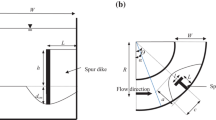
Abstract
A spur dike is a hydraulic structure, protruding in a river or channel used for several purposes like protection of river-bank erosion and deepening of the main channel. The present paper discusses pre-existing research work on flow pattern and prediction of temporal and maximum scours depth around the spur dikes placed in different locations at 90\(^\circ \) and 180° curved channels. The equations having approximately 2.367, 4.47, 0.17, and 0.271 (average) times with their corresponding experimental data. The parameters, influencing the scour process and flow pattern, have been identified as the ratio of flow intensity to critical velocity (V/Vc ≥ 1) is below 1 and special kind of bedding material is approximately 10 % greater than under live-bed condition and many more. The numerical value of the Froude number and the geometry of the bed surface material are also discussed in this paper. Based on these parameters, the empirical formulations and experimental studies on local scours around the straight, L-shaped, T-shaped spurs, placed at 30°, 45°, 60°, 120°, and 180° azimuthal angles have been discussed. Various numerical schemes proposed in almost seventy-five literatures have been summarized. A critical review of numerical and experimental results found in different works related to temporal and maximum scour depth, flow characteristics, and bed topography around the dike shows that the data and accompanying results are insufficient for the design of spurs used as river structures in curved channels. There are needs to carry out extensive experiments, under various flow conditions, to examine the flow behavior and scouring processes around the spurs. Due to complex flow pattern and scouring processes, taking place around the spur, it becomes difficult to understand the real physics behind these phenomenon and therefore, data-driven models are suggested to arrive at more reasonable relationships required to be used for design purposes.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(a\) :
-
Width of scour
- \(a_{1} ,\;a_{2} ,\;a_{3} \;{\text{and}}\;a_{4}\) :
-
Constants
- \(B\) :
-
Wing length of spur dike
- \(c\) :
-
Upstream length of scour
- \(d\) :
-
Downstream length of scour
- \({d}_{z}\) :
-
Scour depth at any time instant \(t\)
- \({D}_{m}\) :
-
Maximum scour depth
- \({d}_{50}\) :
-
Median diameter of bed sediment
- \(Fr\) :
-
Froude number of approach flow
- \(g\) :
-
Acceleration due to gravity
- \({k}_{i}\) where \(i\) :
-
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6: constants
- \(K_{\theta } ,\;K_{L} ,\;K_{{{\text{Fr}}}}\) :
-
Functions of \(\theta \), \(Fr,\) and \(L,\) respectively
- \(L\) :
-
Length of spur dike
- \({R}_{c}\) :
-
Lenter radius of the bend
- \({t}_{e}\) :
-
Time required to reach equilibrium or maximum scour depth
- \(V\) :
-
Approach velocity
- \({V}_{c}\) :
-
Bed particle critical velocity
- \({V}_{*c}\) :
-
Critical shear velocity
- \({V}_{0}\) :
-
Scour volume
- \(W\) :
-
Width of channel
- \(y\) :
-
Approach flow depth
- \(\varphi \) :
-
Maximum dimension of scour parameters
- \(\tau \) :
-
Bed shear stress
- \(\theta \) :
-
Inclination angle of spur dike
References
Akbari M, Vaghefi M, Chiew YM (2021) Effect of T-shaped spur dike length on mean flow characteristics along a 180-degree sharp bend. J Hydrol Hydromech 69(1):98–107
Biswas P, Barbhuiya AK (2015) Experimental study on scour at 90° horizontal forced bend and its protection using riprap. Aquat Proced 4:797–804
Breusers HNC (1963) Discussion of ’sediment transportation mechanics: erosion of sediment ’by task force on preparation of sedimentation manual. J Hydraulic Div Am Soc Civ Eng 89:277–281
Breusers HNC (1967) Time scale of two-dimensional local scour. In: Proc. 12th Congress IAHR3:C32IAHR.
Chabert J, Engeldinger P (1956) Study of scour around bridge piers. Rep Prepared for the Laboratoire National d’Hydraulique.
