Summary
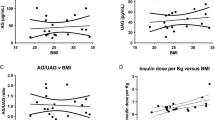
The association between fasting plasma ghrelin levels and insulin resistance and blood pressure (BP) in octogenarians was investigated in this study. A total of 487 unrelated octogenarians (including 203 men and 284 women) were enrolled in this cross-sectional study at the Healthy Care Center of Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University, China, from October 2008 to April 2009. Plasma ghrelin was determined by using the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Insulin sensitivity was assessed using the homeostasis model of assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). The age of the participants ranged from 80 to 89 years (mean=83.9±4.8 years) with a body mass index (BMI) of 25.3±4.9 kg/m2. Plasma ghrelin levels were 20.94±5.34 μg/L, being 20.89±5.53 μg/L in men and 21.38±3.73 μg/L in women respectively. Plasma ghrelin was not associated with systolic (P=0.981) or diastolic (P=0.724) BP, waist circumference (P=0.278), fasting insulin (P=0.246), fasting blood glucose (FBG) (P=0.693) and HOMA-IR (P=0.232). In the control cohort, no significant differences in plasma ghrelin were found between genders (P=0.489), and among subjects with hypertension (BP>140/90 mmHg) (P=0.284) and type 2 diabetes (P=0.776). In conclusion, fasting plasma ghrelin levels are not directly correlated with insulin resistance and BP among octogenarians.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, et al. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature, 1999,402(6762):656–660
Sakata I, Nakamura K, Yamazaki M, et al. Ghrelin-producing cells exist as two types of cells, closed- and opened-type cells, in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Peptides, 2002,23(3):531–536
Cummings DE. Ghrelin and the short- and long-term regulation of appetite and body weight. Physiol Behav, 2006,89(1):71–84
Shiiya T, Nakazato M, Mizuta M, et al. Plasma ghrelin levels in lean and obese humans and the effect of glucose on ghrelin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2002,87(1):240–244
Nakagawa E, Nagaya N, Okumura H, et al. Hyperglycaemia suppresses the secretion of ghrelin, a novel growth-hormone-releasing peptide: responses to the intravenous and oral administration of glucose. Clin Sci (Lond), 2002,103(3):325–328
Adeghate E, Ponery AS. Ghrelin stimulates insulin secretion from the pancreas of normal and diabetic rats. J Neuroendocrinol, 2002,14(7):555–560
Egido EM, Rodriguez-Gallardo J, Silvestre RA, et al. Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on insulin and pancreatic somatostatin secretion. Eur J Endocrinol, 2002,146(2): 241–244
Daghestani MH, Ozand PT, Al-Himadi AR, et al. Hormonal levels of leptin, insulin, ghrelin, and neuropeptide Y in lean, overweight, and obese Saudi females. Saudi Med J, 2007,28(8):1191–1197
Caixas A, Bashore C, Nash W, et al. Insulin, unlike food intake, does not suppress ghrelin in human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2002,87(4):1902
Poykko SM, Kellokoski E, Horkko S, et al. Low plasma ghrelin is associated with insulin resistance, hypertension, and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, 2003,52(10):2546–2553
Nagaya N, Kojima M, Uematsu M, et al. Hemodynamic and hormonal effects of human ghrelin in healthy volunteers. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, 2001,280(5):R1483–1487
Enomoto M, Nagaya N, Uematsu M, et al. Cardiovascular and hormonal effects of subcutaneous administration of ghrelin, a novel growth hormone-releasing peptide, in healthy humans. Clin Sci (Lond), 2003,105(4):431–435
Okumura H, Nagaya N, Enomoto M, et al. Vasodilatory effect of ghrelin, an endogenous peptide from the stomach. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 2002,39(6):779–783
Makino Y, Hosoda H, Shibata K, et al. Alteration of plasma ghrelin levels associated with the blood pressure in pregnancy. Hypertension, 2002,39(3):781–784
Oner-Iyidogan Y, Kocak H, Gurdol F, et al. Circulating ghrelin levels in obese women: a possible association with hypertension. Scand J Clin Lab Invest, 2007,67(5): 568–576
Schutte AE, Huisman HW, Schutte R, et al. Aging influences the level and functions of fasting plasma ghrelin levels: the POWIRS-Study. Regul Pept, 2007,139(1–3):65–71
Kotani K, Sakane N, Saiga K, et al. Serum ghrelin and carotid atherosclerosis in older Japanese people with metabolic syndrome. Arch Med Res, 2006,37(7):903–906
Langenberg C, Bergstrom J, Laughlin GA, et al. Ghrelin and the metabolic syndrome in older adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2005,90(12):6448–6453
Chapman IM. Endocrinology of anorexia of ageing. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2004,18(3):437–452
Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, et al. A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes, 2001,50(8):1714–1719
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, et al. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia, 1985,28(7):412–419
Rigamonti AE, Pincelli AI, Corra B, et al. Plasma ghrelin concentrations in elderly subjects: comparison with anorexic and obese patients. J Endocrinol, 2002,175(1): R1–5
Smith RG, Jiang H, Sun Y. Developments in ghrelin biology and potential clinical relevance. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2005,16(9):436–442
Purnell JQ, Weigle DS, Breen P, et al. Ghrelin levels correlate with insulin levels, insulin resistance, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, but not with gender, menopausal status, or cortisol levels in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2003,88(22):5747–5752
Bauer JM, Wirth R, Troegner J, et al. Ghrelin, anthropometry and nutritional assessment in geriatric hospital patients. Z Gerontol Geriatr, 2007,40(1):31–36
Bertoli S, Magni P, Krogh V, et al. Is ghrelin a signal of decreased fat-free mass in elderly subjects. Eur J Endocrinol, 2006,155(2):321–330
Moran LJ, Luscombe-Marsh ND, Noakes M, et al. The satiating effect of dietary protein is unrelated to postprandial ghrelin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2005,90(9):5205–5211
Espelund U, Hansen TK, Hojlund K, et al. Fasting unmasks a strong inverse association between ghrelin and cortisol in serum: studies in obese and normal-weight subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2005,90(2):741–746
Makovey J, Naganathan V, Seibel M, et al. Gender differences in plasma ghrelin and its relations to body composition and bone—an opposite-sex twin study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf), 2007,66(4):530–537
Tai K, Visvanathan R, Hammond AJ, et al. Fasting ghrelin is related to skeletal muscle mass in healthy adults. Eur J Nutr, 2009,48(3):176–183
Akamiza T, Murayama T, Teramukai S, et al. Plasma ghrelin levels in healthy elderly volunteers: the levels of acylated ghrelin in elderly females correlate positively with serum IGF-I levels and bowel movement frequency and negatively with systolic blood pressure. J Endocrinol, 2006,188(2):333–344
Matsumura K, Tsuchihashi T, Fujii K, et al. Neural regulation of blood pressure by leptin and the related peptides. Regul Pept, 2003,114(2–3):79–86
Elsayed NM, Hamed ST, El-Khatib MM, et al. The relation between dual energy x-ray absorptiometry measurement of body fat composition and plasma ghrelin in patients with end-stage renal disease. Saudi Med J, 2009(1),30:109–115
Mizia-Stec K, Zahorska-Markiewicz B, Olszanecka-Glinianowicz M, et al. Ghrelin as a potential blood pressure reducing factor in obese women during weight loss treatment. Endokrynol Pol, 2008,59(3):207–211
Liu J, Lin H, Cheng P, et al. Effects of ghrelin on the proliferation and differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci, 2009,29(2): 227–230
Roemmler J, Otto B, Steffin B, et al. Serum leptin and ghrelin levels in active and inactive acromegalic patients during an oral glucose tolerance test. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes, 2009,117(3):135–141
Poykko SM, Ukkola O, Kauma H, et al. The negative association between plasma ghrelin and IGF-I is modified by obesity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia, 2005,48(2):309–316
Barazzoni R, Zanetti M, Ferreira C, et al. Relationships between desacylated and acylated ghrelin and insulin sensitivity in the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2007,92(2):3935–3940
Yukawa M, Cummings DE, Matthys CC, et al. Effect of aging on the response of ghrelin to acute weight loss. J Am Geriatr Soc, 2006,54(4):648–653
Marzullo P, Verti B, Savia G, et al. The relationship between active ghrelin levels and human obesity involves alterations in resting energy expenditure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2004,89(2):936–939
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The two authors contributed equally to the work.
This project was supported by grants from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 30600294) and Shanghai Scientific and Technological Innovation Plan (No. 08411951300).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Shao, L., Teng, L. et al. Relationship between plasma ghrelin levels and insulin resistance and blood pressure in octogenarians. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 30, 307–311 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-010-0347-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-010-0347-2