Summary
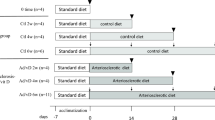
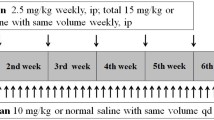
The inhibitory effect of astilbin on transplant arteriosclerosis in murine model of thoracic aorta transplantation was examined. Model of rat thoracic aorta transplantation was established. Ninety rats were divided into three groups. In isograft group, the thoracic aorta of Brown Norway (BN) rat was anastomosed with the abdominal aorta of another BN rat. In allograft group, the thoracic aorta of BN rat was anastomosed with the abdominal aorta of Lewis rat. In astilbin group, the rats receiving allo-transplantation were given astilbin 5 mg/kg per day for a time of 28 days. The donor thoracic aorta and the recipient abdominal aorta were anastomosed by means of a polyethylene cannula (inner diameter: 1.5 mm, length: 3 mm length). The grafts were histologically examined for structural changes. The areas of arterial lumen and endatrium were calculated. Our results showed that, in the allograft group, 28 days after allografting, conspicuous proliferation of smooth muscles and infiltration with a great number of inflammatory cells were found in the tunica intima and tunica media. Astilbin significantly inhibited the proliferation of smooth muscles and ameliorated the infiltration of inflammatory cells thereyby prevent against the development of transplant arteriosclerosis. It is concluded that asltilbin can effectively prevent the development of arteriosclerosis in allotransplant by inhibiting the proliferation of smooth muscles and inhibit the proliferation of smooth muscles in tunica of intima and media and reducing infiltration of the inflammatory cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grauhan O, Patzurek J, Hummel M, et al. Donor-transmitted coronary atherosclerosis. J Heart Lung Transplant, 2003, 22(5):568–573
Moien-Afshari F, McManus BM, Laher I. Immunosuppression and transplant vascular disease: benefits and adverse effects. Pharmacol Ther, 2003, 100(2):141–156
Yan R, Xu Q. Astilbin selectively facilitates the apoptosis of interleukin-2-dependent phytohemagglutinin-activated jurkat cells. Pharmacol Res, 2001, 44(2):135–139
Gao SH, Li P, Pan TC, et al. Astilbin induces apoptosis of activated T cells of mouse heart transplantation model with acute rejection in vitro. Chin J Exp Surg, 2004, 21(4):502
Han LK, Ninomiya H, Taniguchi M, et al. Norepinephrine-augmenting lipolytic effectors from Astilbe thunbergii rhizomes. J Nat Prod, 1998, 61(8):1006–1011
Motoyashiki T, Miyake M, Morita T, et al. Enhancement of the vanadate-stimulated release of lipoprotein lipase activity by astilbin from the leaves of Engelhardtia chrysolepis. Biol Pharm Bull, 1998, 21(5):517–519
Gao SH, Pan TC. Protective effects of astilbin on rat isolated heart reperfusion injury. Chin J Pract Chin Mod Med (Chinese), 2003, 3(16):1693–1694
Teranishi K, Poston RS, Reiz BA, et al. Effect of low molecular weight heparin on suppression of chronic graft vascular disease in a rat cardiac allograft model. Transplant Proc, 1998, 30:1009–1011
Gao SH, Chen T, Pan TC. Effect of astilbin on expression of Bax, Bcl-2 and caspase-3 in allograft reactive T cells. Chin J Pract Chin Mod Med (Chinese), 2003, 3(16):2110–2111
Gao SH, LI Ping, Pan TC. Effect of astilbin on expression of Fas, FasL, TNF-R1 and TNF-R2 in allograft reactive T cells. Chin J Pract Mod Med (Chinese), 2004, 4(17):217–218
Cai Y, Chen T, Xu Q, et al. Astilbin suppresses collagen-induced arthritis via the dysfunction of lymphocytes. Inflamm Res, 2003, 52(8):334–340.
Cai Y, Chen, T, Xu Q, et al. Astilbin suppresses delayed-type hypersensitivity by inhibiting lymphocyte migration. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2003, 55(5):691–696
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The project was supported by a grant from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 30500656).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Li, P., Zhang, Y. et al. The inhibitory effect of astilbin on the arteriosclerosis of murine thoracic aorta transplant. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 29, 212–214 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0215-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0215-0