Summary
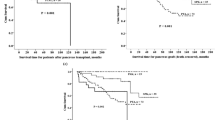
It is currently estimated that 50 million Chinese have diabetic mellitus (DM) with more than 90% of these being afflicted with type 2 DM. Concomitantly, the socio-economic improvements in China are supporting the adoption of pancreas-kidney transplantations as a treatment option for these patients. Recipient candidate pool has yet to be expanded and the final effect to be improved in clinical practice. To date, more than 250 pancreas-kidney transplants have been performed on patients with type 1 and type 2 DM. To improve the outcome, a new surgical technique that involves anastomosis of the graft duodenum to recipient jejunum side-to-side but not Roux-en-Y, has been devised for enteric drainage. Furthermore, the systemic venous drainage (SVD) has been used as the method of choice for endocrine secretions. Graft and recipient long-term survival in China was similar to that in America and Europe. Three-year survival rate of pancreas and kidney grafts was 92.2% and 90.2%, respectively, in our center. No difference in survival and graft function between type 1 and type 2 DM recipients was noted. It is concluded that pancreas-kidney transplantation is an effective way for the treatment of type 1 DM and some type 2 DM complicated with uremia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robertson RP, Davis C, Larsen J, et al. American Diabetes Association: Pancreas transplantation for patients with Type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care, 2003, 26(Suppl 1):S120
Sasaki TM, Gray RS, Ratner RE, et al. Successful long-term kidney-pancreas transplants in diabetes patients with high C-peptide levels. Transplantation, 1998, 65:1510–1512
Guessner AC, Sutherland DER. Pancreas transplant outcomes for United States (US) and Non-US cases as reported to the United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) and to the international pancreas transplant registry (IPTR) as of June 2004. Clin Transplant, 2005, 19:433–455
Kelly WD, Lillehei RC, Merkel FK, et al. Allotransplantation of the pancreas and duodenum along with kidney in diabetic nephropathy. Surgery, 1967, 61:827–837
Sollinger HW, Odorico JS, Knechtle SJ, et al. Experience with 500 simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants. Am Surg, 1998, 228:284–296
Blanchet P, Droupy S, Eschwege P, et al. Urodynamic testing predicts long-term urological complications following simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation. Clin Transplant, 2003, 17:26–31
Black PC, Plaskon LA, Miller J, et al. Cystoenteric conversion and reduction cystoplasty for treatment of bladder dysfunction after pancreas transplantation. Transplantation, 2003, 170:1913–1917
Yang L, Wu G, Liu S. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation: a report of 19 cases. Chin J General Surg (Chinese), 2005, 14:370–373
Zhang Y, Yang T, Liang P. Clinical study of surviving in simultaneous pancreas kidney transplantation. J Fourth Military Med Univ (Chinese), 2001, 22:810
Zheng S, Liang T, Chen J. Management and treatment of the complications following simultaneous kidney pancreaticoduodenal transplantation. Chin J Organ Transplant (Chinese), 2000, 21:177–179
Philosophe B, Farney AC, Schweitzer EJ, et al. Superiority of portal venous drainage over systemic venous drainage in pancreas transplantation: a retrospective study. Ann Surg, 2001, 234:689–696
Philosophe B. Portal versus systemic delivery of insulin: immunological benefits for pancreas transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant, 2002, 7:180–184
Stratta RJ, Rohr MS, Adams PL, et al. Kidney and pancreas transplantation at Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Centre. Clin Transplant, 2003:229–245
Petruzzo P, Konan PG, Feitosa LC, et al. A randomized trial in simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation: portal versus systemic venous drainage of the pancreas allograft. Transplant Proc, 2000, 32:2776–2777
Demartines N, Schiesser M, Clavien PA. An evidence-based analysis of simultaneous pancreas-kidney and pancreas transplantation alone. Am J Transplant, 2005, 5:2688–2697
Peng Z, Xu J, Fan Y. Portal venous and enteric drainage in simultaneous pancreas kidney transplantation. Chin J Surgery (Chinese), 2004, 42:940
Drognitz O, Benz S, Pfeffer F, et al. Long-term follow-up of 78 simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplants at a single-center institution in Europe. Transplantation, 2004, 78:1802–1808
Chen S, Xia S, He G. Simultaneous kidney pancreaticoduodenal transplantation: a report of 1 case. Chin J Organ Transplant (Chinese), 1990, 11:63–65
Orsenigo E, Socci C, Fiorina P, et al. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation: short- and long-term results. Transplant Proc, 2004, 36:586–588
Monroy-Cuadros M, Salazar A, Yilmaz S, et al. Bladder vs enteric drainage in simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2006, 21:483–487
Zhang Y, Guan D, Xu D. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation: a report of 19 cases. Chin J Organ Transplant (Chinese), 2007, 28:195–198
Ming C, Zeng F, Zhang W. Technology and application of simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation with modified enteric drainage. Chin J Surg (Chinese), 2007, 45:326–330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was supported by grants from the Chinese Ministry of Public Health for Key Clinical Projects (No. 353 [2007]) and the Hepatic Surgery Clinical Research Centre of Hubei, China (2007).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ming, C., Gong, N. & Chen, X. The current state of pancreas-kidney transplantation in China: The indications, surgical techniques and outcome. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 29, 269–272 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0301-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0301-3