Chen FY, Ikeda S (1997) Horizontal separation flows in shallow open channels with spur dikes. J. Hydrosci & Hydraul Eng (JSCE) 15(2):15–30
Chen NS, Li CH (1989) Numerical solution of the flow around a spur dike with turbulent model. J Nanjing Hydraul Res Inst 3:11–23
Chiew YM (1984) Local scour at bridge piers (Doctoral dissertation, ResearchSpace@ Auckland).
Coleman SE, Lauchlan CS, Melville BW (2003) Clear-water scour development at bridge abutments. J Hydraul Res 41(5):521–531
Coscarella F, Gaudio R, Manes C (2020) Near-bed eddy scales and clear-water local scouring around vertical cylinders. J Hydraul Res 58(6):968–981
Duan JG (2009) Mean flow and turbulence around experimental spur dike advances in water resources. J Hydraul Div 32:1717–1725
Ettema R, Muste M (2004) Scale effects in flume experiments on flow around a spur dike in flatbed channel. J Hydraul Eng 130(7):635–646
Fazli M, Ghodsian M, Neyshabouri SAAS (2008) Scour and flow field around a spur dike in a 90° bend. Int J Sedim Res 23(1):56–68
Fei-Yong C, Ikeda S (1997) Horizontal separation flows in shallow open channels with spur dikes. J Hydrosci Hydraul Eng 15(2):15–30
Gaur S, Johannet A, Graillot D, Omar PJ (2021) Modeling of groundwater level using artificial neural network algorithm and WA-SVR model. In: Pande C.B., Moharir K.N. (Eds) groundwater resources development and planning in the semi-arid region. Springer, Cham, 129–150, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-68124-1_7
Ghodsian M, Vaghefi M (2009) Experimental study on scour and flow field in a scour hole around a T-shape spur dike in a 90° bend. Int J Sedim Res 24(2):145–158
Giglou AN, Mccorquodale AJ, Solari J (2018) Numerical study on the effect of the spur dikes on sedimentation pattern. Ain Shams Eng J 9(4):2057–2066
Gill MA (1972) Erosion of sand beds around spur dikes. J Hydraul Div 98(9):1587–1602
Giri S, Shimizu Y, Fujita M (2003) Flow characteristics in a mildly meandering channel with & without river training structure. Proc Hydraul Eng 47:835–840
Karami H, Basser H, Ardeshir A, Hosseini SH (2012) Verification of numerical study of scour around spur dikes using experimental data. Water and Environ J 28(1):124–134
Kikkawa H, Ikeda S, Kitagawa A (1976) Flow and bed topography in curved open channels. J Hydraul Div 102(9):1327–1342
Kohli A, Hager WH (2001) Buildings scour in floodplains. In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Water and Maritime Engineering 148(2): 61-80
Koken M, Constantinescu G (2008) An investigation of the flow and scour mechanisms around isolated spur dikes in a shallow open channel: 2 Conditions corresponding to the final stages of the erosion and deposition process. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007WR006491
Kothari UC, Ranga Raju KG (2001) Scour around spur dikes and bridge abutments. J Hydraul Res 39(4):367–374
Kwan RT, Melville BW (1994) Local scour and flow measurements at bridge abutments. J Hydraul Res 32(5):661–673
Laursen EM, Toch A (1953) A generalized model study of scour around bridge piers and abutments (No. HR-24). State University of Iowa
Laursen EM (1952) Observations on the nature of scour. proceedings of 5th hydraulic conference state university of Iowa Bulletin 34: 179–197
Manes C, Brocchini M (2015) Local scour around structures and the phenomenology of turbulence. J Fluid Mech 779:309
Masjedi A, Bejestan MS, Moradi A (2010a) a) Experimental study on the time development of local scour at a spur dike in a 180°-flume bend. J Food Agric Environ 8(2):904–907
Masjedi A, Bejestan MS, Rahnavard P (2010b) b) Experimental study on the time development of local scour on around single T-shape spur dike in a 180-degree flume bend. Res J Environ Sci 4(6):530–539
Masjedi A, Dehkordi V, Alinejadi M, Taeedi A (2010c) c) Experimental study on scour depth in around a t-shape spur dike in a 180-degree bend. World Appl Sci J 10(10):1146–1152
