Summary
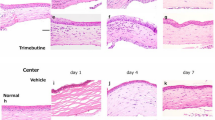
The effects of A771726, the active metabolite of leflunomide, on experimental rat corneal neovascularization (NV) in vivo and on cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro were studied. The corneal NV was induced by alkali burn in 40 SD rats. The rats were randomly divided into 4 groups with 10 rats in each group. Group A was treated with 0.9% sodium chloride (control group), and group B, group C and group D were given different concentrations of A771726 eye drops (0.5%, 1.0%, 2.0% respectively) 4 times daily during days 0–28. The occurrence and development of corneal NV were observed at 4, 7, 14, 21 and 28 day after alkali burn by a slit lamp microscope. The cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (ECV-304) were incubated with A771726 solution at different concentrations (20, 40, 80, 160, 320 mol/L) for 36 h. The proliferation of cells was assessed by methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium (MTT), and the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in cells was detected by using immunofluorescence under the laser confocal microscope. The rat model showed that the onset of corneal NV was delayed and progression of corneal NV was inhibited in the groups C and D. The corneal NV areas in groups C and D were significantly smaller than in groups A and B (P<0.01). No significant difference was found in corneal NV areas between groups C and group D (P>0.05). A771726 solution (⩾40 μmol/L) could inhibit proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and decrease the expression of PCNA in cells significantly. A771726, as the active metabolite of leflunomide, strongly prevented corneal NV induced by alkali burn in the in vivo model, and inhibited proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells in the in vitro model. Therefore, A771726 may serve as an angiogenic inhibitor in the treatment of corneal NV.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Freitas A M, Melo B C, Mendonca C N et al. Causes and risk factors for graft failure in surgeries performed by physicians in fellowship training. Cornea, 2006, 25(3):251–256
McChesney L P, Xiao F, Sankary H N et al. An evaluation of leflunomide in the canine renal transplantation model. Transplantation, 1994,57(12):1717–1722
Williams J W, Mital D, Chong A et al. Experiences with leflunomide in solid organ transplantation. Transplantation, 2002,73(3):358–366
Seo K, Choi J, Park M et al. Angiogenesis effects of nerve growth factor (NGF) on rat corneas. J Vet Sci, 2001,2(2):125–130
Rossant J, Howard L. Signaling pathways in vascular development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 2002,18(2):541–573
Kirsch B M, Zeyda M, Stuhlmeier K et al. The active metabolite of leflunomide, A771726, interferes with dendritic cell function. Arthritis Res Ther, 2005,7(3):694–703
Fox R L, Herrmann M L, Franqou C G et al. Mechanism of action for leflunomide in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol, 1999,93(3):198–208
Shawver L K, Schwartz D P, Mann E et al. Inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor-mediated signal transduction and tumor growth by N-[4-(trifluoromethyl)-phenyl]5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxamide. Clin Cancer Res, 1997,3(7):1167–1177
Philipp W, Speicher L, Humpel C. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in inflamed and vascularized human corneas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2000,41(9):2514–2522
Claesson-Welsh L. Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Biochem Soc Trans, 2003,31(Pt1):20–24
Urushibara M, Takayanagi H, Koga T et al. The antirheumatic drug leflunomide inhibits osteoclastogenesis by interfering with receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand-stimulated induction of nuclear factor of activated T cells cl. Arthritis Rheum, 2004,50(3):794–804
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Hao, N. & Bian, F. The active metabolite of leflunomide A771726 inhibits corneal neovascularization. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 28, 364–368 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0332-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0332-1