Summary
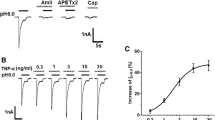
To investigate the effect of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) on IA and IK currents in cultured murine trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons, whole-cell patch clamp technique was used to record the IA and IK currents before and after 20 ng/mL IL-1β perfusion. Our results showed that 20 ng/mL IL-1β inhibited IA currents (18.3 ± 10.7)% (n=6, P<0.05). IL-1β at 20 ng/mL had no effect on G-V curve of IA but moved the H-infinity curve V0.5 from −36.6±6.1 mV to −42.4±5.2 mV (n=5, P<0.01). However, 20 ng/mL IL-1β had effect on neither the amplitude nor the G-V curve of IK. IL-1β was found to selectively inhibit IA current in TG neurons and the effect may contribute to hyperalgesia under various inflammatory conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferreira S H. The role of interleukins and nitric oxide in the mediation of inflammatory pain and its control by peripheral analgesic. Drugs, 1993,46:1–9
Sellami S, de Beaurepairre R. Hypothalamic and thalamic sites of action of interleukin-1 b on food intake, body temperature and pain sensitivity in the rat. Brain Res, 1995, 694: 69–77
Hou, Li W, Wang X. Mechanism of interleukin-1 beta-induced calcitonin gene-related peptide production from dorsal root ganglion neurons of neonatal rats. Neurosci Res 2003, 73: 188–97
Morioka N, Takeda K, Kumagai K et al. Interleukin-1beta-induced substance P release from rat cultured primary afferent neurons driven by two phospholipase A2 enzymes: secretory type IIA and cytosolic type IV. J Neurochem, 2002,80:989–97
Maier S F, Wiertelak E P, Martin D et al. Interleukin-1 mediates the behavioral hyperalgesia produced by lithium chloride and endotoxin. Brain Res, 1993, 623: 321–4
Jeanjean A P, Moussaoui S M, Maloteaux J-M et al. Interleukin-1 b induces long-term increase of axonally transported opiate receptors and substance P. Neuroscience, 1995,68:151–7
Vitkovic L, Bockaert J, Jacque C, ’Inflammatory’ cytokines: neuromodulators in normal brain? J Neurochem, 2000,74: 457–71
Reeve A J, Patel S, Fox A et al. Urban, Intrathecally administered endotoxin or cytokines produce allodynia, hyperalgesia and changes in spinal cord neuronal responses to nociceptive stimuli in the rat. Eur Pain, 2000,4: 247–57
Liu L, Simon S A. Capsaicn-induced currents with distinct desensitization and Ca2+ dependence in rat trigeminal ganglion cells. J Neurophysiol, 1996,75:1503–14
Hodgkin A L, Huxley A F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol, 1952,117:500–544
Rudy B, McBain, C J. Kv3 channels: voltage-gated K channels designed for high-frequency repetitive firing. Trends Neurosci, 2001,24:517–526
Bekkers J M, Delaney A J. Modulation of excitability by a-dendrotoxin-sensitive potassium channels in neocortical pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci, 2001,21: 6553–6560
Stansfeld, C E. 4-Aminopyridine and dendrotoxin induce repetitive firing in rat visceral sensory neurones by blocking a slowly inactivating outward current. Neurosci Lett, 1986,64: 299–304
Brew H M, Forsythe I D. Two voltage-dependent Kt conductances with complementary functions in postsynaptic integration at a central auditory synapse. J Neurosci, 1995, 15:8011–8022
Tempel B L, Jan Y N, Jan L Y. Cloning of a probable potassium channel gene from mouse brain. Nature, 1988, 332:837–839
Nisenbaum E S. Contribution of a slowly inactivating potassium current to the transition to firing of neostriatal spiny projection neurons. J Neurophysiol, 1994,71:1174–1189
Connor J A, Stevens C F. Prediction of repetitive firing behaviour from voltage clamp data on an isolated neurone soma. J Physiol, 1971,213:1–53
Stuhmer W, Ruppersberg J P, Schroter K H et al. Molecular basis of functional diversity of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. EMBO J, 1989,8:3235–3244
Storm J F. Potassium currents in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Prog Brain Res, 1990,83:161–187
Johnston D, Hoffman D A, Magee, J C et al. Dendritic potassium channels in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Physiol, 2000, 25:75–81
Mathie A, Wooltorton J R, Watkins C S. Voltage-activated potassium channels in mammalian neurons and their block by novel pharmacological agents. Gen Pharmacol, 1998, 30:13–24
Michael S G, Michael J S, Jon D L. Characterization of six voltage-gated K+ currents in adult rat sensory neurons. J Neurophysiol, 1996,75:2629–2624
Nashmi R and Fehlings M G. Role of voltage-gated K+ channels in the pathophysiology of spinal cord injury. Modulator, 2001,14:5–8
Pearce R J and Duchen M R. Differential expression of membrane currents in dissociated mouse primary sensory neurons. Neuroscience, 1994,63: 1041–1056
Rasband M N, Park E W, Vanderah T W et al. Distinct potassium channels on pain-sensing neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001, 98:13373–13378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
PAN Jianping, female, born in 1979, Master in Pharmacology
The project was supported by a grant from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 30271500).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, J., Liu, L., Yang, F. et al. Effect of interleukin-1β on IA and IK currents in cultured murine trigeminal ganglion neurons. J. Huazhong Univ. Sc. Technol. 27, 131–134 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0205-z
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0205-z