Summary
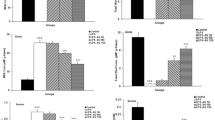
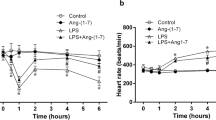
Studies showed that the use of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) substitutes or intracellular cAMP activators increased intracellular cAMP level, causing anti-inflammatory effects. This study was to investigate the effects of pretreatment with meglumine cyclic adenylate (MCA), a compound of meglumine and cAMP, on systemic inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in rats. Eighteen adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into 3 groups (n=6 each): control group (NS group), LPS group (LPS group) and LPS with MCA pretreatment group (MCA group). Systemic inflammation was induced with LPS 10 mg/kg injected via the femoral vein in LPS and MCA groups. In MCA group, MCA 2 mg/kg was injected via the femoral vein 20 min before LPS injection, and the equal volume of normal saline was given in NS and LPS groups at the same time. Three hours after LPS injection, the blood samples were taken from the abdominal aorta for determination of plasma concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, cAMP by ELISA and NF-κBp65 expression by Western blotting. The experimental results showed that inflammatory and antiinflammatory indices were increased in LPS group compared to NS group; inflammatory indices were declined and anti-inflammatory indices were increased in MCA group relative to LPS group. Our study suggested that MCA pretreatment may attenuate LPS-induced systemic inflammation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang W, Tang Y, Li L. HMGB1, a potent proinflammatory cytokine in sepsis. Cytokine, 2010,51:119–126
Schulte W, Bernhagen J, Bucala R. Cytokines in sepsis: potent immunoregulators and potential therapeutic targetsan updated view. Mediators Inflamm, 2013,2013:165974
Deree J, Martins JO, Melbostad H, et al. Insights into the regulation of TNF-alpha production in human mononuclear cells: the effects of non-specific phosphodiesterase inhibition. Clinics, 2008, 63(3):321–328
Coon TA, McKelvey AC, Weathington NM, et al. Novel PDE4 inhibitors derived from Chinese medicine forsythia. PLoS One, 2014,9(12):e115937
Kamenetsky M, Middelhaufe S, Bank EM, et al. Molecular details of cAMP generation in mammalian cells: a tale of two systems. J Mol Biol, 2006,362(4):623–639
Vakilzadeh G, Khodagholi F, Ghadiri T, et al. Protective effect of a cAMP analogue on behavioral deficits and neuropathological changes in cuprizone model of demyelination. Mol Neurobiol, 2015, 52(1):130–141
Ji H, Zhang Y, Shen XD, et al. Neuropeptide PACAP in mouse liver ischemia and reperfusion injury: immunomodulation by the cAMP-PKA pathway. Hepatology, 2013,57(3):1225–1237
Zidek Z. Adenosine-cyclic AMP pathways and cytokine expression. Eur Cytokine Netw, 1999,10(3):319–328
Gobejishvili L, Barve S, Joshi-Barve S, et al. Chronic ethanol-mediated decrease in cAMP primes macrophages to enhanced LPS-inducible NF-kappaB activity and TNF expression: relevance to alcoholic liver disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2006,291(4):G681–G688
Pavlov VA, Ochani M, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, et al. Central muscarinic cholinergic regulation of the systemic inflammatory response during endotoxemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2006,103(13):5219–5223
Wacker C, Prkno A, brunkhorst FM, et al. Procalcitonin as a diagnostic marker for sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis, 2013,13:426–435
Palmiere C, Augsburger M. Markers for sepsis diagnosis in the forensic setting: state of the art. Croat Med J, 2014,55(2):103–114
Su L, Feng L, Song Q, et al. Diagnostic value of dynamics serum sCd163, sTREM-1, PCT, and CRP in differentiating sepsis, severity assessment, and prognostic prediction. Mediators Inflamm, 2013,2013:969875
Samraj RS, Zingarelli B, Wong HR. Role of biomarkers in sepsis care. Shock, 2013,40:358–365
American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference. Definition for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med, 1992,20:864–74
Lyle NH, Pena OM, Boyd JH, et al. Barriers to the effective treatment of sepsis: antimicrobial agents, sepsis definitions, and host-directed therapies. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2014,1323:101–114
Fink MP, Warren HS. Strategies to improve drug development for sepsis. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2014,13(10):741–58
Kellum JA, Kong L, Fink MP, et al. Understanding the inflammatory cytokine response in pneumonia and sepsis: results of the genetic and inflammatory Markers of Sepsis (GenIMS) Study. Arch Intern Med, 2007,167:1655–1656
Prucha M, Bellingan G, Zazula R. Sepsis biomarkers. Clin Chim Acta, 2015,440:97–103
Lu YC, Yeh WC, Ohashi PS. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction Pathway. Cytokine, 2008,42(2):145–151
Tsutsuki H, Yahiro K, Suzuki K, et al. Subtilase cytotoxin enhances escherichia coli survival in macrophages by suppression of nitric oxide production through the inhibition of NF-?B activation. Infect Immun, 2012,80(11):3939–3951
Schick MA, Wunder C, Wollborn J, et al. Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibition as a therapeutic approach to treat capillary leakage in systemic inflammation. J Physiol, 2012, 590(Pt 11):2693–2708
Chen H, Zhu W, Feng J, Li S. Protective effect of diallyl trisulfide on liver in rats with sepsis and the mechanism. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2012,32(5):657–662
Shi JR, Mao LG, Jiang RA, et al. Monoammonium glycorrhizinate inhibited the inflammation of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int Immunopharmacol, 2010,10(10):1235–1241
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
This work was financially supported by the Science and Technology Bureau of Wuhan, Hubei Province, China (No. 2013060602010255).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Chen, Jl., Liu, H. et al. Effects of meglumine cyclic adenylate pretreatment on systemic inflammatory response syndrome induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 37, 332–336 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-017-1736-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-017-1736-6