Abstract
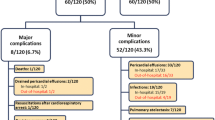
Objective: The aims of this retrospective study were to investigate and evaluate the safety and efficacy of three approaches for closure of secundum atrial septal defect (ASD). Methods: In this study, we reviewed clinical data for transcatheter occlusion (TCO, n=63), transthoracic occlusion (TTO, n=55), and right anterolateral minithoracotomy (RALT, n=60) techniques used for ASD closure. We compared the safety and efficacy of the three approaches. Results: ASD size in the TTO group was similar to that in the RALT group (P=0.645) and significantly larger than that in the TCO group (P<0.001). The RALT group had more non-central types of ASD than the TTO and TCO groups (P=0.019 and P<0.001). The operative time in the TTO group was shorter than that in the TCO and RALT groups (P<0.001 and P<0.001). The ventilation time and intensive care unit duration were shorter in the TTO group than in the RALT group (P<0.001 and P<0.001). Hospital duration in the TCO group was shorter than that in the TTO and RALT groups (P<0.001 and P<0.001). There were no residual shunt and mortality in any group in hospital or during follow-up. There was no significant difference in the incidence of total complications among the three groups (P=0.738). Conclusion: TCO, TTO, and RALT can be performed with favorable cosmetic and clinical results for closing ASD. Appropriate patient selection is an important factor for successful closure. These techniques are promising alternatives to standard median sternotomy and merit additional study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaplan S. Congenital heart disease in adolescents and adults: natural and postoperative history across age groups. Cardiol Clin, 1993,11(4):543–556
Guo QK, Lu ZQ, Cheng SF, et al. Off-pump occlusion of trans-thoracic minimalinvasive surgery (OPOTTMIS) on simple congenital heart diseases (ASD, VSD and PDA) attached consecutive 210 cases report: A single institute experience. J Cardiothorac Surg, 2011,6:48
Lloyd TR, Rao PS, Beekman RH, et al. Atrial septal defect occlusion with the buttoned device (a multi-institutional U.S. trial). Am J Cardiol, 1994,73(4):286–291
Perry SB, Van der Velde ME, Bridges ND, et al. Transcatheter closure of atrial and ventricular septal defects. Herz, 1993,18(2):135–142
Berger F, Vogel M, Alexi-Meskishvili V, et al. Comparison of results and complications of surgical and Amplatzer device closure of atrial septal defects. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 1999,118:674–680
Du ZD, Cao QL, Rhodes J, et al. Choice of device size and results of transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect using the Amplatzer septal occluder. J Interv Cardiol, 2002,15(4):287–292
Lancaster LL, Mavroudis C, Rees AH, et al. Surgical approach to atrial septal defect in female. Right thoracotomy versus sternotomy. Am Surg, 1990,56:218–221
Massetti M, Babatasi G, Rossi A, et al. Operation for atrial septal defect through a right anterolateral thoracotomy: current outcome. Ann Thorac Surg, 1996, 62(4):1100–1103
Masura J, Gavora P, Formanek A, et al. Transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defects using the new self-centering Amplatzer septal occluder: initial human experience. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn, 1997,42(4):388–393
Thanopoulos BD, Laskari CV, Tsaousis GS, et al. Closure of atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer occlusion device: preliminary results. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1998,31(5):1110–1116
Vasquez AF, Lasala JM. Atrial septal defect closure. Cardiol Clin, 2013,31(3):385–400
Tao L, Zeng XJ, Ma XJ, et al. The experience of occluding secundum atrial septal defect. Ann Thorac Surg, 2008,85(2):695
Hongxin L, Wenbin G, Lijun S, et al. Intraoperative device closure of secundum atrial septal defect with a right anterior minithoracotomy in 100 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2007,134(4):946–951
Hijazi ZM, Cao Q, Patel HT, et al. Transesophageal echocardiographic results of catheter closure of atrial septal defect in children and adults using the Amplatzer device. Am J Cardiol, 2000,85(11):1387–1390
Sharafuddin MJA, Gu X, Titus JL, et al. Transvenous closure of secundum atrial septal defects: preliminary results with a new self-expanding Nitinol prosthesis in a swine model. Circulation, 1997,95(8):2162–2168
Abadir S, Sarquella-Brugada G, Mivelaz Y, et al. Advances in paediatric interventional cardiology since 2000. Arch Cardiovasc Dis, 2009,102(6–7):569–582
Rao PS. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect: are we there yet? J Am Coll Cardiol, 1998,31:1117–1119
Cardis E, Vrijheid M, Blettner M, et al. The 15-Country Collaborative Study of Cancer Risk among Radiation Workers in the Nuclear Industry: estimates of radiation-related cancer risks. Radiat Res, 2007,167(4):396–416
Andreassi MG, Ait-Ali L, Botto N, et al. Cardiac catheterization and long-term chromosomal damage in children with congenital heart disease. Eur Heart J, 2006,27(22):2703–2708
Fazel R, Krumholz HM, Wang Y, et al. Exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation from medical imaging procedures. N Engl J Med, 2009,361(9):849–857
Ait-Ali L, Andreassi MG, Foffa I, et al. Cumulative patient effective dose and acute radiation-induced chromosomal DNA damage in children with congenital heart disease. Heart, 2010,96(4):269–274
Signorello LB, Mulvihill JJ, Green DM, et al. Stillbirth and neonatal death in relation to radiation exposure before conception: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet, 2010,376(9741):624–630
Däbritz S, Sachweh J, Walter M, et al. Closure of atrial septal defects via limited right anterolateral thoracotomy as a minimal invasive approach in female patients. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 1999,15(1):18–23
Xu M, Zhu S, Wang X, et al. Two Different Minimally Invasive Techniques for Female Patients with Atrial Septal Defects: Totally Thoracoscopic Technique and Right Anterolateral Thoracotomy Technique. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2015,21(5):459–465
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this article to disclose.
Author Nian-guo DONG is a member of the Editorial Board for [Current Medical Science]. The paper was handled by the other editor and has undergone rigorous peer review process. Author Nian-guo DONG was not involved in the journal’s review of, or decisions related to, this manuscript.
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81873502 and No. 31330029).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, H., Wu, L., Shang, Xk. et al. Outcomes of Three Different Minimal Invasive Approaches for Secundum Atrial Septal Defect Closure: A Single Institute Experience. CURR MED SCI 41, 1225–1230 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-021-2466-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-021-2466-3