Abstract
Objective
MiRNAs have been recently implicated in the pathogenesis of ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury. This study aimed to investigate the miRNA expression profiles in the early stages after lung transplantation (LT) and to study the involvement of the Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathway in lung IR injury following LT.
Methods
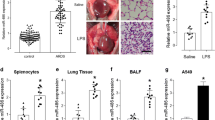
We established the left LT model in mice and selected the miRNA-122 as a research target. The mice were injected with a miRNA-122-specific inhibitor, following which pathological changes in the lung tissue were studied using different lung injury indicators. In addition, we performed deep sequencing of transplanted lung tissues to identify differentially expressed (DE) miRNAs and their target genes. These target genes were used to further perform gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis.
Results
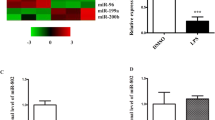
A total of 12 DE miRNAs were selected, and 2476 target genes were identified. The GO enrichment analysis predicted 6063 terms, and the KEGG analysis predicted 1554 biological pathways. Compared with the control group, inhibiting the expression of miRNA-122 significantly reduced the lung injury and lung wet/dry ratio (P<0.05). In addition, the activity of myeloperoxidase and the expression levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and TLR2/4 were decreased (P<0.05); whereas the expression of interleukin-10 was increased (P<0.05). Furthermore, the inhibition of miRNA-122 suppressed the IR injury-induced activation of the TLR signaling pathway.
Conclusion
Our findings showed the differential expression of several miRNAs in the early inflammatory response following LT. Of these, miRNA-122 promoted IR injury following LT, whereas its inhibition prevented IR injury in a TLR-dependent manner.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Simonson B, Das S. MicroRNA Therapeutics: the Next Magic Bullet? Mini Rev Med Chem, 2015,15(6):467–474
Rodriguez A, Griffiths-Jones S, Ashurst JL, et al. Identification of Mammalian microRNA Host Genes and Transcription Units. Genome Res, 2004,14(10a):1902–1910
Zhou L, Zang G, Zhang G, et al. MicroRNA and mRNA signatures in ischemia reperfusion injury in heart transplantation. PLoS One, 2013,8(11):e79805
Hu Y, Deng H, Xu S, et al. MicroRNAs Regulate Mitochondrial Function in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Int J Mol Sci, 2015,16(10):24895–24917
Rancan L, Simon C, Marchal-Duval E, et al. Lidocaine Administration Controls MicroRNAs Alterations Observed After Lung Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Anesth Analg, 2016,123(6):1437–1447
Buermans HP, Ariyurek Y, Ommen G, et al. New methods for next generation sequencing based microRNA expression profiling. BMC Genomics, 2010,11:716
Campbell JD, Liu G, Luo L, et al. Assessment of microRNA differential expression and detection in multiplexed small RNA sequencing data. Rna, 2015, 21(2):164–171
Siegel TN, Gunasekera K, Cross GAM, et al. Gene expression in Trypanosoma brucei: lessons from high-throughput RNA sequencing. Trends Parasitol, 2011, 27(10):434–441
Qin H, Sha J, Jiang C, et al. miR-122 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther, 2015,8:3175–3184
Shibata C, Ohno M, Otsuka M, et al. The flavonoid apigenin inhibits hepatitis C virus replication by decreasing mature microRNA122 levels. Virology, 2014,462–463:42–48
Xu M, Li D, Yang C, et al. MicroRNA-34a Inhibition of the TLR Signaling Pathway Via CXCL10 Suppresses Breast Cancer Cell Invasion and Migration. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018,46(3):1286–1304
Nahid MA, Satoh M, Chan EK. MicroRNA in TLR signaling and endotoxin tolerance. Cell Mol Immunol, 2011,8(5):388–403
Wu HS, Zhang L, Chen Y, et al. Effect of nitric oxide on toll-like receptor 2 and 4 gene expression in rats with acute lung injury complicated by acute hemorrhage necrotizing pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2005,4(4):609–613
Jin X, Wang L, Wu HS, et al. N-acetylcysteine inhibits activation of toll-like receptor 2 and 4 gene expression in the liver and lung after partial hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2007,6(3):284–289
Zheng Z, Wang J, Huang X, et al. Improvements of the surgical technique on the established mouse model of orthotopic single lung transplantation. PLoS One, 2013,8(11):e81000
Smith KM, Mrozek JD, Simonton SC, et al. Prolonged partial liquid ventilation using conventional and high-frequency ventilatory techniques: gas exchange and lung pathology in an animal model of respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med, 1997,25(11):1888–1897
