Summary
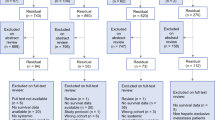
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) combined with radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and TACE alone for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), Pubmed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) and Wanfang Datebases were searched for the randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and retrospective cohort studies from the establishment of the databases to January 2014. The bibliographies of the included studies were searched, too. After study selection, assessment, data collection and analysis were undertaken, we performed this meta-analysis by using the RevMan5.2 software. Seventeen studies involving 1116 patients met the inclusion criteria with 530 treated with RFA-plus-TACE and 586 with TACE alone. The results of meta-analysis showed that the combination of TACE and RFA was obviously associated with higher 1-, 2-, and 3-year overall survival rates (OR1-year=3.98, 95% CI 2.87–5.51, P<0.00001; OR2-year=3.03, 95% CI 2.10–4.38, P<0.00001; OR3-year=7.02, 95% CI 4.14–11.92, P<0.00001) than TACE alone. The tumor complete necrosis rate in patients treated with TACE and RFA was higher than that of TACE alone (OR=13.86, 95% CI 8.04–23.89, P<0.00001). And there was a significant difference in local recurrence rate between two different kinds of treatment (OR=0.24, 95%CI 0.14–0.44, P<0.00001). Additionally, combination of TACE and RFA was associated with higher complete tumor necrosis rates than TACE mono-therapy in the treatment of HCC. However, RFA plus TACE was found to be associated with a lower local recurrence rate than TACE monotherapy. TACE-plus-RFA treatment was associated with a higher response rate (RR) than the TACE-alone treatment (OR=3.90, 95% CI=2.37–6.42, P<0.00001). TACE-plus-RFA treatment did not differ from the TACE-alone treatment in terms of stable disease (SD) rate (OR=0.38, 95% CI=0.11–1.26, P=0.11). Meta-analyses showed that the combination of RFA and TACE was associated with a significantly lower progressive disease (PD) rate (OR=0.15, 95% CI=0.05–0.43, P=0.0005). The rate of AFP reducing or returning to normal in serum in RFA plus TACE group was obviously lower than TACE alone group (OR=4.62, 95% CI 2.56–8.34, P<0.00001). The effect of TACE plus RFA for HCC is better than TACE mono-therapy. The combined therapy can elevate the patients’ overall survival rate, tumor necrosis rate and the rate of AFP reducing or returning to normal in serum and decrease local recurrence rate, PD rate compared with TACE alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang P, Liang M, Zhang Y, et al. Clinical Application of a combination therapy of lentinan, multi-electrode RFA and TACE in HCC. Adv Ther, 2008,25(8):787–794
Kirikoshi H, Saito S, Yoneda M, et al. Outcome of transarterial chemoembolization monotherapy, and in combination with percutaneous ethanol injection, or radiofrequency ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res, 2009,39(6):553–562
Morimoto M, Numata K, Kondo M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combinationed with transarterial chemoembolization for subcapsular hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective cohort study. Eur J Radiol, 2013,82(3):497–503
Wang YB, Chen MH, Yan K, et al. Quality of life after radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization alone. Quality Life Res, 2007,16(3):389–397
Shibata T, Isoda H, Hirokawa Y, et al. Small hepatocellular carcinoma: is radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization more effective than radiofrequecy ablation alone for treatment? Radiology, 2009,252(3):905–913
Dai XD, Wang Y, Cheng Z, et al. Therapeutic effect of trans-arterial chemo-embolization in combination with radio-frequency ablation for the treatment of middle or advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Fangshexue Shijian Zazhi (Chinese), 2010,25(7):799–801
Malagari K, Pomoni M, Spyridopoulos TN, et al. Safety profile of sequential transcatheter chemoembolization with DC Bead™: results of 237 hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2011, 34(4):774–785
Morimoto M, Numata K, Kondou M, et al. Midterm outcomes in patients with intermediate-sized hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized controlled trial for determining the efficacy of radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Cancer, 2010, 116(23):5452–5460
Cai Z, Wan LX, Wang WL, et al. Clinical observation of the TACE combined with RFA treatment in malignant hepatic carcinoma. Zhongguo Shiyong Yiyao Zazhi (Chinese), 2013,8(8):1–3
Huang YH, Xu Q, Shen T, et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Hainan Yixue Zazhi (Chinese), 2013,24(24):3630–3632
Song W, Jiang SF, Long HY, et al. Clinical application of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with percutaneous radiofrequency in the treatment of large hepatic tumors. Chin J Curr Adv Gen Surg (Chinese), 2008, 11(3):203–207
Zhuang GY, Li JQ, Zhao HF, et al. Clinical effect comparison of radiofrequency ablation for liver cancer with different diameter. Chin J Curr Adv Gen Surg (Chinese), 2008,11(5):451–452
Zhou J, Wang F. Clinical effects of transcatheter artery chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation for treating hepatocellular carcinoma. Liaoning Yixue Zazhi (Chinese), 2007,21(6):369–371
Fang ZX, Chen D, Fang ZH, et al. Curative effects of hepatic arterial chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation on larger hepatic carcinoma. Zhonghua Linchuang Yishi Zazhi (Chinese), 2012,6(10):2823–2825
