grey relational analysis based weighted ensemble of ANFIS models. Water 13:3130. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13213130.
Safavi HR, Esmikhani M (2013) Conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater: application of support vector machines (SVMs) and genetic algorithms. Water Resour Manag 27(7):2623–2644
Sahoo S, Russo TA, Elliott J, Foster I (2017) Machine learning algorithms for modeling groundwater level changes in agricultural regions of the U.S. Water Resour Res 53:3878–3895.
Sahoo S, Jha MK (2013) Groundwater-level prediction using multiple linear regression and artificial neural network techniques: a comparative assessment. Hydrogeol J 21(8):1865–1887
Seifi A, Ehteram M, Singh VP, Mosavi A (2020) Modeling and uncertainty analysis of groundwater level using six evolutionary optimization algorithms hybridized with ANFIS, SVM, and ANN. Sustainability 2020(12):4023. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12104023
Sharafati A, Asadollah SBHS, Neshat A (2020) A new artificial intelligence strategy for predicting the groundwater level over the Rafsanjan aquifer in Iran. J Hydrol 591:125468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125468
Sun Y, Wendi D, Kim DE, Liong S-Y (2016) Technical note: Application of artificial neural networks in groundwater table forecasting - a case study in a Singapore swamp forest. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20:1405–1412. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-1405-2016
Supreetha B, Nayak PK, Shenoy NK (2015) Groundwater level prediction using hybrid artificial neural network with genetic algorithm. Int J Earth Sci Eng 8:2609–2615
Suryanarayana C, Sudheer C, Mahammood V, Panigrahi BK (2014) An integrated wavelet-support vector machine for groundwater level prediction in Visakhapatnam India. Neurocomputing 145:324–335
Vapnik V (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer-Verlag, New York
Vapnik V (2013) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, New York
Wu C, Zhang X, Wang W, Lu C, Zhang Y, Qin W, Tick GR, Li B, Shu L (2021) Groundwater level modeling framework by combining the wavelet transform with a long short-term memory data-driven model. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146948
Wunsch A, Liesch T, Broda S (2021) Groundwater level forecasting with artificial neural networks: a comparison of long short-term memory (LSTM), convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and non-linear autoregressive networks with exogenous input (NARX). Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 25:1671–1687. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-25-1671-2021
Xing B, Gan R, Liu G, Liu Z, Zhang J, Ren Y (2016) Monthly mean streamflow prediction based on bat algorithm-support vector machine. J Hydrol Eng 21(2):04015057
Yoon H, Jun S-C, Hyun Y, Bae G-O, Lee K-K (2011a) A comparative study of artificial neural networks and support vector machines for predicting groundwater levels in a coastal aquifer. J Hydrol 396(1–2):128–138
Yoon H, Hyun Y, Ha K, Lee K-K, Kim G-B (2011b) A method to improve the stability and accuracy of ANN- and SVM-based time series models for longterm groundwater level predictions. Comp Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2016.03.002
Zounemat-Kermani M, Kişi Ö, Adamowski J, Ramezani-Charmahineh A (2016) Evaluation of data driven models for river suspended sediment concentration modeling. J Hydrol 535:457–472
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no unknown competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Edited by Dr. Mohammad Valipour (ASSOCIATE EDITOR) / Dr. Michael Nones (CO-EDITOR-IN-CHIEF).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roshni, T., Mirzania, E., Hasanpour Kashani, M. et al. Hybrid support vector regression models with algorithm of innovative gunner for the simulation of groundwater level. Acta Geophys. 70, 1885–1898 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00826-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00826-3