Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of the unfolded protein response, specifically the inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) signaling pathway, in hypoxia-induced autophagy in human umbilical venous endothelial cells (HUVECs).
Methods
The expression of IRE1 and autophagy relative protein in HUVECs with hypoxia was explored by Western blotting, qRT-PCR and confocal microscopy. Further, we evaluated the biological effects of HUVECs by tube formation assay and wound healing assay in vitro. Finally, we examined the function of IRE1 in local blood vessels through animal models.
Results
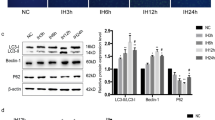
Hypoxia activated the IRE1 signaling pathway and induced autophagy in a time-dependent manner in HUVECs and further influenced the biological effects of HUVECs. Intraperitoneal injection of IRE1 inhibitors inhibited local vascular autophagy levels and lipid accumulation in model animals.
Conclusion
Hypoxia can induce autophagy and activate the IRE1 signaling pathway in HUVECs and the IRE1 signaling pathway is involved in autophagy in hypoxic conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gimbrone MA Jr, García-Cardeña G. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of Atherosclerosis. Circ Res, 2016,118(4):620–636
Poznyak AV, Nikiforov NG, Wu WK, et al. Autophagy and Mitophagy as Essential Components of Atherosclerosis. Cells, 2021,10(2):443
Shao BZ, Han BZ, Zeng YX, et al. The roles of macrophage autophagy in atherosclerosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2016,37(2):150–156
Klionsky DJ, Petroni G, Amaravadi RK, et al. Autophagy in major human diseases. EMBO J, 2021,40(19): e108863
Fernández A, Ordóñez R, Reiter RJ, et al. Melatonin and endoplasmic reticulum stress: relation to autophagy and apoptosis. J Pineal Res, 2015,59(3):292–307
Ogata M, Hino S, Saito A, et al. Autophagy is activated for cell survival after endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol, 2006,26(24):9220–9231
Di M, Wang L, Li M, et al. Dickkopf1 destabilizes atherosclerotic plaques and promotes plaque formation by inducing apoptosis of endothelial cells through activation of ER stress. Cell Death Dis, 2017,8(7):e2917
Lee JW, Ko J, Ju C, et al. Hypoxia signaling in human diseases and therapeutic targets. Exp Mol Med, 2019,51(6):1–13
Arnaud C, Bochaton T, Pépin JL, et al. Obstructive sleep apnoea and cardiovascular consequences: Pathophysiological mechanisms. Arch Cardiovasc Dis, 2020,113(5):350–358
Hultén LM, Levin M. The role of hypoxia in atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol, 2009,20(5):409–414
Guo Q, Jin S, Hu H, et al. Hypoxia in 3T3-L1 adipocytes suppresses adiponectin expression via the PERK and IRE1 unfolded protein response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2017,493(1):346–351
Wang S, Binder P, Fang Q, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the heart: insights into mechanisms and drug targets. Br J Pharmacol, 2018,175(8):1293–1304
Lindholm D, Korhonen L, Eriksson O, et al. Recent Insights into the Role of Unfolded Protein Response in ER Stress in Health and Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2017,5:48
Li T, Jiang S, Lu C, et al. Snapshots: Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Lipid Metabolism and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr Issues Mol Biol, 2018,28:14–28
Perrotta I, Aquila S. The role of oxidative stress and autophagy in atherosclerosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2015:130315
Sasaki Y, Ikeda Y, Iwabayashi M, et al. The Impact of Autophagy on Cardiovascular Senescence and Diseases. Int Heart J, 2017,58(5):666–673
Marsch E, Sluimer JC, Daemen MJ. Hypoxia in atherosclerosis and inflammation. Curr Opin Lipidol, 2013,24(5):393–400
Guo FX, Hu YW, Zheng L, et al. Shear Stress in Autophagy and Its Possible Mechanisms in the Process of Atherosclerosis. DNA Cell Biol, 2017,36(5):335–346
Fong GH. Potential contributions of intimal and plaque hypoxia to atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep, 2015,17(6):510
Tang V, Fu S, Rayner BS, et al. 8-Chloroadenosine induces apoptosis in human coronary artery endothelial cells through the activation of the unfolded protein response. Redox Biol, 2019,26:101274
Yang S, Wu M, Li X, et al. Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Atherosclerosis and Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020:9270107
Qiu ZL, Zhang JP, Guo XC. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and vascular endothelial cell apoptosis. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao (Chinese), 2014,36(1):102–107
Mialet-Perez J, Vindis C. Autophagy in health and disease: focus on the cardiovascular system. Essays Biochem, 2017,61(6):721–732
Henderson JM, Weber C, Santovito D. Beyond Self-Recycling: Cell-Specific Role of Autophagy in Atherosclerosis. Cells, 2021,10(3):625
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, et al. XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell, 2001,107(7):81–91
Grandjean JMD, Madhavan A, Cech L, et al. Pharmacologic IRE1/XBP1s activation confers targeted ER proteostasis reprogramming. Nat Chem Biol, 2020,16(10):1052–1061
Liu C, Yan DY, Wang C, et al. IRE1 signaling pathway mediates protective autophagic response against manganese-induced neuronal apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. Sci Total Environ, 2020,712:136480
Chen Y, Brandizzi F. IRE1: ER stress sensor and cell fate executor. Trends Cell Biol, 2013,23(11):547–555
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
We declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81670409).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, Zq., Wei, Bz., Zhao, M. et al. Hypoxia Affects Autophagy in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells via the IRE1 Unfolded Protein Response. CURR MED SCI 43, 689–695 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-023-2749-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-023-2749-y