Abstract
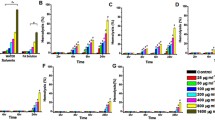
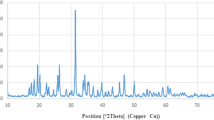
Colloidal semiconductor nanoparticles (quantum dots, QDs) have attracted a lot of interests in numerous biological and medical applications due to their potent fluorescent properties. However, the possible toxic effects of quantum dots remain an issue of debate. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the cytocompatibility of bovine serum albumin (BSA) conjugated zinc oxide QDs for C2C12 cells. In the experiment, ZnO QDs were synthesized by using BSA as the structure directing agent, and the morphology and crystal phase of ZnO QDs were determined by transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffractograms and Fourier transform infrared spectrograph techniques. The inverted fluorescence microscope results showed that ZnO QDs were distributed inside the cells. The toxicity of ZnO QDs was assessed by MTT methods, which revealed that ZnO QDs were highly cytocompatible in the concentration less than 200 µM. However, when the concentration of QDs was higher than 1 000 µM ZnO QDs showed significantly toxicity, which was ascribed to generation of free zinc and formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Furthermore, the morphological observations exhibited that cells treated with ZnO QDs showed altered morphology, depolymerized cytoskeleton and irregular-shaped nuclei. This study provides helpful guidances on the future safe use and manipulation of QDs to make them suitable tools in nanomedicine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rettberg P, Kloss M, Barczyk S, et al. Organic-inorganic Sol-gel Composites Incorporating Emiconductor Nanocrystals for Optical Gain Applications[J]. Adv. Mater., 2009, 21(17): 1 716–1720
Medintz I L, Uyeda H T, Goldman E R, et al. Quantum Dot Bioconjugates for Imaging, Labelling and Sensing[J]. Nat.Mater., 2005, 4(6): 435–446
Mattoussi H, Mauro J M, Goldman E R, et al. Self-assembly of CdSe-Zns Quantum Dot Bioconjugates Using an Engineered Recombinant Protein[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2000, 122(49): 12 142–12 150
Mobarraz M, Chaichi M J, Ganjali M R, et al. Functionalized ZnS Quantum Dots as Luminescent Probes for Detection of Amino Acids[J].Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc., 2012,96: 801–804
Zhang Q, Song C, Zhao T, et al. Photoluminescent Sensing for Acidic Amino Acids Based on the Disruption of Graphene Quantum Dots/Europium Ions Aggregates[J]. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 65: 204–210
Huang X, Li L, Qian H, et al. A Resonance Energy Transfer Between Chemiluminescent Donors and Luminescent Quantum-Dots as Acceptors (Cret)[J]. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 2006, 45(31): 5 140–5 143
Ghrera A S, Pandey M K, Malhotra B D. Quantum Dot Monolayer for Surface Plasmon Resonance Signal Enhancement and DNA Hybridization Detection[J]. Biosens. Bioelectron, 2016, 80: 477–482
Nguyen K C, Rippstein P, Tayabali A F, et al. Mitochondrial Toxicity of Cadmium Telluride Quantum Dot Nanoparticles in Mammalian Hepatocytes[J]. Toxicol. Sci., 2015, 146(1): 31–42
Mahto S K, Yoon T H, Rhee S W. A New Perspective on in Vitro Assessment Method for Evaluating Quantum Dot Toxicity by Using Microfluidics Technology[J]. Biomicrofluidics, 2010, 4(3): 727–731
Rzigalinski B A, Strobl J S. Cadmium-Containing Nanoparticles: Perspectives on Pharmacology and Toxicology of Quantum Dots[J]. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm., 2009, 238(3): 280–288
Hoshino A, Fujioka K, Oku T, et al. Physicochemical Properties and Cellular Toxicity of Nanocrystal Quantum Dots Depend on their Surface Modification[J]. Nano. Lett., 2014, 4(11): 2 163–2 169
Lovrić J, Bazzi H S, Cuie Y, et al. Differences in Subcellular Distribution and Toxicity of Green and Red Emitting CdTe Quantum Dots[J]. J. Mol. Med., 2005, 83(5): 377–385