Tan Y, Zhang T, Peng JJ, et al. Curative effects of hepatic arterial chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation on primary hepatic carcinoma in 76 cases. Xinan Guofang Yiyao Zazhi (Chinese), 2013,23(8):853–855
Zheng L, Guo CY, Li HL, et al. Trans-hepatic artery interventional thermo-chemotherapy and embolism combined with radiofrequency ablation in the treatment for hepatic carcinoma. Linchaung Fangshexue Zazhi (Chinese), 2013,32(7):1032–1035
Wu PH, Zhang FJ, Zhao M, et al. Combination of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and CT-guided radiofrequency ablation in treating advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhonghua Fangshexue Zazhi (Chinese), 2003,37(10):901–904
Deng LP, Zhang HW, Deng XJ, et al. The clinical application of hot lipiodol hepatic arterial chemoembolization combined with cool-tip radiofrequency ablation in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhongnan Yixue Kexue Zazhi (Chinese), 2012,40(3):269–272
He CB, Zhu Y, Zhang JJ, et al. Clinical value of CT-guided radiofrequency ablation in combination with chemotherapy embolism of liver artery in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Weichuang Yixue Zazhi (Chinese), 2013,8(3):279–282
Tang SY, Xie YB, Jiang T, et al. Clinical investigation of TACE, RFA and combined TACE and RFA in the therapy of PHC. Haerbin Yike Daxue Xuebao (Chinese), 2005,39(2):183–187
Kang CB, Wang SL, Rui JA. Research of transcatheter artery chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of large hepatocellular carcinoma. Linchuang Yiliao Zazhi (Chinese), 2007:137-140
Xiong JH, Fan GR, Chen LQ, et al. Therapeutic effect of transarterial chemo-embolization combined with radio frequency ablation for treatment of middle or advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly. Chin J Curr Adv Gen Surg (Chinese), 2013,16(5):355–358
Zhang ZW. Primary liver cancer radiotherapy intervention analysis. Dangdai Yixue Zazhi (Chinese), 2011,17(27): 70–71
Liang MH. Chemical hepatic artery embolism combined radiofrequency ablation efficacy for the treatment of large hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi (Chinese), 2011,31(15):2862–2863
Bloomston M, Binitie O, Fraiji E, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with or without radiofrequency ablation in the management of patients with advanced hepatic malignancy. Am Surg, 2002,68(9):827–831
Sun XJ, He SL, Shen J, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization in combination with radio frequency thermal ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Chin J Clin Med (Chinese), 2011,18(6): 803–808
Meza-Junco J, Montano-Loza AJ, Liu DM, et al. Locoregional radiological treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: Which, when and how? Cancer Treat Rev, 2012,38(1): 54–62
Wang N, Guan Q, Wang K, et al. TACE combined with PEI versus TACE alone in the treatment of HCC: a meta-analysis. Med Oncol, 2011,28(4):1038–1043
Lencioni R, Crocetti L. Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Cancer. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol, 2007,10(1): 38–46
Iezzi R, Cesario V, Siciliani L, et al. Single-step multimodal locoregional treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: balloon-occluded percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation (BO-RFA) plus transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE). Radiol Med, 2013, 118(4):555–569
Kim YS, Lim HK, Rhim H, et al. Ten-year outcomes of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation as first-line therapy of early hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of prognostic factors. J Hepatol, 2013,58(1):89–97
McGahan JP, Sacramento MD. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg, 2004, 198(5):853–854
Kim JH, Won HJ, Shin YM, et al. Medium-sized (3.1-5.0 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma: transarterial chemoembolization plus radiofrequency ablation versus radiofrequency ablation alone. Ann Surg Oncol, 2011,18(6):1624–1629
Lu Z, Wen F, Guo Q, et al. Radiofrequency ablation plus chemoembolization versus radiofrequency ablation alone for hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 25(2):187–194
Li ZR, Kang Z, Qian JS, et al. Radiofrequency ablation with or without transcather arterial chemoembolization for management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao (Chinese), 2007,27(11):1749–1751
Peng ZW, Chen MS, Liang HH, et al. A case-control study comparing percutaneous radiofrequency ablation alone or combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2010,36(3):257–263
Gadaleta C, Catino A, Ranieri G, et al. Single-step therapy-feasibility and Safety of simultaneous transarterial chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation for hepatic malignancies. In Vivo, 2009,23(5):813–820
Duan X, Zhou G, Zheng C, et al. Heat shock protein 70 expression and effect of combined transcatheter arterial embolization and radiofrequency ablation in the rabbit VX2 liver tumour model. Clin Radiol, 2014,69(2): 186–193
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Jh., Zhou, J., Zhang, Xl. et al. Meta-analysis on radiofrequency ablation in combination with transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 34, 692–700 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1338-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1338-5