Summary
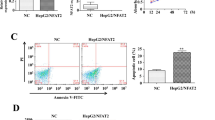
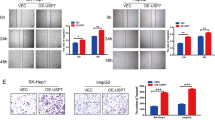
The effect of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors Cip1/Waf1 (p21) on regulatory expression of survivin transcription in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell HepG2 was observed and the related mechanisms explored. Doxorubicin (DOX) was used to treat HepG2. Eukaryotic vector pEGFP-C2-p21 was transfected into HepG2 by lipofectamine and positive clones were screened out by G418. The mRNA expression of p21 and survivin was detected by real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR). Flow cytometry was used to examine the cell cycle, and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to measure the levels of E2F-1 and p300. The results showed that: (1) After treatment with DOX, the expression of p21 was increased, whereas that of survivin was reduced during 24 h of treatment; (2) After transfection of pEGFP-C2-p21 into HepG2, p21 level was significantly enhanced to 2100.11-folds or 980.89-folds in comparison to HepG2 or HepG2-C2 group, and survivin level was markedly down-regulated to 0.54% or 0.59% relative to the control groups; (3) Overexpressed p21 resulted in G1/G0 phase arrest (F=31.59, P<0.01), meanwhile E2F-1 mRNA and p300 mRNA were reduced as compared with those of controls (F E2F-1=125.28, P<0.05; F p300=46.01, P<0.01). It was suggested that p21 could be a potential mediator of survivin suppression at transcription level in HepG2 cell, which might be through the block at G1/G0 phase and down-regulation of transcription factors E2F-1 and p300.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takashima H, Nakajima T, Moriguchi M et al. In vivo expression patterns of survivin and its splicing variants in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int, 2005,25(1):77–84
Lekanne Deprez R H, Fijnvandraat A C, Ruijter J M et al. Sensitivity and accuracy of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction using SYBR green I depends on cDNA synthesis conditions. Anal Biochem, 2002, 307(1):63–69
Li Y R, Wu J M, Wang L et al. Detection of telomerase activity and the expression of telomerase subunits in the patients with acute myelogenous leukemia. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol [Med Sci], 2004,24(1):48–52
Altieri D C. Survivin, versatile modulation of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene, 2003,22(53):8581–8589
Lohr K, Moritz C, Contente A et al. p21/CDKN1A mediates negative regulation of transcription by p53. J Biol Chem, 2003,278(35):32 507–32 516
Zhou M, Gu L, Li F et al. DNA damage induces a novel p53-survivin signaling pathway regulating cell cycle and apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2002,303(1):124–131
Ravizza R, Gariboldi M B, Passarelli L et al. Role of the p53/p21 system in the response of human colon carcinoma cells to doxorubicin. BMC Cancer, 2004,4:92
Li Y, Xie M, Yang J et al. The expression of antiapoptotic protein survivin is transcriptionally upregulated by DEC1 primarily through multiple spl binding sites in the proximal promoter. Oncogene, 2006,25(23):3296–3306
Nawrocki S T, Carew J S, Douglas L et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors enhance lexatumumab-induced apoptosis via a p21Cipl-dependent decrease in survivin levels. Cancer Res, 2007,67(14):6987–6994
Jiang Y, Saavedra H I, Holloway M P et al. Aberrant regulation of survivin by the RB/E2F family of proteins. J Biol Chem, 2004,279(39):40 511–40 520
Chan H M, La Thangue N B. P300/CBP proteins: HATs for transcriptional bridges and scaffolds. J Cell Sci, 2001,114(Pt 13):2363–2373
Mirza A, McGuirk M, Hockenberry T N et al. Human survivin is negatively regulated by wild-type p53 and participates in p53-dependent apoptotic pathway. Oncogene, 2002,21(17):2613–2622
Garcia-Wilson E, Perkins N D, P21WAF1/CIP1 regulates the p300 sumoylation motif CRD1 through a C-terminal domain independently of cyclin/CDK binding. Cell Cycle, 2005,4(8):1113–1119
Ma H, Nguyen C, Lee K S et al. Differential roles for the coactivators CBP and p300 on TCF/-catenin-mediated survivin gene expression. Oncogene, 2005, 24(22):3619–3631
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant from Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 20060487045).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, J., Hu, L., Li, Y. et al. Effect of survivin regulation of transcription level by p21waf1 overexpression in HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 28, 308–313 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0318-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0318-z