Summary
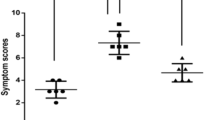
This study examined the possible mechanism of sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) in the treatment of allergic asthma. Forty asthma patients allergic to dust mite were enrolled. They received SLIT with dermatophagoides farinae (Der. f) drops for one year. Thirty healthy subjects served as controls. The levels of IL-4 and IFN-γ of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were determined in allergic asthma patients before and after the SLIT as well as the healthy subjects. The results showed that the level of IL-4 was substantially increased and that of IFN-γ remarkably decreased in the patients before the SLIT as compared with those in the healthy subjects (P<0.05). After the SLIT, the level of IL-4 was significantly reduced and that of IFN-γ elevated in these allergic asthma patients. It was concluded that sublingual immunotherapy is effective for patients with allergic asthma. And it may work by regulating the balance of Th1/Th2 through changing the expression of IL-4 and IFN-γ in PBMCs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asthma Group of Respirology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Prevention Guide of Bronchial Asthma (including definition, diagnosis, treatment and management of bronchial asthma). Zhong Hua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi (Chinese), 2003, 26(3):132–138
Asthma Group of Respirology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Prevention Guide of Bronchial Asthma (including definition, diagnosis, treatment and management of bronchial asthma). Zhong Hua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi (Chinese), 2008, 31(3):177–185
Horiguchi S, Okamoto Y, Yonekura S, et al. A randomized controlled trial of sublingual immunotherapy for Japanese cedar pollinosis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2008, 146(1): 76–84
Tazaki T, Minoguchi K, Yokoe T, et al. Allergen rush immunotherapy increases interleukin (IL)-12 production and IL-12 receptor beta2 chain expression in patients with allergic asthma. Cell Immunol, 2004, 228(1):20–26
Dehlink E, Eiwegger T, Gerstmayr M, et al. Absence of systemic immunologic changes during dose build-up phase and early maintenance period in effective specific sublingual immunotherapy in children. Clin Exp Allergy, 2006, 36(1):32–39
Wang ZX, Li WJ. Starting time of the effect of specific immune curative treatment, Chinese journal of hospital pharmacy, 2009, 29(19):1688–1689
Cosmi L, Santarlasci V, Angeli R. Sublingual immunotherapy with Dermatophagoides monomeric allergoid down-regulates allergen-specific immunoglobulin E and increases both interferon-gamma- and interleukin-10-production. Clin Exp Allergy, 2006, 36(3):261–272
Rolinck-Werninghaus C, Kopp M, Liebke C. Lack of detectable alterations in immune responses during sublingual immunotherapy in children with seasonal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis to grass pollen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2005, 136(2):134–141
Ciprandi G, De Amici M, Murdaca G, Serum IL-4 as a marker of immunological response to sublingual immunotherapy. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents, 2008, 22 (2): 117–123
Savolainen J, Nieminen K, Laaksonen K, et al. Allergen-induced in vitro expression of IL-18, SLAM and GATA-3 mRNA in PBMC during sublingual immunotherapy. Allergy, 2007, 62 (8):949–953
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Li, W., Chen, H. et al. Effect of sublingual immunotherapy on level of cytokines in PBMCs of patients with allergic asthma. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 376–378 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0384-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0384-5