Summary
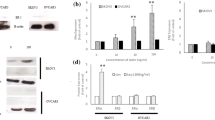
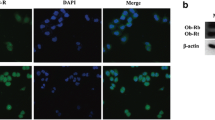
Obesity is an established risk factor for endometrial cancer. Leptin, a secreted protein of the ob gene by white adipose tissue, plays an important role in the regulation of food intake and energy consumption in the brain and acts as a potential growth stimulator in normal and neoplastic cancer cells. However, a direct role for leptin in endometrial cancer has not been demonstrated. In the present study, the effect of leptin on the proliferation of Ishikawa endometrial cancer cells was investigated as well as the possible mechanism(s) underlying this action in endometrial cancers which express both short and long isoforms of leptin receptors. The expression of leptin receptor (ObRb) in Ishikawa cells was detected by RT-PCR and Western blotting. The cells after serum starvation, were treated by leptin with various concentrations (0, 10, 50, 100, 150 ng/mL) for different durations (6, 12, 24 h). The effect of leptin treatment on cell proliferation was examined by MTT assay. Meanwhile, inhibitory effect of Janus tyrosine kinase 2 (JAK2)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) inhibitor AG490 or extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) inhibitor PD98059 on the proliferation of Ishikawa cells induced by leptin was also studied. Ishikawa cells were treated with 100 ng/mL leptin for various periods (0, 20, 40, 60 min), and the levels of STAT3 phosphorylation and ERK1/2 phosphorylation were examined by Western blotting. The results showed that leptin induced the phosphorylation of STAT3 and the activation of ERK1/2 in a time- and dose-dependent manner in the Ishikawa endometrial cancer cells. Blocking STAT3 phosphorylation with the inhibitor AG490, or blocking ERK1/2 activation by the specific ERK1/2 kinase inhibitor, PD98059, abolished leptin-induced proliferation of Ishikawa cells. In addition, leptin was found to potently induce the invasion of endometrial cancer cells in a Matrigel invasion assay. Leptin-stimulated invasion was effectively blocked by pharmacological inhibitors of STAT3 (AG490) and ERK1/2 kinase (PD98059). These results suggested that leptin promotes endometrial cancer growth and invasiveness by activating STAT3 and ERK1/2 signaling pathways and therefore blocking its action at the receptor level can be a rational therapeutic strategy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, et al. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature,1994,372(6):425–432
Caro JF, Sinha MK, Kolaczynski JW, et al. Leptin: the tale of an obesity gene. Diabetes, 1996,45(12):1455–1462
Friedman JM, Halaas JL. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature, 1998,395(5):763–770
Lonnqvist F, Arner P, Nordfors L, et al. Overexpression of the obese (ob) gene in adipose tissue of human obese subjects. Nat Med, 1995,1(8):950–955
Bouloumie A, Drexler HC, Lafontan M, et al. Leptin, the product of Ob gene, promotes angiogenesis. Circ Res, 1998,83(10):1059–1066
Sierra-Honigmann MR, Nath AK, Murakami C, et al. Biological action of leptin as an angiogenicfactor. Science, 1998,281(12):1683–1686
Huang L, Li C. Leptin: a multifunctional hormone. Cell Res, 2000,10(1):81–92
Somasundar P, Frankenberry KA, Skinner H, et al. Prostate cancercell proliferation is influenced by leptin. J Sur Res, 2004,118(1):71–82
Somasunder P, McFadden DW, Hileman SM, et al. Leptin is a growth factor in cancer. J Sur Res, 2004, 116(4):337–349
White DW, Tartaglia LA. Leptin and OB-R: body weight regulation by a cytokine receptor. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 1996,7(3):303–309
Fei H, Okano HJ, Li C, et al. Anatomic localization of alternatively spliced leptin receptors (Ob-R) in mouse brain and other tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1997,94(11):7001–7005
Tartaglia LA, Dembski M, Weng X, et al. Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell, 1995,83(10):1263–1271
Banks AS, Davis SM, Bates SH, et al. Activation of downstream signals by the long form of the leptin receptor. J Biol Chem, 2000,275(7):14563–14572
Rose PG. Endometrial carcinoma. N Engl J Med, 1996, 335(6):640–649
Judd HL, Shamonki IM, Frumar AM, et al. Origin of serum estradiol in postmenopausal women. Obstet Gynecol, 1982,59(8):680–686
Deslypere JP. Obesity and cancer. Metabolism, 1995, 44(1):24–27
Carroll KK. Obesity as a risk factor for certain types of cancer. Lipids, 1998,33(9):1055–1059
