Summary
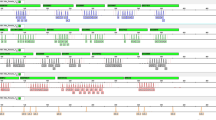
X-chromosome short tandem repeats (X-STR) analysis has been confirmed to be effective for kinship testing such as in deficiency paternity cases. The aim of this study was to develop a new multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) system that can simultaneously amplify 9 X-STR loci (GATA172D05, DXS10159, DXS6797, HPRTB, DXS10079, DXS6789, DXS9895, DXS10146 and GATA31E08) in the same PCR reaction, and to obtain the database of the 9 X-STR loci in three ethnic populations in China. The genetic data of 815 (404 females and 411 males) unrelated Han Chinese from Hubei province, and Yi and Zhuang Chinese from Yunnan province were analyzed by using this multiplex system. The results showed that a total of 93 alleles for all these loci were found, and 7 to 20 alleles for each locus were observed. All of the analyzed loci were in agreement with Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium after Bonferroni correction in the three studied populations. The polymorphism information content (PIC) and power of discrimination (PD) in females were 0.6566–0.8531 and 0.8639–0.9684, respectively. Pairwise comparisons of allele frequency distribution showed significant differences in the most of these loci between different populations. The results indicate that this multiplex system is very useful for forensic analysis of different ethnic populations in China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shin SH, Yu JS, Park SW, et al. Genetic analysis of 18 X-linked short tandem repeat markers in Korean population. Forensic Sci Int, 2005,147(1):35–41
Edelmann J, Hering S, Augustin C, et al. Characterisation of the STR markers DXS10146, DXS10134 and DXS10147 located within a 79.1 kb region at Xq28. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2008,2(1):41–46
Gusmão L, Sánchez-Diz P, Alves C, et al. A GEP-ISFG collaborative study on the optimization of an X-STR decaplex: data on 15 Iberian and Latin American populations. Int J Legal Med, 2009,123(3):227–234
Tie J, Uchigasaki S, Oshida S. Genetic polymorphisms of eight X-chromosomal STR loci in the population of Japanese. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2010,4(4):e105–e108
Edelmann J, Hering S, Augustin C, et al. Validation of six closely linked STRs located in the chromosome X centromere region. Int J Legal Med, 2010,124(1):83–87
Ribeiro-Rodrigues EM, Palha Tde J, Bittencourt EA, et al. Extensive survey of 12 X-STRs reveals genetic heterogeneity among Brazilian populations. Int J Legal Med, 2011,125(3):445–452
Kapińska E, Wysocka J, Cybulska L, et al. Examples of application of X chromosomal markers in familial investigations and personal identification. Arch Med Sadowej Kryminol, 2012,62(3):152–159
Nothnagel M, Szibor R, Vollrath O, et al. Collaborative genetic mapping of 12 forensic short tandem repeat (STR) loci on the human X chromosome. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2012,6(6):778–784
Liu QL, Wang JZ, Quan L, et al. Allele and haplotype diversity of 26 X-STR loci in four nationality populations from China. PLoS One, 2013,8(6):e65570
Liu QL, Li ZD, Li CT, et al. X chromosomal recombination-A family study analyzing 26 X-STR Loci in Chinese Han three-generation pedigrees. Electrophoresis, 2013, 34(20–21):3016–3022
Szibor R, Krawczak M, Hering S, et al. Use of X-linked markers for forensic purposes. Int J Legal Med, 2003,117(2):67–74
Szibor R. X-chromosomal markers: past, present and future. Forensic Sci Int Genet, 2007,1(2):93–99
Walsh BS, Petzger DA, Higuchi R. Chelex-100 as medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material. Biotechniques, 1991,10(4):506–513
Edelman J, Hering S, Michael M, et al. 16 X-chromosome STR loci frequency data from a German population. Forensic Sci Int, 2001,124(2–3):215–218
Excoffier L, Lischer HE. Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour, 2010,10(3):564–567
Edwards A, Hammond HA, Jin L, et al. Genetic variation at five trimeric and tetrameric tandem repeat loci in four human population groups. Genomics, 1992,12(2):241–253
Botstein D, White RI, Skolnich M, et al. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet, 1980,32(3):314–331
Desmarais D, Zhong Y, Chakraborty R, et al. Development of a highly polymorphic STR marker for identity testing purposes at the human androgen receptor gene (HUMARA). J Forensic Sci, 1998,43(5):1046–1049
Szibor R, Edelmann J, Hering S, et al. Cell line DNA typing in forensic genetics-the necessity of reliable standards. Forensic Sci Int, 2003,138(1–3):37–43
Hering S, Kuhlisch E, Szibor R. Development of the X-linked tetrameric microsatellite marker HumDXS6789 for forensic purposes. Forensic Sci Int, 2001,119(1):42–46
Huang D, Yang Q, Yu C, et al. Development of the X-linked tetrameric microsatellite markers HumDXS6803 and HumDXS9895 for forensic purpose. Forensic Sci Int, 2003,133(3):246–249
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Dx., Ma, Hd., Yang, Rz. et al. Development of a 9-locus X-STR multiplex PCR system for genetic analysis of three ethnic populations in China. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 35, 183–187 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-015-1408-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-015-1408-3