Summary
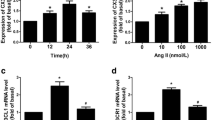
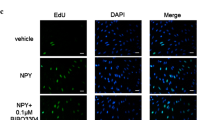
This study examined the relationship between PDGF-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and Nur77 expression and the effect of atorvastatin on VSMC proliferation and Nur77 in PDGF-treated VSMCs. Rat VSMCs were isolated and cultured. After incubation with atorvastatin or Nur77 siRNA, the cells were stimulated with PDGF and detected for BrdU incorporation to measure the proliferation of the VSMCs. Quantitative PCR and Western blotting were used to determine the Nur77 protein and the CREB phosphorylation level, to observe their relations with PDGF-induced VSMC proliferation. Our results showed that PDGF increased the BrdU incorporation in VSMCs, suggesting that it induced the proliferation of the cells. The VSMC proliferation was associated with increased Nur77 expression and elevated CREB phosphorylation. Atorvastatin inhibited the PDGF-induced VSMC proliferation, suppressed Nur77 expression. After silencing of Nur77 gene, the PDGF-induced VSMC proliferation was decreased. It was concluded that PDGF-induced VSMC proliferation was related to the Nur77 expression and CREB phosphorylation. Atorvastatin reduced the Nur77 expression and, at the same time, inhibited the VSMC proliferation.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Welt FG, Rongers C. Inflammation and restenosis in the stent era. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2002,22(11): 1769–1776
Topol EJ, Seruys PW. Frontiers in interventional cardiology. Circulation, 1998,98(17):1802–820
Law RE, Meehan WP, Xi XP, et al. Troglitazone inhibits vascular smooth muscles cell growth and intimal hyperplasia. J Clin Invest, 1996,98(8):1897–1905
Law RE, Goetze S, Xi XP, et al. Expression and function of PPARgamma in rat and human vascular smooth muscle cells. Circulation, 2002,101(11):1311–1318
de Vries CJ, van Achterberg TA, Horrevoets AJ, et al. Differential display identification of 40 genes with altered expression in activated human smooth muscle cells. Local expression in atherosclerotic lesions of smags, smooth muscle activation-specific genes. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(31):23939–23947
Baker KD, Shewchuk LM, Kozlova T, et al. The Drosophila orphan nuclear receptor DHR38 mediates an atypical ecdysteroid signaling pathway. Cell, 2003,113(6):731–742
Wang Z, Benoit G, Liu J, et al. Structure and function of Nurr1 identifies a class of ligand-independent nuclear receptors. Nature, 2003,423(6939):555–560
Fahrner TJ, Carroll SL, Milbrandt J. The NGFI-B protein, an inducible member of the thyroid/steroid receptor family, is rapidly modified posttranslationally. Mol Cell Biol, 1990,10(12):6454–6459
Wilson TE, Fahrner TJ, Johnston M, et al. Identification of the DNA binding site for NGFI-B by genetic selection in yeast. Science, 1991,252(5010):1296–1300
Arkenbout EK, van Bragt M, Eldering E, et al. TR3 orphan receptor is expressed in vascular endothelial cells and mediates cell cycle arrest. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2003,23(9):1535–1540
Martinez-González J, Badimon L. The NR4A subfamily of nuclear receptors: new early genes regulated by growth factors in vascular cells. Cardiovasc Res, 2005,65(3): 609–618
Pei L, Castrillo A, Tontonoz P. Regulation of macrophage inflammatory gene expression by the orphan nuclear receptor Nur77. Mol Endocrinol, 2006, 20(4):786–794
Peter I. Bonta PI, Claudia M, et al. Nuclear receptors Nur77, Nurr1, and NOR-1 expressed in atherosclerotic lesion macrophages reduce lipid loading and inflammatory responses. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2006,26(10): 2288–2294
Weissberg PL, Bennett MR. Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med, 1999,340(24):115–126
Martinez-Gonzalez L, Lina Badimon L. The NR4A subfamily of nuclear receptors: new early genes regulated by growth factors in vascular cells. Cardiovasc Res, 2005, 65(3):609–618
Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell, 1995,83(6):841–850
Claudel T, Leibowitz MD, Fievet C, et al. Reduction of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice by activation of the retinoid X receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2001,98(5):2610–2615
Harant H, Lindley IJ. Negative cross-talk between the human orphan nuclear receptor Nur77/NAK-1/TR3 and nuclear factor-kappaB. Nucleic Acids Res, 2004,32(17): 5280–5290
de Léséleuc L, Denis F. Inhibition of apoptosis by Nur77 through NF-κB activity modulation. Cell Death and Differ, 2006,13(2):293–300
Arkenbout EK, de Waard V, van Bragt M, et al. Protective function of transcription factor TR3 orphan receptor in atherogenesis: decreased lesion formation in carotid artery ligation model in TR3 transgenic mice. Circulation, 2002,106(12):1530–1535
de Waard V, Arkenbout EK, Vos M, et al. TR3 nuclear orphan receptor prevents cyclic stretch-induced proliferation of venous smooth muscle cells. Am J Pathol, 2006, 168(6):2027–2035
Pires NM, Pols TW, de Vries MR, et al. Activation of nuclear receptor Nur77 by 6-mercaptopurine protects against neointima formation. Circulation, 2007,115(4): 493–500
Nomiyama T, Nakamachi T, Gizard F, et al. The NR4A orphan nuclear receptor NOR1 is induced by platelet-derived growth factor and mediates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. J Biol Chem, 2006,281(44): 33467–33476
Takemoto M, Liao JK. Pleiotropic effects of 3-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase inhibitors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2001,21(11):1712–1729
Libby P, Aikawa M. Stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques: new mechanisms and clinical targets. Nat Med, 2002, 8(11):1257–1262
Kohno M, Shinomiya K, Abe S, et al. Mizushige, Inhibition of migration and proliferation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells by a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, pravastatin. Hypertens Res, 2002,25(2):279–285
Porter KE, Naik J, Turner NA, et al. Simvastatin inhibits human saphenous vein neointima formation via inhibition of smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. J Vasc Surg, 2002,36(1):150–157
Hernández-Presa MA, Ortego M, Tuñón J, et al. Simvastatin reduces NF-κB activity in peripheral mononuclear and in plaque cells of rabbit atheroma more markedly than lipid lowering diet. Cardiovasc Res, 2003,57(1):168–177
Pei L, Castrillo A, Chen M, et al. Induction of NR4A orphan nuclear receptor expression in macrophages in response to inflammatory stimuli. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(32):29265–29272
Bonta PI, van Tiel CM, Vos M, et al. Nuclear receptors Nur77, Nurr1, and NOR-1 expressed in atherosclerotic lesion macrophages reduce lipid loading and inflammatory responses. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2006,26(10): 2288–2294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant from the Program for Scientific Research of Municipal Government (No. 2009-WW76).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Dong, X., Zhou, W. et al. PDGF-induced proliferation of smooth muscular cells is related to the regulation of CREB phosphorylation and Nur77 expression. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 169–173 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0245-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0245-2