Petridou E, Belechri M, Dessypris N, et al. Leptin and body mass index in relation to endometrialcancer risk. Ann Nutr & Metab, 2002,46(2):147–151
Yuan SS, Tsai KB, Chung YF, et al. Aberrant expression and possibleinvolvement of the leptin receptor in endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol, 2004,92(7):769–775
Koda M, Sulkowska M, Wincewicz A, et al. Expression of leptin, leptin receptor, and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in human endometrial cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2007,95(1):90–98
Cymbaluk A, Chudecka-Glaz A, Rzepka-Gorska I. Leptin levels in serum depending on body mass index in patients with endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol, 2006,26(9):629–640
Ahima RS, Osei SY. Leptin signaling. Physi Behav 2004, 81(3):223–241
Bjorbeak C, Buchholz RM, Davis SM, et al. Divergent roles of SHP-2 in ERK activation by leptin receptors. J Biol Chem, 2001,276(5):4747–4755
Dien J, Amin HM, Chiu N, et al. Signal transducers and activators of transcription-3 up-regulates tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 expression and decreases invasiveness of breast cancer. Am J Pathol, 2006,169(5): 633–642
Suiqing C, Min Z, Lirong C. Overexpression of phosphorylated-STAT3 correlated with the invasion and metastasis of cutaneous squamous cell arcinoma. J Dermatol, 2005,32(4):354–360
Choo MK, Sakurai H, Koizumi K, et al. Stimulation of cultured colon 26 cells with TNF-alpha promotes lung metastasis through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Cancer Lett, 2005,230(1):47–55
Lama G, Mangiola A, Anile C, et al. Activated ERK1/2 expression in glioblastoma multiforme and in peritumor tissue. Int J Oncol, 2007,30(11):1333–1342
Pai R, Lin C, Tran T, et al. Leptin activates STAT and ERK2 pathways and induces gastric cancer cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2005,331(8): 984–992
Hu X, Juneja SC, Maihle NJ, et al. Leptin-A growth factor in normal and malignant breast cells and for normal mammary gland development. J Nati Cancer Inst, 2002,94(10):1704–1711
Rose DP, Komninou D, Stephenson GD. Obesity, adipocytokines, and insulin resistance in breast cancer. Obes Rev, 2004,5(2):153–165
Choi JH, Park SH, Leung PC, et al. Expression of leptin receptors and potential effects of leptin on the cell growth and activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in ovarian cancer cells. J Clinl Endocrin Metab, 2005,90(2): 207–210
Baumann H, Morella KK, White DW, et al. The full-length leptin receptor has signaling capabilities of interleukin 6-type cytokine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996,93(9):8374–8388
Tanabe K, Okuya S, Tanizawa Y, et al. Leptin induces proliferation of pancreatic beta cell line MIN6 through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1997,241(6):765–768
Bendinelli P, Maroni P, Pecori Giraldi F, et al. Leptin activates Stat3, Stat1 and AP-1 in mouse adipose tissue. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2000,168(1):11–20
Zabeau L, Lavens D, Peelman F, et al. The ins and outs of leptin receptor activation. FEBS Lett, 2003,546(1):45–55
Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J, et al. STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene, 2000,19(7):2474–2488
Barre B, Avril S, Coqueret O. Opposite regulation of myc and p21waf1 transcription by STAT3 proteins. J Biol Chem, 2003,278(4):2990–2996
Kiuchi N, Nakajima K, Ichiba M, et al. STAT3 is required for the gp130-mediated full activation of the c-myc gene. J Exp Med, 1999,189(1):63–73
Shirogane T, Fukada T, Muller JM, et al. Synergistic roles for Pim-1 and c-Myc in STAT3-mediated cell cycle progression and antiapoptosis. Immunity, 1999,11(6):709–719
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, et al. Constitutive activation of Stat3 signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma cells. Immunity, 1999, 10(2):105–115
Giraud S, Bienvenu F, Avril S, et al. Functional interaction of STAT3 transcription factor with the coactivator NcoA/SRC1a. J Biol Chem, 2002,277(8):8004–8011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Lv, L., Xiao, W. et al. Leptin activates STAT3 and ERK1/2 pathways and induces endometrial cancer cell proliferation. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 365–370 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0382-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0382-7