Abstract
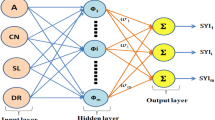
The study was performed to estimate the weekly sediment load in Thal canal located in Mianwali district Punjab, Pakistan. Past records of sediments and discharge have been considered as the input parameters. The best input combinations have been identified with the help of advanced algorithms including full, sequential and increasing embedding, genetic algorithm and hill climbing in combination with the gamma test. Model training has been carried out using two artificial neural network-based algorithms, namely Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno (BFGS), back-propagation and a local linear regression technique. A variety of statistical parameters including R square, root mean squared error, mean square error and mean bias error (MBE) has been calculated in order to evaluate the best models. The results strongly suggested that BFGS-based model performed better than all other models with remarkably low values of MBE. Significantly high values of correlation coefficient (R square) in both training and testing evidenced a close similarity between actual and predicted sediment load values for the same model.

(Source: Google Map)




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahart RJ, White SM (2001) Modelling sediment transfer in Malawi: comparing back-propagation neural network solutions against a multiple linear regression benchmark using small data sets. Phys Chem Earth (B) 26(1):19–24
Ackers JC, Butler D, May RWP (1996) Design of sewers to control sediment problems. Constr Ind Res Inf Assoc (CIRIA) 141:181
Adib A, Mahmoodi A (2017) Prediction of suspended sediment load using ANN GA conjunction model with Markov chain approach at flood conditions. KSCE J Civ Eng 21(1):447–457
Agalbjorn S, Koncar N, Jones AJ (1997) A note on the gamm test. Neural Comput Appl 5:131
Alp M, Cigizoglu HK (2007) Suspended sediment load simulation by two artificial neural network methods using hydrometeorological data. Environ Model Softw 22:2–13
Ashkarian S, Kiamanesh H, Hedayat N (2010) Simulation of flow pattern using FLOW 3D in Dez Diversion Dam in Dezful. In: Proceedings of national conference on water, soil, plant sciences and agricultural mechanization, Islamic Azad University- Dezful Branch, Dezful, Iran
Ashley RM, Wotherspoon DJJ, Coghlan BP et al (1992) The erosion and movement of sediments and associated pollutants in combined sewers. Water Sci Technol 25(8):101–114
Atieh M, Mehltretter SL, Gharabaghi B et al (2015) Integrative neural networks model for prediction of sediment rating curve parameters for ungauged basins. J Hydrol 531:1095–1107
Azamathulla HMd, Ab Ghani A, Chang CK et al (2010) Machine learning approach to predict sediment load: a case study. Clean-Soil Air Water 38(10):969–976
Ballio F, Tait S (2012) Sediment transport mechanics. Acta Geophys 60(6):1493–1499
Bhattacharya B, Price RK, Solomatine DP (2007) Machine learning approach to modelling sediment transport. J Hyraulic Eng 133(4):440–450
Bong CHJ, Lau TL, Ab Ghani A (2013) Verification of equations for incipient motion studies for a rigid rectangular channel. Water Sci Technol 67(2):395–403
Buyukyildiz M, Kumcu SY (2017) An estimation of the suspended sediment load using adaptive network based fuzzy inference system, support vector machine and artificial neural network models. Water Resour Manag 31(4):1343–1359
Cannon AJ, Whitfield PH (2002) Downscaling recent stream-flow conditions in British Columbia, Canada using ensemble neural networks. J Hydrol 259:136–151
Chang FJ, Tsai MJ (2016) A nonlinear spatio-temporal lumping of radar rainfall for modeling multi-step-ahead inflow forecasts by data-driven techniques. J Hydrol 535:256–269
Chang FJ, Wang YC, Tsai WP (2016) Modelling intelligent water resources allocation for multi-users. Water Resour Manag 30:1395–1413
Choubin B, Malekian A (2017) Combined gamma and M-test-based ANN and ARIMA models for groundwater fluctuation forecasting in semiarid regions. Environ Earth Sci 76:538
Choubin B, Darabi H, Rahmati O et al (2018) River suspended sediment modelling using the CART model: a comparative study of machine learning techniques. Sci Total Environ 615:272–281
Cigizoglu HK (2003a) Estimation, forecasting and extrapolation of flow data by artificial neural networks. Hydrol Sci J 48(3):349–361
Cigizoglu HK (2003b) Incorporation of ARMA models into flow forecasting by artificial neural networks. Environmetrics 14(4):417–427
