Summary
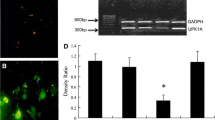
Previous researches showed that the expression level of E-Cad in most infiltrating cancer cells was reduced or negative. This study explored whether 4HPR restrained the infiltration of bladder cancer cells through regulating the expression of E-Cad. The infiltrating bladder cancer cells T24 were cultured, and then treated by a proper dosage of drug. Their viability was a determined by MTT method. Western blotting and RT-PCR were adopted to detect the changes of E-Cad gene expression at both protein and mRNA levels. Moreover, immunofluorescent staining and confocal fluorescence microscopy were employed for the observation of the expression of E-Cad. The result showed that, at both mRNA and protein levels, the expression level of E-Cad in T24 cells treated by 4HPR was significantly higher than that of control group, while the β-Cat expression was also relocated from the cell nucleus to cytoplasm. Our findings suggested that the regulatory function of 4HPR on infiltration of bladder cancer cells T24 is at least partly achieved by regulating the expression of E-Cad.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sabichi AL, Lerner SP, Grossman HB, et al. Retinoids in the chemoprevention of bladder cancer. Curr Opin Oncol, 1998,10(5):479–484
Millán-Rodríguez F, Chéchile-Toniolo G, Salvador-Bayarri J, et al. Multivariate analysis of the prognostic factors of primary superficial bladder cancer. J Urol, 2000,163(1):73–78
Rosenberg JE, Carroll PR, Small EJ. Update on chemotherapy for advanced bladder cancer. J Urol, 2005,174(1):14–20
Czyzewska J, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K, Ustymowicz M, et al. The expression of E-cadherin-catenin complex in patients with advanced gastric cancer: role in formation of metastasis. Folia Histochem Cytobiol, 2010,48(1):37–45
Bringuier PP, Umbas R, Schaafsma HE, et al. Decreased E-cadherin immunoreactivity correlates with poor survival in patients with bladder tumors. Cancer Res, 1993, 53(14):3241–3245.
Yang LJ, Liu YQ, Gu B, et al. Effect of forced E-cadherin expression on adhesion and proliferation of human breast carcinoma cells. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi (Chinese), 2010,39(12):842–847
Behrens J, Mareel MM, Van Roy FM, et al. Dissecting tumor cell invasion: epithelial cells acquire invasive properties after the loss of uvomorulin-mediated cell-cell adhesion. J Cell Biol, 1989,108(6):2435–2447
Paulson JD, Oldham JW, Preston RF, et al. Lack of genotoxicity of the cancer chemopreventive agent N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide. Fundam Appl Toxicol, 1985,5(1):144–150
Chiesa F, Tradati N, Marazza M, et al. Fenretinide (4-HPR) in chemoprevention of oral leukoplakia. J Cell Biochem (Suppl), 1993,17F:255–261
Ferrari N, Morini M, Pfeffer U, et al. Inhibition of Kaposi’s sarcoma in vivo by fenretinide. Clin Cancer Res, 2003,9(16 Pt 1):6020–6029
Garaventa A, Luksch R, Lo Piccolo MS, et al. Phase I trial and pharmacokinetics of fenretinide in children with neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res, 2003,9(6):2032–2039
Kim HJ, Chakravarti N, Oridate N, et al. N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide-induced apoptosis triggered by reactive oxygen species is mediated by activation of MAPKs in head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Oncogene, 2006,25(19):2785–2794
Davis RJ. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell, 2000,103(2):193–200
Wu JM, DiPietrantonio AM, Hsieh TC. Mechanism of fenretinide (4-HPR)-induced cell death. Apoptosis, 2001,6(5):377–388
Bindels EM, Vermey M, De Both NJ, et al. Influence of the microenvironment on invasiveness of human bladder carcinoma cell lines. Virchows Arch, 2001,439(4):552–559
Mao Q, Li Y, Zheng X, et al. Up-regulation of E-cadherin by small activating RNA inhibits cell invasion and migration in 5637 human bladder cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2008,375(4):566–570
Cowin P. Unraveling the cytoplasmic interactions of the cadherin superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1994, 91(23):10 759–10 761
Simeone AM, Tari AM. How retinoids regulate breast cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2004,61(12):1475–1484
Formelli F, Barua AB, Olson JA. Bioactivities of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide and retinoyl beta-glucuronide. FASEB J, 1996,10(9):1014–1024
Clifford JL, Menter DG, Wang M, et al. Retinoid receptor-dependent and -independent effects of N-(4-hydroxyp henyl)retinamide in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res, 1999,59(1):14–18
Appierto V, Cavadini E, Pergolizzi R, et al. Decrease in drug accumulation and in tumour aggressiveness marker expression in a fenretinide-induced resistant ovarian tumour cell line. Br J Cancer, 2001,84(11):1528–1534
Sabichi AL, Hendricks DT, Bober MA, et al. Retinoic acid receptor beta expression and growth inhibition of gynecologic cancer cells by the synthetic retinoid N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide. J Natl Cancer Inst, 1998,90(8):597–605
Ulukaya E, Wood EJ. Fenretinide and its relation to cancer. Cancer Treat Rev, 1999,25(4):229–235
Su B, Mershon SM, Stonerock LA, et al. 4-Hydroxyphenylretinamide (4HPR) derivatives regulate aromatase activity and expression in breast cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2008,109(1–2):40–46
Nelson WJ, Nusse R. Convergence of Wnt, beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science, 2004, 303(5663):1483–1487
Batsché E, Muchardt C, Behrens J, et al. RB and c-Myc activate expression of the E-cadherin gene in epithelial cells through interaction with transcription factor AP-2. Mol Cell Biol, 1998,18(7):3647–3658
Brewer M, Kirkpatrick ND, Wharton JT, et al. 4-HPR modulates gene expression in ovarian cells. Int J Cancer, 2006,119(5):1005–1013
Shishodia S, Gutierrez AM, Lotan R, et al. N-(4-hydrox yphenyl)retinamide inhibits invasion, suppresses osteoclastogenesis, and potentiates apoptosis through downregulation of I(kappa)B(alpha) kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated gene products. Cancer Res, 2005, 65(20):9555–9565
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The two authors contributed equally to this work.
This project was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30972975).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, E., Li, J., Yang, G. et al. Impact of 4HPR on the expression of E-Cad in human bladder transitional epithelial cancer cells T24. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 32, 237–241 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-012-0042-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-012-0042-6