Abstract
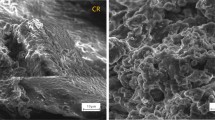
The physical performance of recycled asphalt was used as the main evaluation index to study the optimal range of a self-made rejuvenator. Through the penetration, viscosity and gel permeation chromatography (GPC) tests, the diffusion degree of the rejuvenator under different temperatures and time process was analyzed, and the diffusion efficiency of the rejuvenator was evaluated from the macro and micro perspective. The regeneration mechanism of the rejuvenator in the aged asphalt was also analyzed using the Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and chemical composition tests. The research results showed that the optimum rejuvenator content was about 3%. Higher temperature and longer time were beneficial to improving the permeability and diffusion of the rejuvenator. During the aging process, the light components were reduced, and more macromolecular asphaltenes were generated as well as a large number of carbonyl and sulfoxide. After diffusion and regeneration, the light components in the asphalt were supplemented, the wrinkles and gullies of the aged asphalt were almost improved to the surface state of the matrix asphalt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sultan S A, Guo Z. Evaluating the Performance of Sustainable Perpetual Pavements Using Recycled Asphalt Pavement in China[J]. International Journal of Transportation Science and Technology, 2016, 5(3): 200–209
Alaye Q E A, Ling X Z, Dong Z, et al. Evaluation of Mixture Performance Recycled Asphalt Pavement Materials as Base Layer with or without Rejuvenator into the Asphalt[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2020, 35(3): 579–597
Zahoor M, Nizamuddin S, Madapusi S, et al. Sustainable Asphalt Rejuvenation Using Waste Cooking Oil: A Comprehensive Review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 278: 123304
Cong P, Hao H, Zhang Y, et al. Investigation of Diffusion of Rejuvenator in Aged Asphalt[J]. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 2016, 9(4): 280–288
Li H, Liu G, Dong B, et al. Research on the Development and Regeneration Performance of Asphalt Rejuvenator Based on the Mixed Waste Engine Oil and Waste Cooking Oil[J]. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 2019, 12(3): 336–346
Kuang D, Yu J, Chen H, et al. Effect of Rejuvenators on Performance and Microstructure of Aged Asphalt[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2014, 29(2): 341–345
Kuang D, Jiao Y, Ye Z, et al. Diffusibility Enhancement of Rejuvenator by Epoxidized Soybean Oil and Its Influence on the Performance of Recycled Hot Mix Asphalt Mixtures[J]. Materials, 2018, 11(5): 833
Kuang D, Feng Z, Yu J, et al. A New Approach for Evaluating Rejuvenator Diffusing into Aged Bitumen[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2011, 26(1): 43–46
Ma T, Huang X, Zhao Y, et al. Evaluation of the Diffusion and Distribution of the Rejuvenator for Hot Asphalt Recycling[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 98: 530–536
Wang F, Wang Y, Zhang Q, et al. Study on Regenrating Effect and Diffusion Ability of Asphalt Recycling Agents [J]. Petrochemical Technology & Application, 2012, 30(01): 13–18
Karlsson R, Isacsson U, Ekblad J. Rheological Characterisation of Bitumen Diffusion[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42(1): 101–108
Karlsson R, Isacsson U. Application of FTIR-ATR to Characterization of Bitumen Rejuvenator Diffusion[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2003, 15(2): 157–165
Su J, Wang Y, Yang P, et al. Evaluating and Modeling the Internal Diffusion Behaviors of Microencapsulated Rejuvenator in Aged Bitumen by FTIR-ATR Tests[J]. Materials, 2016, 9(11): 932
Darabi M K, Rahmani E, Little D N, et al. A Computational-experimental Method to Determine the Effective Diffusivity of Asphalt Concrete[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 143(9): 04 017 076
Rad F Y, Sefidmazgi N R, Bahia H. Application of Diffusion Mechanism: Degree of Blending Between Fresh and Recycled Asphalt Pavement Binder in Dynamic Shear Rheometer[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2014, 2444(1): 71–77
Baqersad M, Ali H. Rheological and Chemical Characteristics of Asphalt Binders Recycled Using Different Recycling Agents[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 228: 116738
Li H, Dong B, Wang W, et al. Effect of Waste Engine Oil and Waste Cooking Oil on Performance Improvement of Aged Asphalt[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(9): 1767
Xu M, Zhang Y. Study of Rejuvenators Dynamic Diffusion Behavior into Aged Asphalt and Its Effects[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 261: 120673
Xiao Y, Li C, Wan M, et al. Study of the Diffusion of Rejuvenators and Its Effect on Aged Bitumen Binder[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(4): 397
Mollenhauer K, Pierard N, Tusar M, et al. Development and Validation of a Laboratory Aging Method for the Accelerated Simulation of Reclaimed Asphalt[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2010, 25(4): 631–636
Hofko B, Cannone Falchetto A, Grenfell J, et al. Effect of Short-Term Ageing Temperature on Bitumen Properties[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2017, 18(sup2): 108–117
Loise V, Caputo P, Porto M, et al. Unravelling the Role of a Green Rejuvenator Agent in Contrasting the Aging Effect on Bitumen: A Dynamics Rheology, Nuclear Magnetic Relaxometry and Self-Diffusion Study[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2020, 603: 125182
Xiao Y, Yan B, Zhang X, et al. Study the Diffusion Characteristics of Rejuvenator Oil in Aged Asphalt Binder by Image Thresholding and GC—MS Tracer Analysis[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 249: 118782
Ma Y, Hu W, Polaczyk P A, et al. Rheological and Aging Characteristics of the Recycled Asphalt Binders with Different Rejuvenator Incorporation Methods[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 262: 121 249
Xu G, Wang H, Sun W. Molecular Dynamics Study of Rejuvenator Effect on RAP Binder: Diffusion Behavior and Molecular Structure[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2018, 158: 1046–1054
Wang F, Zhang L, Yan B, et al. Diffusion Mechanism of Rejuvenator and Its Effects on the Physical and Rheological Performance of Aged Asphalt Binder[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(24): 4130-
Kaseer F, Martin A E, Arámbula-Mercado E. Use of Recycling Agents in Asphalt Mixtures with High Recycled Materials Contents in the United States: A Literature Review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 211: 974–987
Li B, Yang J, Chen Z, et al. Microstructure Morphologies of Asphalt Binders Using Atomic Force Microscopy[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2016, 31(6): 1261–1266
Ding Y, Huang B, Shu X, et al. Use of Molecular Dynamics to Investigate Diffusion between Virgin and Aged Asphalt Binders[J]. Fuel, 2016, 174: 267–273
Li H, Zhang F, Feng Z, et al. Study on Waste Engine Oil and Waste Cooking Oil on Performance Improvement of Aged Asphalt and Application in Reclaimed Asphalt Mixture[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 276: 122 138
Funding
Funded by the Science and Technology Project of Henan Department of Transportation(No.2020J-2-3), Shaanxi Transportation Science and Technology Project (Nos.17-05K, 19-10K, 19-28K)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Yang, F., Zhang, F. et al. Diffusion and Regeneration Mechanism of Waste Composite Oils Rejuvenator in Aged Asphalt. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 36, 664–671 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-021-2458-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-021-2458-y