Cigizoglu HK (2004) Estimation and forecasting of daily suspended sediment data by multi layer perceptrons. Adv Water Resour 27:185–195
De Sutter R, Rushforth P, Tait S et al (2003) Validation of existing bed load transport formulas using in-sewer sediment. J Hydraul Eng 129(4):325–333
Duru U, Arabi M, Whol EE (2018) Modeling stream flow and sediment yield using the SWAT model: a case study of Ankara River basin, Turkey. Phys Geogr 39(3):264–289
El-Zaemey AKS (1991) Sediment transport over Deposited beds in sewers. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Newcastle upon Tyne
Fletcher R (1987) Practical methods of optimization. Wiley, New York
Freiwan M, Cigizoglu HK (2005) Prediction of total monthly rainfall in Jordan using feed forward backpropagation method. Fresenius Environ Bull 14(2):142–151
Ghani Ab, Salem A, Abdullah AM et al (1999) Incipient motion of sediment particles over loose deposited beds in a rigid rectangular channel. In: Eighth international conference on urban storm drainage. Sydney, p 157–163
Hall T (1999) Precipitation forecasting using a neural network. Weather Forecast 14:338–345
Han D, Yan W (2009) Validation of the Gamma test for model input data selection: with a case study in evaporation estimation, In: Fifth international conference on natural computation, Tianjin, China, p 469–473
Hassan M, Shamim MA, Hashmi HN et al (2015a) Predicting stream flows to a multipurpose reservoir using artificial neural networks and regression techniques. Earth Sci Inf 8(2):337–352
Hassan M, Shamim MA, Sikandar A et al (2015b) Development of sediment load estimation models by using artificial neural networking techniques. Environ Monit Assess 187:686
Himanshu SK, Pandey A, Shrestha P (2017) Application of SWAT in an Indian river basin for modeling runoff, sediment and water balance. Environ Earth Sci 76(1):3
Jaafar WZW, Liu J, Han D (2011) Input variable selection for median flood regionalization. Water Resour Res 47(7):W07503
Jones AJ, Tsui A, De Oliveira AG (2002) Neural models of arbitrary chaotic systems: construction and the role of time delayed feedback in control and synchronization. Complex Int 9:1–9
Kisi O, Cimen M (2012) Precipitation forecasting by using wavelet support vector machine conjunction model. Eng Appl Artif Intell 25:783–792
Kumar R, Singh S, Singh A et al (2018) Dynamics of suspended sediment load with respect to summer discharge and temperatures in Shaune Garang glacierized catchment, Western Himalaya. Acta Geophys 66(5):1109–1120
Lafdani EK, Nia AM, Ahmadi A (2013) Daily suspended sediment load prediction using artificial neural networks and support vector machines. J Hydrol 478:50–62
Litta AJ, Idicula SM, Mohanty UC (2013) Artificial neural network model in prediction of meteorological parameters during monsoon thunderstorms. Int J Atmos Sci 2013(525383):14
Loveless JH (1992) Sediment transport in rigid boundary channels with particular reference to the condition of incipient deposition, Ph.D. Thesis. University of London
Melesse AM, Ahmad S, McClain ME (2011) Suspended sediment load prediction of river systems: an artificial neural network approach. Agric Water Manag 98(5):855–866
Mohammadi M (2005) The initiation of sediment motion in fixed bed channels. Iran J Sci Technol 29(B3):365–372
Mustafa M, Isa M, Rezaur R (2011) A comparison of artificial neural networks for prediction of suspended sediment discharge in river—a case study in Malaysia. Int J Civil Environ Struct Constr Archit Eng 5(9):368–372
Nagy HM, Watanabe K, Hirano M (2002) Prediction of sediment load concentration in rivers using artificial neural network model. J Hydraulic Eng (ASCE) 128(6):588–595
Nourani V, Alizadeh F, Roushangar K (2016) Evaluation of a two-stage SVM and spatial statistics methods for modeling monthly river suspended sediment load. Water Resour Manag 30(1):393–407
Novak P, Nalluri C (1984) Incipient motion of sediment particles over fixed beds. J Hydraul 22(3):181–197
Ochiere HO, Onyando JO, Kamau DN (2015) Simulation of sediment transport in the canal using the Hec-Ras (Hydrologic Engineering Centre: river analysis system) In an Underground Canal in Southwest Kano Irrigation Scheme-Kenya. Int J Eng Sci Invent 4(9):15–31
Ota JJ, Nalluri C (2003) Urban storm sewer design: approach in consideration of sediments. J Hydraul Eng 129(4):291–297
Partal T, Cigizoglu HK (2008) Estimation and forecasting of daily suspended sediment data using wavelet–neural networks. J Hydrol 358:317–331
Reddy SB (2003) Estimation of watershed runoff using artificial neural networks. Ph.D Thesis in Agric. Engineering (unpubl.). Post Graduate School, IARI, New Delhi
