Summary
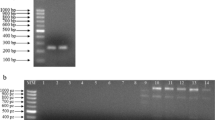
In order to analyze the in vivo expression of Candida albicans secreted aspartyl proteinases (SAP) in human vaginal infection, the vaginal secretion from 29 human subjects was collected by vaginal swab, and the expression of SAP1-SAP6 was detected by reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction using specific primer sets. It was found that Sap2 and Sap5 were the most common genes expressed during infection; Sap3 and Sap4 were detected in all subjects and all 6 SAP genes were simultaneously expressed in some patients with vaginal candidiasis. It was suggested that the SAP family is expressed by Candida albicans during infection in human and that Candida albicans infection is associated with the differential expression of individual SAP genes which may be involved in the pathogenesis of vaginal candidasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hube B, Naglik J R. Extracellular hydrolases. In: Calderone R A, ed. Candida and candidiasis. Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology Press, 2002.107–122
Hube B, Naglik J. Candida albicans proteinases: resolving the mystery of a gene family. Microbiology, 2001,147:1997–2005
Hube B. Extracellular proteinases of human pathogenic fungi. In: Ernst J F, Schmidt A, eds. Contributions to microbiology: dimorphism in human pathogenic and apathogenic yeasts. Basel: S. Karger AG, 2000.126–137
Naglik J R, Newport G, White T C et al. In vivo analysis of secreted aspartyl proteinase expression in human oral candidiasis. Infect Immun, 1999,67:2482–2490
Losberger C, Ernst J F. Sequence of the Candida albicans gene encoding actin. Nucleic Acids Res, 1989,17:9488
Cobb B D, Clarkson J M. A simple procedure for optimizing the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using modified Taguchi methods. Nucleic Acids Res, 1994,22:3801–3805
White T C, Agabian N. Candida albicans secreted aspartyl proteinases: isoenzyme pattern is determined by cell type, and levels are determined by environmental factors. J Bacteriol, 1995,177:5215–5221
Colina A R, Aumont F, Deslauriers N et al. Evidence for degradation of gastrointestinal mucin by Candida albicans secretory aspartyl proteinase. Infect Immun, 1996,64:4514–4519
Ripeau J S, Fiorillo M, Aumont F et al. Evidence for differential expression of Candida albicans virulence genes during oral infection in intact and human immunodeficiency virus type 1-transgenic mice. J Infect Dis, 2002,185:1094–1102
Staib P, Kretschmar M, Nichterlein T et al. Differential activation of a Candida albicans virulence gene family during infection. PNAS, 2000,97:6102–6107
Schaller M, Schäfer W, Korting H C et al. Differential expression of secreted aspartyl proteinases in a model of human oral candidiasis and in patient samples from the oral cavity. Mol Microbiol, 1998,29:605–615
De bernardis F, Cassone A, Sturtevant J et al. Expression of Candida albicans Sap1 and Sap2 in experimental vaginitis. Infect Immun, 1995,63:1887–1892
Schaller M, Korting H C, Schafer W et al. Secreted aspartic proteinase (Sap) activity contributes to tissue damage in a model of human oral candidiasis. Mol Microbiol, 1999,34:169–180
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
LIN Nengxing, male, born in 1974, M.D., Ph.D, Doctor in Charge
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, N., Feng, J., Tu, Y. et al. Expression of Candida albicans secreted aspartyl proteinase in acute vaginal candidiasis. J. Huazhong Univ. Sc. Technol. 27, 333–335 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0330-8
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0330-8