Chang E, Yu W W, Colvin V L, et al. Quantifying the Influence of Surface Coatings on Quantum Dot Uptake in Cells[J]. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol., 2005, 1(4): 397–401
Jaiswal J K, Mattoussi H, Mauro J M, et al. Long-Term Multiple Color Imaging of Live Cells Using Quantum Dot Bioconjugates[J]. Nat. Biotechnol., 2002, 21(1): 47–51
Chan W C, Nie S. Quantum Dot Bioconjugates for Ultrasensitive Non-isotopic Detection[J]. Science, 1998, 281(5 385): 2 016–2 018
Fu R P, Sun F F, Chen K Z. Preparation and Fluorescent Property of ZnO Nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2007, 38: 2 076–2 078
Zhu Z M, Chen T L, Gu Y, et al. Zinc Oxide Nanowires Grown by Vapor-phase Transport Using Selected Metal Catalysts: Acomparative Study[J]. Chem. Mater., 2005, 17(16): 4 227–4 234
Li M, Zhai J, Liu H, et al. Electrochemical Deposition of Conductive Superhydrophobic Zinc Oxide Thin Films[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107(37): 9 954–9 957
Li M, Si X J. Research Progress on Preparation and Application of Zinc Oxide[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry and Technology, 2010, 1: 51–53
Cao Y, Wang HJ, Cao C, et al. Synthesis and Anti-ultraviolet Properties of Monodisperse BSA-conjugated Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles[J]. Mater. Lett., 2011, 66: 340–34
Wang H, Joseph J A. Quantifying Cellular Oxidative Stress by Dichlorofluorescein Assay Using Microplate Reader[J]. Free Radical. Bio. Med., 1999, 27: 612–616
An X L, Li Q Z, Liu H P, et al. FT-IR Study of the Interaction between Bovine Serum Albumins and Cetyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University (Natural Science), 2005, 30: 699–702
Ye Q, Hu R, Lin Z Y, et al. In situ ATR-FTIR Study on the Interaction of HA with Bovine Serum Albumin[J]. Chem. Res. Chinese U., 2006, 27: 1 552–1 554
Zhuang J, Chi Y H, Liu M. Preparation and Optic Properties of Water-Soluble Zno Quantum Dots[J]. Chem. J. Chinese U., 2007, 28(12): 2 246–2 251
Liu M, Zhang J, Chi Y H. Preparation and Luminescence Properties of Zno Quantum-Dots Capped with SiO2 in Dilute Water-Free Solution[J]. Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2006, 22(4): 651–655
Stohs S J, Bagchi D, Hassoun E, et al. Oxidative Mechanisms in the Toxicity of Chromium and Cadmium Ions[J]. J. Environ. Pathol. Tox., 2001, 20(2): 77–88
Wim W, Beyersmann D. Cadmium-Induced Apoptosis in C6 Glioma Cells: Influence of Oxidative Stress[J]. Biometals, 2004, 17(1): 65–78
Xu H, Qu F, Xu H, et al. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Antibacterial Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles on Escherichia Coli, O157:H7[J]. Biometals, 2012, 25(1): 45–53
Choi A O, Brown S E, Szyf M, et al. Quantum Dot-Induced Epigenetic and Genotoxic Changes in Human Breast Cancer Cells[J]. J. Mol. Med., 2008, 86(3): 291–302
Mahto S K, Park C, Yoon T H, et al. Assessment of Cytocompatibility of Surface-Modified Cdse/Znse Quantum Dots for Balb/3t3 Fibroblast Cells[J]. Toxicol. in Vitro, 2010, 24(4): 1 070–1 077
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the Chinese Medicine Science & Technology Foundation of Guangdong Province (No.20151257), Medical Science and Technology Development Foundation of Guangdong Province (No.A2016355), Excellent Young Scientist Training Foundation of Guangdong Province in 2014 (No.4CX16054G), Innovation Team Construction Foundationin Ordinary University of Guangdong Province (No.2015KCXTD022), Unique Innovation Foundation in Ordinary University of Guangdong Province (No.2015KTSCX049) and Undergraduate Science & Technology Innovation Foundation of Guangdong Province (Nos. 201610571041 and 201610571015)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Li, B., Zheng, B. et al. Assessment of Toxicity of BSA-conjugated Zinc Oxide Quantum Dots for C2C12 Cells. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 34, 736–743 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2111-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2111-1