Summary
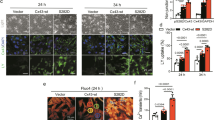
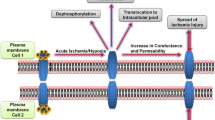
In order to confirm the hypothesis that during acute hypoxia, the antiarrhythmic peptide (AAP10) could improve conductance by changing the phosphorylation state of connexin43 (Cx43), isolated perfused rat hearts were randomly divided into three groups: control, hypoxia and AAP10 (n=9 in each group). The change in Cx43 phosphorylation was tested by Western-blot; the distribution of Cx43 was observed by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. Western-blot analysis revealed that the expression of total Cx43 protein was significantly decreased during acute hypoxia, while nonphosphorylated Cx43 (NP-Cx43) was unchanged. AAP10 could increase the expression of total Cx43 protein, but had no effects on the NP-Cx43 protein. Immunofluorescence study showed that during acute hypoxia, both total Cx43 and NP-Cx43 proteins were greatly decreased, while AAP10 only increased the expression of total Cx43 protein, but had no effect of the NP-Cx43 protein expression. These findings suggested that the decrease of intercellular communication may be associated with the reduction of phosphorylated Cx43 (p-Cx43) and translocation of NP-Cx43 from the surface of gap junction into intracellular pools during acute hypoxia. AAP10 can improve intercelluar communication by enhancing phosphorylation of Cx43.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zipes D P, Wellens H J J. Sudden cardiac death. Circulation, 1998,98;2334–2351
Janse M J, Wit A L. Electrophysiological mechanisms of ventricular arrhythmias resulting from myocardial ischemia and infarction. Physiol Rev, 1989,69:1049–1169
Gutstein D E, Morley G E, Tamaddon H et al. Conduction slowing and sudden arrhythmic death in mice with cardiac-restricted inactivation of connexin43. Carc Res, 2001,88:333–339
Kléber A G. Mechanisms of ventricular arrhythmias: a perspective. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 1991,17:S1–S8
Beardslee M A, Lerner D L, Tadros P N et al. Dephosphorylation and intracellular redistribution of ventricular connexin43 during electrical uncoupling induced by ischemia. Circ Res, 2000, 87:656–662
Beyer E C, Goodenough D A, Paul D L. Connexin family of gap junction proteins. J Membr Biol, 1990,116:187–194
Kumar N M, Gilula N B. The gap junction communication channel. Cell, 1996,84:381–388
Lampe P D, Lau A F. The effects of connexia phosphorylation on gap junctional communication. Int J Biochem, Cell Biol, 2004, 36:1171–1186
Grover R, Dhein S. Structure-activity relationships of novel peptides related to the antiarrhythmic peptide AAP10 which reduce the dispersion of epicardial action potential duration. Peptides, 2001,22(7):1011–1021
Muller A, Schaefer T, Linke W et al. Actions of the antiarrhythmic peptide AAP10 on intercellular coupling. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 1997,356(1):76–82
Dhein S, Weng S, Grover R et al. Protein kinase C alpha mediates the effect of antiarrhythmic peptide on gap junction conductance. Cell Commun Adhes, 2001,8(4–6):257–264
Weng S, Lauven M, Schaefer T et al. Pharmacological modification of gap junction coupling by an antiarrhythmic peptide via protein kinase C activation. Faseb J, 2002,16(9):1114–1116
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Wang Rong, Female, born in 1979, Ph.D.
This project was supported by a grant from National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 30370573).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Zhang, C., Ruan, Y. et al. Changes in phosphorylation of connexin43 in rats during acute myocardial hypoxia and effects of antiarrhythmic peptide on the phosphorylation. J. Huazhong Univ. Sc. Technol. 27, 241–244 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0306-8
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0306-8