Remesan R, Shamim MA, Han D (2008) ANFIS and NNARX based rainfall-runoff modeling. In: IEEE International conference on systems, man and cybernetics. Singapore, p 1453–1458
Remesan R, Shamim MA, Han D (2008b) Model input data selection using gamma test for daily solar radiation estimation. Hydrol Process 22:4301–4309
Rezaei K, Guest B, Friedrich A et al (2009) Feed forward neural network and interpolation function models to predict the soil and subsurface sediments distribution in Bam, Iran. Acta Geophys 57(2):271–293
Safari MJS, Mohammadi M, Gilanizadehdizaj G (2013) Investigation on incipient deposition and incipient motion of sediment particles in rigid boundary channels. Water Soil Sci 23(3):13–24
Safari MJS, Mohammadi M, Gilanizadehdizaj G (2014) On the effect of cross-sectional shape on incipient motion and deposition of sediments in fixed bed channels. J Hydrol Hydromech 62(1):75–81
Safari MJS, Aksoy H, Mohammadi M (2015) Incipient deposition of sediment in rigid boundary open channels. Environ Fluid Mech 15(5):1053–1068
Safari MJS, Aksoy H, Mohammadi M (2016) Artificial neural network and regression models for flow velocity at sediment incipient deposition. J Hydrol 541:1420–1429
Sajedi AH (2010) Analytical study of the sediment formation using the SHARC computer model: a case study of the western water Intake in the Dez diversion weir in Dezfu Iran. M.Sc dissertation, I.Azad University, Dezful, Iran
Sajedipoor AH, Hedayat N, Rohani A et al (2010) Analytical study of sedimentation formation in lined canals using the SHARC Software: a case study of the Sabilli Canal in Dezful, Iran. Int J Environ Chem Ecol Geol Geophys Eng 4:11
Sarangi A, Bhattacharya AK (2005) Comparison of artificial neural network and regression models for sediment loss prediction from Banha watershed in India. Agric Water Manag 78:195–208
Shamim MA, Bray M, Remesan R et al (2015a) A hybrid modelling approach for assessing solar radiation. Theoret Appl Climatol 122(3–4):403–420
Shamim MA, Hassan M, Ahmad S et al (2015b) A comparison of artificial neural networks (ANN) and local linear regression (LLR) techniques for predicting monthly reservoir levels. J Korean Soc Civil Eng 20:971
Shirin H, N Hedayat, H Kiamanesh (2010) Investigating the sedimentation process using the SHARC software: a case study of the in the Eastern water intake of the Dez Diversion Weir in Dezful. In: Proceedings of the national conference in water, soil, plant and agricultural mechanization, Islamic, Azad University, Dezful, Iran
Talebi A, Mahjoobi J, Dastorani MT et al (2017) Estimation of suspended sediment load using regression trees and model trees approaches (Case study: Hyderabad drainage basin in Iran). ISH J Hydraul Eng 23(2):212–219
Thompson J, Sattar AM, Gharabaghi B et al (2016) Event-based total suspended sediment particle size distribution model. J Hydrol 536:236–246
Tsai WP, Chang FJ, Chang LC et al (2015) AI techniques for optimizing multi-objective reservoir operation upon human and riverine ecosystem demands. J Hydrol 530:634–644
Wang YM, Traore S, Kerh T (2008) Monitoring event-based suspended sediment concentration by artificial neural network models. WSEAS Trans Comput 7(5):559–568
Yang CT, Marsooli R, Aalami MT (2009) Evaluation of total load sediment transport formulas using ANN. Int J Sedim Res 24(3):274–286
Yilmaz B, Aras E, Nacar S et al (2018) Estimating suspended sediment load with multivariate adaptive regression spline, teaching-learning based optimization, and artificial bee colony models. Sci Total Environ 639:826–840
Yitian L, Gu RR (2003) Modeling flow and sediment transport in a river system using an artificial neural network. Environ Manag 31(1):122–134
Zhang B, Govindaraju R (2003) Geomorphology based artificial neural networks (GANNs) for estimation of direct runoff over watersheds. J Hydrol 273:18–34
Zhu YM, Lu XX, Zhou Y (2007) Suspended sediment flux modeling with artificial neural network: an example of the Longchuanjiang River in the Upper Yangtze Catchment, China. Geomorphology 84:111–125
Zhuo L, Han D, Dai Q (2016) Soil moisture deficit estimation using satellite multi-angle brightness temperature. J Hydrol 539:392–405
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, F., Hassan, M. & Hashmi, H.N. Developing nonlinear models for sediment load estimation in an irrigation canal. Acta Geophys. 66, 1485–1494 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-018-0221-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-018-0221-3