Summary
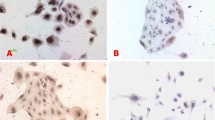
The effect of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) on invasive capability of early pregnant extravillous cytotrophoblasts (EVTs) was investigated in vitro. Primary EVTs were obtained by complex phosphoesterasum digestion and gradient centrifugation from villous tissue aseptically taken from healthy pregnant women. Cytokeratin7 (CK7), vimentin (Vim) and c-erbB-2 were immunocytochemically detected to identify source of cells, and HCMVpp65 antigen was assayed to determine the infection state of primary EVTs by immunocytochemical staining. The EVTs were divided into two groups: control group and HCMV group, and the expression of c-erbB-2, matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9 proteins was detected in two groups by immunocytochemistry and Western blotting. Enzymic activity changes of MMP-2 and MMP-9 were tested by gelatin zymography in primary EVTs infected with HCMV. The invasion of primary EVTs was detected by cell invasion assay in vitro after they were infected by HCMV. The cell source identification showed that the cells obtained were highly-pure primary EVTs, and primary EVTs could be infected by HCMV. Primary EVTs could express c-erbB-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9 proteins, and as compared with control group, the protein expression was decreased significantly in HCMV groups (P<0.05). Primary EVTs could secrete active MMP-2 and MMP-9 in vitro, and the activity of two MMPs was decreased significantly in HCMV groups (P<0.05). The in vitro cell invasion assay showed that the number of primary EVTs permeating Matrigel in HCMV group was decreased (P<0.05). We are led to conclude that HCMV can infect primary EVTs and inhibit their invasion capability, suggesting that the impaired EVT’s invasion capability might be related to the abnormal expression of c-erbB-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9 proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hyde TB, Schmid DS, Cannon MJ. Cytomegalovirus seroconversion rates and risk factors: implications for congenital CMV. Rev Med Virol, 2010,20(5):311–326
Rauwel B, Mariamé B, Martin H, et al. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma by human cytomegalovirus for de novo replication impairs migration and invasiveness of cytotrophoblasts from early placentas. J Virol, 2010,84(6):2946–2954
Lorenzi T, Marzioni D, Giannubilo S, et al. Expression patterns of two serine protease HtrA1 forms in human placentas complicated by preeclampsia with and without intrauterine growth restriction. Placenta, 2009,30(1):35–40
Apps R, Sharkey A, Gardner L, et al. Genome-wide expression profile of first trimester villous and extravillous human trophoblast cells. Placenta, 2011,32(1): 33–43
Handschuh K, Guibourdenche J, Tsatsaris V, et al. Human chorionic gonadotrop in expression in human trophoblasts from early placenta: comparative study between villous and extravillous trophoblastic cells. Placenta, 2007,28(2–3):175–184
LaMarca HL, Nelson AB, Scandurro AB, et al. Human cytomegalovirus-induced inhibition of cytotrophoblast invasion in a first trimester extravillous cytotrophoblast cell line. Placenta, 2006,27(2–3):137–147
El-Hashash AH, Warburton D, Kimber SJ. Genes and signals regulating murine trophoblast cell development. Mech Dev, 2010,127(1–2):1–20
Malassine A, Handschuh K, Tsatsaris V, et al. Expression of HERV-W Env glycoprote in (syncytin) in the extravillous trophoblast of first trimester human placenta. Placenta, 2005,26(7):556–562
Knöfler M. Critical growth factors and signalling pathways controlling human trophoblast invasion. Int J Dev Biol, 2010,54(2–3):269–280
Oki N, Matsuo H, Nakago S, et al. Effects of 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine on the invasive potential and the expression of integrins and matrix metalloproteinases in cultured early placental extravillous trophoblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2004,89(10):5213–5221
Kliman H J. Uteroplacental blood flow: the story of ecidualization,menstuation and trophoblast invasion. Am J Pathol, 2000,157(6):1759–1768
Ioannidis I, Dimo B, Karameris A, et al. Comparative study of the immunohistochemical expression of metalloproteinases 2, 7and 9 between clearly invasive carcinomas and “in situ” trophoblast invasion. Neoplasma, 2010,57(1):20–28
Cohen M, Wuillemin C, Irion O, et al. Regulation of MMP-9 by p53 in first trimester cytotrophoblastic cells. Hum Reprod, 2008,23(10):2273–2281
Duzyj CM, Barnea ER, Li M, et al. Preimplantation factor promotes first trimester trophoblast invasion. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2010,203(4):402.e1–402.e 4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The two authors contributed equally to this work.
This project was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30672243) and Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 2009CDB216).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Zheng, X., Chen, J. et al. Effect of human cytomegalovirus on invasive capability of early pregnant extravillous cytotrophoblasts. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 819–823 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0683-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0683-x