Abstract
Objective
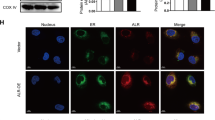
The goal of this study is to investigate the role and mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis regulated by thrombospondin 1 (TSP1) in human renal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2 cells).
Methods
HK-2 cells were exposed to high concentrations of glucose (HG). The endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibitor 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA) was administered by transfecting TSP1 or an empty vector to explore the mechanism of the endoplasmic reticulum response regulated by TSP1 and stress in renal cell apoptosis. The effects of TSP1 and 4-PBA on the proliferation and apoptosis of HK-2 cells under HG conditions were assessed using Cell counting kit-8 and flow cytometry. Western blotting was used to detect the apoptosis- and endoplasmic reticulum stress-related protein expression regulated by TSP1 and 4-PBA.
Results
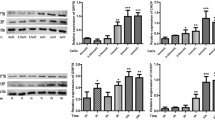
HG treatment induced high cell apoptosis, abundantly expressed TSP1 level and restrained viability in HK-2 cells. Overexpression of TSP1 significantly inhibited the proliferation of and facilitated apoptosis of HK-2 cells under HG conditions. Administration of endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibitor 4-PBA after overexpression of TSP1 antagonized the inhibitory proliferation and promoted apoptosis rate in HG-triggered HK-2 cells induced by TSP1 overexpression. 4-PBA treatment significantly hindered the expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers, such as PERK, ATF4, ATF6, p-eIF2α, IRE1, CHOP and XBP1, suggesting that the administration of 4-PBA was successful.
Conclusion
Overexpression of TSP1 activated endoplasmic reticulum stress by regulating the ATF6-CHOP axis. TSP1 restrained cell proliferation, and promoted apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress by activating the ATF6-CHOP axis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, et al. Chronic kidney disease: global dimension and perspectives. Lancet, 2013,382(9888): 260–72
Bigé N, Boffa JJ, Lepeytre F, et al. Role of thrombospondin-1 in the development of kidney diseases. Med Sci (Paris), 2013,29(12):1131–1137
Suades R, Padró T, Alonso R, et al. High levels of TSP1+/CD142+ platelet-derived microparticles characterise young patients with high cardiovascular risk and subclinical atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost, 2015,114(6):1310–1321
Labrousse-Arias D, Castillo-González R, Rogers NM, et al. HIF-2α-mediated induction of pulmonary thrombospondin-1 contributes to hypoxia-driven vascular remodelling and vasoconstriction. Cardiovasc Res, 2016,109(1):115–130
Tomas NM, Beck LH, Jr., Meyer-Schwesinger C, et al. Thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing 7A in idiopathic membranous nephropathy. N Engl J Med, 2014,371(24):2277–2287
Zeisberg M, Tampe B, LeBleu V, et al. Thrombospondin-1 deficiency causes a shift from fibroproliferative to inflammatory kidney disease and delays onset of renal failure. Am J Pathol, 2014,184(10):2687–2698
Rashid HO, Yadav RK, Kim HR, et al. ER stress: Autophagy induction, inhibition and selection. Autophagy, 2015, 11(11):1956–1977
Zhou X, Lu B, Fu D, et al. Huoxue Qianyang decoction ameliorates cardiac remodeling in obese spontaneously hypertensive rats in association with ATF6-CHOP endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling pathway regulation. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020,121:109518
Shu S, Zhu J, Liu Z, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress is activated in post-ischemic kidneys to promote chronic kidney disease. EBioMedicine, 2018,37:269–280
Ricciardi CA, Gnudi L. Endoplasmic Reticulum stress in chronic kidney disease. New molecular targets from bench to the bedside. G Ital Nefrol, 2019,36(6):2019–vol6
Cunha DA, Cito M, Carlsson PO, et al. Thrombospondin 1 protects pancreatic β-cells from lipotoxicity via the PERK-NRF2 pathway. Cell Death Differ, 2016,23(12):1995–2006
Gao P, Li L, Ji L, et al. Nrf2 ameliorates diabetic nephropathy progression by transcriptional repression of TGFβl through interactions with c-Jun and SP1. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2014,1839(11):1110–1120
Thakar CV, Zahedi K, Revelo MP, et al. Identification of thrombospondin 1 (TSP-1) as a novel mediator of cell injury in kidney ischemia. J Clin Invest, 2005,115(12):3451–3459
Lossi L, Castagna C, Merighi A. Caspase-3 Mediated Cell Death in the Normal Development of the Mammalian Cerebellum. Int J Mol Sci, 2018,19(12):3999
Crowley LC, Waterhouse NJ. Detecting Cleaved Caspase-3 in Apoptotic Cells by Flow Cytometry. Cold Spring Harb Protoc, 2016,2016(11):958–962
Taniguchi M, Yoshida H. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in kidney function and disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens, 2015,24(4):345–350
Mo JS, Choi D, Han YR, et al. Morin has protective potential against ER stress induced apoptosis in renal proximal tubular HK-2 cells. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019,112:108659
Peng PA, Wang L, Ma Q, et al. Valsartan protects HK-2 cells from contrast media-induced apoptosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Biol Int, 2015,39(12):1408–1417
Lv JC, Zhang LX. Prevalence and Disease Burden of Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019,1165: 3–15
Zhang L, Wang F, Wang L, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet, 2012,379(9818):815–822
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This study was supported by a grant from Chinese Society of Nephrology (No. 14050430580).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, Ll., Du, X. Thrombospondin 1 Promotes Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Apoptosis in HK-2 Cells by Upregulating ATF6-CHOP. CURR MED SCI 42, 341–347 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-022-2513-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-022-2513-8