Summary
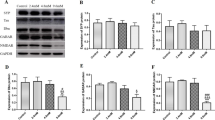
To observe the chelation of GRP78 with lead (Pb) and its localization changes, astroglial cells from Wistar rat brain were primarily cultured in medium with acetate Pb. The processes were terminated at different time points. The immunoprecipitation (IP) and Western blotting were used for GRP78 purification and expression and the Pb concentration was determined by employing atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS). The localization change of GRP78 was observed with colloid gold immunoelectron microscopy. The results showed that the expression of GRP78 was increased significantly in the cells treated with 1.0 μmol/L acetate Pb for 24 h and peaked at 96–192 h (P<0.01), and at the 12th day, the expression of GRP78 began to decrease but was still higher than normal (P<0.05). Pb content started to increase when cells were treated by acetate Pb for 24 h, and the peak appeared at 8 day (P<0.01), and then Pb content decreased gradually, but was still higher than normal (P<0.05). GRP78 protein expression began to remarkably increase when it transferred from ER to the cytosol around the nuclei 24 h after treatment with Pb. It is concluded that GRP78 in astroglia could strongly chelate with Pb ions and it might be a target protein of Pb.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qian Y, Harris ED, Zheng Y, et al. Lead targets GRP78, a molecular chaperone, in C6 rat glioma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2000,163(3):260–266
Zhu ZW, Yang RL, Dong GJ, et al. Study on the neurotoxic effects of low-level lead exposure in rats. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 2005,(7):686–692
Suresh C, Dennis AO, Heinz J, et al. Melatonin protection against lead-induced changes in human neruoblastoma cell cultures. Int J Toxicol, 2006,25(6):459–464
Sierra EM, Tiffany-Castiglioni E. Reduction of glutamine synthetase activity in astroglia exposed in culture to low levels of inorganic lead. Toxicology, 1991,65(3):295–304
Bradbury MW, Deane R. Permeability of the blood-brain barrier to lead. Neurotoxicology, 1993,14(2–3):131–136
Lindahl LS, Bird L, Legare MB, et al. Differential ability of astroglia and neuronal cells to accumulate lead: dependence on cell type and on degree of differentiation. Toxicol Sci, 1999,50(2):236–243
Tiffany-Castiglioni E. Cell culture models for lead toxicity in neuronal and glial cells. Neurotoxicology, 1993,14(4): 513–536
Little E, Ramakrishnan M, Roy B, et al. The glucose-regulated proteins (GRP78 and GRP94): Functions, gene regulation, and applications. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr, 1994,4(1):1–18
Hendershot L, Wei J, Gaut J, et al. Inhibition of immunoglobulin folding and secretion by dominant negative Bip ATPase mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996,93(11):5269–5274
Audesirk G, Shugarts D, Nelson G, et al. 1989. Organic and inorganic lead inhibit neurite growth in vertebrate and invertebrate neurons in culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol, 1989,25(12):1121–1128
Qian Y, Zheng Y, Ramos KS, et al. GRP78 compartmentalized redistribution in Pb-treated glia: role of GRP78 in lead-induced oxidative stress. Neurotoxicology, 2005,26(2):267–275
Qian Y, Tiffany-Castiglioni E, Harris ED. Copper transport and kinetics in cultured C6 rat glioma cells. Am J Physiol, 1995,269(4 pt 1):C892–C898
Legare ME, Barhoumi, Hebert E, et al. Analysis of Pb2+ entry into cultured astroglia. Toxicol Sci, 1998,46(1): 90–100
Butrimovitz GP, Purdy WC. The determination of Zinc in blood plasma by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta, 1977,94(1):63–73
Laitusis AL, Brostrom MA, Brostrom CO. The dynamic role of GRP78/BiP in the coordination of mRNA translation with protein processing. J Biol Chem, 1999,274(11):486–493
Mir AH, Christopher MLB, Jonathan P, et al. Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor in human astrocytes by lead. J Biol Chem, 2000,275(36):27874–27882
Hendershot L, Wei J, Gaut J, et al. Inhibition of immunoglobulin folding and secretion by dominant negative Bip ATPase mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1996, 93(11):5269–5274
Castiglioni AJ, Peterson SL, Sanabria EL, et al. Structural changes in astrocytes induced by seizures in a mode of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci Res, 1990,26(3),334-341
Liberman E, Fong YL, Selby M J, et al. Activation of the grp78 and grp 94 promoters by hepatitis c virus E2 evelope protein. J Virol, 1999,73(5):3718–3722
Cai B, Tomida A, Mikami K, et al. Down-regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway by binging of GRP78/Bip to the receptor under glucose starved stress conditions. J Cell Physiol, 1998,177(2): 282–288
Fernandez PM, Tabbara SO, Jacobs L K, et al. Overexpression of the glucose-regulated stress gene GRP78 in malignant but not benign human breast lesions. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2000,59(1):15–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 39970651).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Ye, L., Wang, B. et al. Chelation of GRP78 with lead and its localization changes in the astroglia of rats exposed to lead. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 29, 492–497 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0420-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0420-x