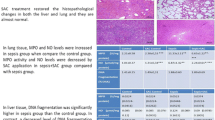
Summary
Dynamic changes in mRNA expressions of liver tissue apoptosis-promoting genes Fas and Bax and apoptosis-inhibiting gene Bcl-2 of vibrio vulnificus sepsis rats were detected and the effects of antibacterial agents were examined. The rat model with Vibrio vulnificus sepsis (VV group) was established and some of the Vibrio vulnificus sepsis rats were treated with antibacterial agents (AA group). The mRNA expressions of Fas, Bax and Bcl-2 were measured by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). As compared with normal control group (NC group), the expressions of Fas and Bax mRNA in liver tissue at all different time points in VV group were increased significantly (P<0.05), and the highest levels of Fas and Bax mRNA expressions were 6 and 12 h after the infection, respectively. At the same time, the expression of Bcl-2 mRNA in liver tissue at all different time points in VV group were decreased significantly (P<0.05), and the lowest level of Bcl-2 mRNA expression appeared 2 h after the infection. The mRNA expressions of Bcl-2 in liver tissue 9 and 12 h after the infection in AA group were increased significantly (P<0.05) compared with NC group, while the expressions of Fas and Bax mRNA were not significantly different from those of NC group. Compared with VV group, the expression of Fas mRNA in AA group was decreased (P<0.05) and Bax mRNA was decreased significantly 12 and 16 h after the infection (P<0.05), while the expressions of Bcl-2 mRNA were increased significantly 9, 12 and 16 h after the infection (P<0.05). It is concluded that the mRNA expressions of liver tissue apoptosis-promoting genes Fas and Bax were increased remarkably in vibrio vulnificus sepsis rats, whereas the expression of apoptosis-inhibiting gene Bcl-2 mRNA was decreased obviously in sepsis rats in early stage. The treatment with cefoperazone sodium and levofloxacin lactate could inhibit the expression of Fas mRNA and Bax mRNA and enhance the expression of Bcl-2 mRNA at the same time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strom MS, Paranjpye RN. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of Vibrio vulnificus. Microbes Infect, 2000,2(2):177–188
Hlady WG, Klontz KC. The epidemiology of Vibrio infections in Florida, 1981–1993. Infect Dis, 1996,173(5): 1176–1183
Shapiro RL, Altekruse S, Hutwagner L, et al. The role of Gulf Coast oysters harvested in warmer months in vibrio vulnificus infections in the United States, 1988–1996. Vibrio Working Group. J Infect Dis, 1998,178(3):752–759
Klontz KC, Lieb S, Schreiber M, et al. Syndromes of Vibrio vulnificus infections. Clinical and epidemiologic features in Florida cases, 1981–1987. Ann Intern Med, 1988, 109(4):318–323
Shapiro RL, Altekruse S, Hutwagner L, et al. The role of gulf oysters harvested in warmer months in Vibrio vulnificus infections in the United States, 1988–1996. Vibrio Working Group. J Infect Dis, 1998,178(3):752–759
Lu ZQ, Zhang XH, Zhou TL, et al. The combination experimental therapy with antimicrobial agents in Vibrio vulnificus infection in mouse. Chin J Infect Dis (Chinese), 2003, 21(5):242–245
Lu ZQ, Lu CJ, Qiu QM. A protocol of diagnose and treatment of vibrio vulnificus sepsis (draft). Chin J Crit Care Med (Chinese), 2007,27(8):690–692
Lu ZQ, Zhou CL, LI BX, et al. The epidemiological character of 12 vibrio vulnificus septicemia. Chin J epidemiol, 2003,24(10):900
Song SF, Wang JX, Song JH. Research progress of apoptosis. Acta Acad Med Nei Mongol (Chinese), 2004, 26(3):233–236
Kashimoto T, Ueno S, Hanajima M, et al. Vibrio vulnificus induces macrophage apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun, 2003,71(1):533–535
Sheng ZY, Hu S. Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 1999,185–188
Hong GL, Lu ZQ. Study situation of Vibrio vulnificus sepsis in chronic hepatic diseases. Chin J Microecol (Chinese), 2007,19(2):236–238
Li HY, Liang H, Lu ZQ, et al. Effect of antibacterial agents to the pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in serum of rats with vibrio vulnificus sepsis. Chin Crit Care Med (Chinese), 2007,19(1):53–54
Lu ZQ, Liang H, Li JR, et al. The expression and the dynamic change of lipopolysaccharide eceptor mCD14 in peripheral blood of the rats with Vibrio vulnificus sepsis. Chin J Emerg Resusc Disaster Med (Chinese), 2006, 1(4–5):152–155
Hong GL, Lu ZQ, Qiu QM, et al. Dynamic changes of blood coagulation factors in rat model of alcoholic liver disease with Vibrio vulnificus sepsis. Chin J Crit Care Med (Chinese), 2007, 27(11):999–1001
Lu ZQ, Qiu QM, Zhou TL, et al. Dynamic changes of serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 in rat of liver disease with Vibrio vulnificus sepsis. Chin J Emerg Med (Chinese), 2008,17(3):244–247
Lu ZQ, Zhao CH, Li HP, et al. Combined effects of antimicrobial agents and ulinastatin on vibrio vulnificus sepsis in rats with alcohol liver disease. Chin J Emerg Med (Chinese), 2005,114(16):474–478
Zhang Y, Wu LJ, Tashiro S, et al. Evodiamine induces tumor cell death through different pathways: apoptosis and necrosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2004,25(1):83–89
Papoff G, Cascino I, Eroma A, et al. An N-terminal domain shared by Fas soluble variants presents cell death in vitro. J Immunol, 1996,156(12):4622–4630
Jones BE, Loc R, Liu H, et al. Role of caspases and NF-kappaB signaling in hydrogen peroxide and superoxide induced hepatocyte apoptosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Live Physiol, 2000,278(5):693–697
Zhou NN, Zhu XF, Zhou JM, et al. 2-methoxyestradiol induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2004,25(11):1515–1520
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, et al. Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochromec from mitochondria blocked. Science, 1997,275(5301):1129–1132
Kirsch DG, Doseff, A, Nelson-Chau B, et al. Caspase-3-dependent cleavage of Bcl-2 promotes release of cytochrome c. J Biol Chem, 1999,274:21155–21161
Cheng EH, Levine B, Boise LH, et al. Bax-independent inhibition of apoptosis by Bcl-xL. Nature, 1996,379(6565): 554–556
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant for supporting key research programs from Zhejiang Province (No. 07-F04), and a Science and Technology Fund of Zhejiang Province (No. 2005C30009).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Z., Li, M., Liang, H. et al. Dynamic expressions of liver tissue apoptosis-related genes of Vibrio vulnificus sepsis rats and the effects of antibacterial agents. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 29, 193–197 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0211-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0211-4