Summary
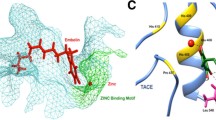
The crystal structural data of TACE, MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3 and MMP-9 were obtained from PDB database, and then their catalytic domains’ properties including conformation, molecular surface hydrophobicity and electrostatic potential were analyzed and compared by using Insight II molecular modeling software. It was found that the conformation and molecular surface hydrophobicity of catalytic domains of TACE and MMPs were not obviously different, but the molecular surface electrostatic potential of catalytic domain of TACE and MMPs had obvious differences. The findings are helpful in the Rational Drug Design of TACE selective inhibitor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Newton R C, Decicco C P. Therapeutic potential and strategies for inhibiting tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Med Chem, 1999,42:2295–314
Onrust S V, Lamb H M. Infliximab: A Review of its Use in Crohn’s Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bio Drugs, 1998,10(5):397–422
Murray K M, Dahl S L. Recombinant Human Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor (P75) Fc Fusion Protein (TNFR:Fc) in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Pharmacother, 1997,31:1335–8
Black R A, Rauch C T, Kozlosky C J et al. A metalloproteinase disintegrin that releases tumor-necrosis factor-α from cells. Nature, 1997,385:729–33
Maskos K, Fernandez-Catalan C, Huber R et al. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human tumor necrosis factor-α-converting enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1998,95(7):3408–3412
Woessner J F. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Connective Tissue Remodeling. FASEB J, 1991,5:2145–54
Rothenberg M, Nelson A, Hande K. New drugs on the horizon: matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Oncologist, 1998,3:271–4
Lovejoy B, Welch A R, Carr S et al. Crystal structures of MMP-1 and-13 reveal the structural basis for selectivity of collagenase inhibitors. Nat Struct Biol, 1999,6(3):217–221
Feng Y, Likos J, Zhu L et al. 1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments for a truncated and inhibited catalytic domain of matrix metalloproteinase-2. J Biomol NMR, 2000,17(1):85–86
Pavlovsky A G, Williams M G, Ye Q Z et al. X-ray structure of human stromelysin catalytic domain complexed with nonpeptide inhibitors: implications for inhibitor selectivity. Protein Sci, 1999,8(7):1455–1462
Rowsell S, Hawtin P, Minshull C A et al. Crystal structure of human MMP-9 in complex with a reverse hydroxamate inhibitor. J Mol Biol, 2002,319(1):173–181
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grants No.31371309).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Feng, W., Yang, Y. et al. Comparison of properties of tumor necrosis factor-α converting enzyme (TACE) and some matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) in catalytic domains. J. Huazhong Univ. Sc. Technol. 26, 637–639 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-006-0601-9
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-006-0601-9