Masjedi A, Akbari I, Abyar H (2011) Evaluating scour at L-shape spur dike in a 180-degree bend. World Appl Sci J 15(12):1740–1745
Mayerle R, Wang SSY, Toro FM (1995) Verification of a three-dimensional numerical model simulation of the flow in the vicinity of spur dikes. J Hydraul Res 33(2):243–256
Mehraein M, Ghodsian M, Mashizi MK, Vaghef M (2017) Experimental study on flow pattern and scour hole dimensions around a t-shaped spur dike in a channel bend under emerged and submerged conditions. Int J Civ Eng 15(7):1019–1034
Melville BW (1992) Local scour at bridge abutments. J Hydraul Eng 118(4):615–631
Molinas A, Kheireldin K, Wu B (1998) Shear stress around vertical wall abutments. J Hydraul Eng 124(8):822–830
Odgaard AJ, Bergs MA (1988) Flow processes in a curved alluvial channel. Water Resour Res 24(1):45–56
Omar PJ, Kumar V (2021) Land surface temperature retrieval from TIRS data and its relationship with land surface indices. Arab J Geosci 14(18):1–14
Omar PJ, Gaur S, Dwivedi SB, Dikshit PKS (2019) Groundwater modelling using an analytic element method and finite difference method: an insight into lower ganga river basin. J Earth Syst Sci 128(7):1–10
Omar PJ, Gaur S, Dwivedi SB, Dikshit PKS (2020) A modular three-dimensional scenario-based numerical modelling of groundwater flow. Water Resour Manage 34(6):1913–1932
Omar PJ, Shivhare N, Dwivedi SB, Gaur S, Dikshit PKS (2021) Study of methods available for groundwater and surfacewater interaction: a Case Study on Varanasi, India. In: Chauhan M.S., Ojha C.S.P. (Eds) The Ganga River Basin: A Hydrometeorological Approach. Society of Earth Scientists Series. Springer, Cham, 67–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60869-9_5.
Oslen NRB (1999, 2000, 2001) Computational fluid dynamics in hydraulic and sedimentation engineering. Class NotesDepartment of Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering, Norwegian University of Science and Technology Norway
Oslen NRB (2018) A three-dimensional numerical model for simulation of sediment movement in water intakes with multiblock option. User's ManualDepartment of Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering, Norwegian University of Science and Technology Norway
Pagliara S, Kurdistani SM (2015) Clear water scour at J-Hook Vanes in channel bends for stream restorations. Ecol Eng 83:386–393
Pandey M, Ahmad Z, Sharma PK (2018) Scour around impermeable spur dikes: a review. ISH J Hydraul Eng 24(1):25–44
Pandey M, Valyrakis M, Qi M, Sharma A, Lodhi AS (2021) Experimental assessment and prediction of temporal scour depth around a spur dike. Int J Sedim Res 36(1):17–28
Peng J (2004) Flow and local scour around spur-dike. The Yellow River Press Publications, Zheng Zhou, China
Radan P, Vaghefi M (2016) Flow and scour pattern around submerged and non-submerged T-shaped spur dikes in a 90° bend using the SSIIM model. Intl j River Basin Manag 14(2):219–232
Rajaratnam N, Nwachukwu BA (1983) Flow near groin-like structures. J Hydraul Eng 109(3):463–480
Rashedipoor A, Masjedi A, Shojaenjad R (2012) Investigation on scour hole around spur dike in a 180 degree flume bend. World Appl Sci J 19(7):924–928
Rouse H (1965) Engineering hydraulics: sediment transportation
Rozovski I (1957) Flow of water in bends of open channels. is program for Sci. Trans Jerusalem
Sharma K, Mohapatra PK (2012) Separation zone in flow past a spur dyke on rigid bed meandering channel. J Hydraul Eng 138(10):897–901
Shekhar S, Chauhan MS, Omar PJ, Jha M (2021) River discharge study in river Ganga, Varanasi using conventional and modern techniques. In: Chauhan M.S., Ojha C.S.P. (Eds) The Ganga River Basin: A Hydrometeorological Approach. Society of Earth Scientists Series. Springer, Cham. pp 101–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60869-9_7.
