Summary
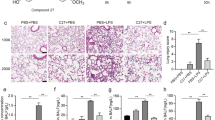
To explore the dynamic expression and role of Aquaporin5 (AQP5) in lung development and hyperoxia lung injury, gestation 21-day Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (term=22 days) were randomly assigned to air group and hyperoxia group within 12–24 h after birth. The rats in hypreoxia group were continuously exposed to about 85% oxygen and those in air group to room air. After 1 to 14 days of exposure, total lung RNA was extracted and the expression of AQP5 mRNA was detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Immunohistochemistry and western-blot were used to detect the expression of AQP5 protein. The results showed that the expression of AQP5 in premature rats lung could be detected at various time points after birth, and the positive staining was restricted to the type I alveolar epithelial cells. In air group, the AQP5 expression was detected in a very low level at day 1, but exhibited a persistent increase after birth. Compared with the air group, the expression of AQP5 in hyperoxia group was increased at day 1, and had significant difference in mRNA level (P<0.05), but decreased significantly in mRNA and protein levels after 4 to 14 days (P<0.01 or P<0.05 respectively). It was concluded that AQP5 might play a key role in the alveolar period of premature rats by regulating the lung water balance. Hyperoxia exposure leads to a down-regulation of the AQP5 expression, which may be an important factor for the development of hyperoxia lung injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu H, Wintour E M. Aquaporins in development. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2005,3(1):18
Liu H, Hooper S B, Arnugan A et al. Aquaporin gene expression and regulation in the ovine fetal lung. J Physiol, 2003,551(2):503–514
Dobbs L G, Gonzalez R, Matthay M A et al. Highly water-permeable type I alveolar epithelial cells confer high water permeability between the airspace and vasculature in rat lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 1998,95(6):2991–2996
Chang L W, Rong Z H, Zhang Q S. Effect of retinoic acid on lung injury in hyperoxia-exposed newborn rats. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol [Med Sci], 2003, 23(1):71–74
Verkman A S, Matthay M A, Song Y L. Aquaporin water channels and lung physiology. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2000,278(5):867–879
Borok Z, Verkman A S. Lung Edema Clearance: 20 Years of Progress, Invited Review: Role of aquaporin water channels in fluid transport in lung and airways. J Appl Physiol, 2002,93(10):2199–2206
Ma T, Fukuda N, Song Y. Lung fluid transport in aquaporin-5 knockout mice. J Clin Invest, 2000,105(1):93–100
McMurtry I F. Pre-and postnatal lung development, maturation, and plasticity. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2002,282(3):341–344
Zelenina M, Zelenin S, Aperia A. Water channels (aquaporins) and their role for postnatal adaptation. Pediatr Res, 2005,57(5):47–53
Ma L Y, Chang L W, Quan Y F. Effect of hyperoxia on nitric oxide synthase expression in the lung of preterm rats. Chin J Contemp Pediatr (Chinese), 2001, 3(3):232–235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
LU Hongyan, female, born in 1969, M.D., Ph.D.
This project was supported by a grant from National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 30471824).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Chang, L., Li, W. et al. Effects of hyperoxia on the dynamic expression of Aquaporin5 in premature rats lung development. J. Huazhong Univ. Sc. Technol. 27, 318–320 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0326-4
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0326-4