Lin L, Li M, Lin L, et al. FPPS mediates TGF-beta1-induced non-small cell lung cancer cell invasion and the EMT process via the RhoA/Rock1 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018,496(2):536–541
He Q, Zhao X, Bi S, et al. Pretreatment with Erythropoietin Attenuates Lung Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Toll-Like Receptor-4/Nuclear Factor-kappaB (TLR4/NF-kappaB) Pathway. Med Sci Monit, 2018,24:1251–1257
Fanelli V, Costamagna A, Carosso F, et al. Effects of liver ischemia-reperfusion injury on respiratory mechanics and driving pressure during orthotopic liver transplantation. Minerva Anestesiol, 2019,85(5):494–504
Wang J, Cao H, Hong X, et al. MicroRNA screening and functional study of obliterative bronchiolitis in a rat model simulating lung transplantation. Genet Mol Res, 2015,14(4):19309–19316
Zheng Z, Chiu S, Akbarpour M, et al. Donor pulmonary intravascular nonclassical monocytes recruit recipient neutrophils and mediate primary lung allograft dysfunction. Sci Transl Med, 2017,9(394):eaal4508
Varga ZV, Zvara A, Farago N, et al. MicroRNAs associated with ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection by ischemic pre- and postconditioning: protectomiRs. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2014, 307(2):H216–227
Lorenzen JM, Kaucsar T, Schauerte C, et al. MicroRNA-24 antagonism prevents renal ischemia reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2014,25(12):2717–2729
Li P, Shen M, Gao F, et al. An Antagomir to MicroRNA-106b-5p Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Rats Via Inhibiting Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress. Mol Neurobiol, 2017,54(4):2901–2921
Ma D, Jia H, Qin M, et al. MiR-122 Induces Radiosensitization in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Line. Int J Mol Sci, 2015,16(9):22137–22150
Gracia A, Quintela AF, Miranda J, et al. Are miRNA-103, miRNA-107 and miRNA-122 Involved in the Prevention of Liver Steatosis Induced by Resveratrol? Nutrients, 2017,9(4):360
Xu Z, Sharma M, Gelman A, et al. Significant role for microRNA-21 affecting toll-like receptor pathway in primary graft dysfunction after human lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant, 2017,36(3): 331–339
Wang H, Zhang X, Zheng X, et al. Prevention of allograft rejection in heart transplantation through concurrent gene silencing of TLR and Kinase signaling pathways. Sci Rep, 2016,6:33869
Sadis C, Detienne S, Vokear B, et al. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway delays TLR-induced skin allograft rejection in mice: cholinergic pathway modulates alloreactivity. PLoS One, 2013,8(11):e79984
Zheng Z, Wang J, Hu H, et al. Short-term inhalation of nitric oxide inhibits activations of toll-like receptor 2 and 4 in the lung after ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2013,33(2):219–223
Luo J, Zhan J, You H, et al. MicroRNA146a/Tolllike receptor 4 signaling protects against severe burninduced remote acute lung injury in rats via antiinflammation. Mol Med Rep, 2018,17(6):8377–8384
Acknowledgments
First of all, I would like to express my sincere thanks to all those who have helped me in the course of my writing this paper. I would also like to take this opportunity to show my sincere gratitude to my supervisors, Zhi-kun ZHENG and Jin-song LI. They gave me many useful suggestions on my writing and tried their best to improve my thesis. Secondly, I would like to express my gratitude to my classmates who offered me references and information on time. Last but not the least, I would like to thank my teachers and their staff. Without their help, it would be much more difficult for me to finish my study and this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author Jin-song LI is a member of the Editorial Board for Current Medical Science. The paper was handled by the other editor and has undergone rigorous peer review process. Author Jin-song LI was not involved in the journal’s review of, or decision related to, this manuscript.
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81600074) and Hubei Natural Science Foundation (No. 2017CFB473).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Wang, Yl., Liu, Q. et al. MiRNA-122 Promotes Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury after Lung Transplantation via the Toll-like Receptor Signaling Pathway. CURR MED SCI 41, 1231–1238 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-021-2487-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-021-2487-y