Shukry A (1950) Flow around bends in an open flume. Trans ASCE 115:751–779
Singh RK, Pandey M, Pu JH, Pasupuleti S, Villuri VGK (2020) Experimental study of clear-water contraction scour. Water Supply 20(3):943–952
Tang X, Ding X, Chen Z (2006) Large eddy simulations of three-dimensional flows around a spur dike. Tsinghua Sci Technol 11(1):117–123
Tingsanchali T, Maheswaran S (1990) 2-D depth-averaged flow computation near groyne. J Hydraul Eng 116(1):71–86
Tripathi RP, Pandey KK (2021) Experimental study of local scour around T-shaped spur dike in a meandering channel. Water Supply 21(2):542–552
Vaghefi M, Shakerdargah M, Fiouz AR, Akbari M (2014) Numerical Investigation of the effect of froude number on flow pattern around a single T-shaped spur dike in a bend channel. Intl J Eng Res 3(5):351–355
Vaghefi M, Ghodsian M, Salehi Neyshaboori SAA (2009) Experimental study on the effect of a T-shaped spurs dike length on scour in a 90° -channel bend. Arab J Sci Eng 34(2):337
Vaghefi M, Ghodsian M, Neyshabouri SAAS (2012) Experimental study on scour around a T-shaped spur dike in a channel bends. J Hydraul Eng 138(5):471–474
Vaghefi M, Safarpoor Y, Hashemi SS (2015) Effects of relative curvature on the scour pattern in a 90° bend with a T-shaped spur dike using a numerical method. Intl J River Basin Manag 13(4):501–514
Vaghefi M, Safarpoor Y, Akbari M (2016) Numerical investigation of flow pattern and components of three-dimensional velocity around a submerged T-shaped spur dike in a 90° bend. J Cent South Univ 23(11):2984–2998
Vaghefi M, Ghodsian M, Akbari M (2017a) Experimental investigation on 3D flow around a single T-shaped spur dike in a bend. Periodica Polytechnica Civil Eng 61(3):462–470
Vaghefi M, Safarpoor Y, Akbari M (2017b) Numerical comparison of the parameters influencing the turbulent flow using a T-shaped spur dike in a 90° bend. J Appl Fluid Mech 10(1):231–241
Vaghefi M, Safarpoor Y, Hashemi SS (2017c) Effect of T-shaped spur dike on flow separation in a 90° bend using SSIIM model. J Natl Sci Found of Sri Lanka. https://doi.org/10.4038/jnsfsr.v45i2.8181
Versteeg HK, Malalasekera W (2007) An introduction to computational fluid dynamics: the finite volume method. Pearson Educ. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2005)131:9(782)
Wim SJU (2005) Effects of groyne layout on the flow in groyne fields: laboratory experiments. J Hydraul Eng 131(9):782–791
Xiufanga Z, Pingyi M, Chengyu Y (2012) Experimental Study on flow turbulence distribution arounda spur dike with different structure. Procedia Eng 28:772–775
Yazdi J, Sarkardeh H, Azamathulla HM, Ghani AA (2010) 3D simulation of flow around a single spur dike with free-surface flow. Intl J River Basin Manag 8(1):55–62
Yossef MFM, Vriend HJ (2011) Flow details near river groynes: experimental investigation. J Hydraul Eng 137(5):504–516
Zaghloul NA (1983) Local scour around spur-dikes. J Hydrol 60(1–4):123–140
Zhang H, Nakagawa H (2008) Scour around spur dyke: recent advances and future researches.
Zhou Y (2001) Large-eddy simulation of 3-D flow motion around submerged spur-dike. J Yangtze River Sci Res Inst. 18(5):28–36
Zhou K, Duan JG, Bombardelli FA (2020) Experimental and theoretical study of local scour around three-pier group. J Hydraul Eng 146(10):04020069
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by Dr. Giulio Dolcetti (GUEST EDITOR) / Dr. Michael Nones (CO-EDITOR-IN-CHIEF).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, R.P., Pandey, K.K. Scour around spur dike in curved channel: a review. Acta Geophys. 70, 2469–2485 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00795-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00795-7