Abstract
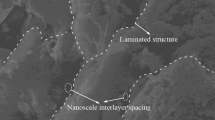
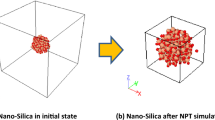
In order to inhibit and remove the thin ice and extend the lifetime of the damaged bridge, the self-healing mechanism and hydrophobic performance of asphalt modified by siloxane and polyurethane (ASP) were studied by dynamic shear rheology (DSR), fluorescence microscope (FM), atomic force microscope (AFM), the fracture-healing-re-fracture test and molecular simulations. The experimental results indicated that the self-healing capability of ASP increased with increasing heating time and temperature. Furthermore, the addition of siloxane could improve the reaction energy barrier and complex modulus, and it is believed that the self-healing is a viscosity driven process, consisting of two parts namely crack closure and properties recovery. Contact angle of ASP increased with the increasing siloxane content and it deduced that the siloxane could improve the hydrophobic performance of ASP and the ASP molecule model could simulate well the self-healing mechanism and hydrophobic performance of ASP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
VRIES I J D, POLDER R B. Hydrophobic Treatment of Concrete[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 1997, 11(4): 259–265
TITTARELLI F, MORICONI G. The Effect of Silane-based Hydrophobic Admixture on Corrosion of Galvanized Reinforcing Steel in Concrete[J]. Corrosion Science, 2010, 52(9): 2 958–2 963
MEDEIROS M, HELENE P. Efficacy of Surface Hydrophobic Agents in Reducing Water and Chloride Ion Penetration in Concrete[J]. Materials and Structures, 2008, 41(1): 59–71
LIU Z, HANSEN W. Effect of Hydrophobic Surface Treatment on Freeze-thaw Durability of Concrete[J]. Cement & Concrete Composites, 2016, 69: 49–60
LIU W, XU K, WANG C, et al. Carbon Nanofibers Reinforced Soy Polyol-based Polyurethane Nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2016, 3(3): 1–10
GWON J G, KIM S K, KIM J H. Development of Cell Morphologies in Manufacturing Flexible Polyurethane Urea Foams as Sound Absorption Materials[J]. Journal of Porous Materials, 2016, 23(2): 1–9
SONEBI M. Factorial Design Modelling of Mix Proportion Parameters of Underwater Composite Cement Grouts[J]. Cement & Concrete Research, 2001, 31(11): 1 553–1 560
LACHEMI M, HOSSAIN K M A, LAMBROS V, et al. Performance of New Viscosity Modifying Admixtures in Enhancing the Rheological Properties of Cement Paste[J]. Cement & Concrete Research, 2004, 34(2): 185–193
SUN D, HU J, ZHU X. Size Optimization and Self-healing Evaluation of Micro-capsules in Asphalt Binder[J]. Colloid and Polymer Science, 2015, 293(12): 3 505–3 516
HUANG L, TAN L, ZHENG W. Renovated Comprehensive Multilevel Evaluation Approach to Self-Healing of Asphalt Mixtures[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 16(1): B4014 002
SUN D, LIN T, ZHU X, et al. Calculation and Evaluation of Activation Energy as a Self-healing Indication of Asphalt Mastic[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2015, 95(2): 431–436
áLVARO G, SCHLANGEN E, VEN M V D, et al. A Simple Model to Define Induction Heating in Asphalt Mastic[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2012, 31(6): 38–46
QIU J, VEN M, WU S, et al. Evaluating Self Healing Capability of Bituminous Mastics[J]. Experimental Mechanics, 2012, 52(8): 1 163–1 171
QIU J, VEN M, WU S P, et al. Investigating Self-Healing Behaviour of Pure Bitumen Using Dynamic Shear Rheometer[J]. Fuel, 2011, 90(8): 2 710–2 720
CHEN Y, SIMMS R, KOH C, et al. Development of a Test Method for Evaluation and Quantification of Healing in Asphalt Mixture[J]. Road Materials & Pavement Design, 2013, 14(4): 901–920
CORDIER P, TOURNILHAC F, SOULIE-ZIAKOVIC C, et al. Self-healing and Thermoreversible Rubber from Supra-molecular Assembly[J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7181): 977–980
WHITE S R, SOTTOS N R, GEUBELLE P H, et al. Autonomic Healing of Polymer Composites[J]. Nature, 2001, 409(6 822): 794
áLVARO G. Self-healing of Open Cracks in Asphalt Mastic[J]. Fuel, 2012, 93(1): 264–272
JONES F R, ZHANG W, HAYES S A. Thermally Induced Self Healing of Thermosetting Resins and Matrices in Smart Composites[M]. Amstel dam: Springer Netherlands, 2007
VAN D Z, RIVERA P, DINGEMANS T. Modern Materials for Aerospace Applications[D]. Delft: Delft University of Technology, 2007
SMITH K A, SANDEEP T A, BALAZS A C. Healing Surface Defects with Nanoparticle-Filled Polymer Coatings: Effect of Particle Geometry[J]. Macromolecules, 2005, 38(24): 10 138–10 147
SANTAGATA E, BAGLIERI O, TSANTILIS L, et al. Evaluation of Self Healing Properties of Bituminous Binders Taking into Account Steric Hardening Effects[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2013, 41(41): 60–67
LIU Q, SCHLANGEN E, VEN M, et al. Evaluation of the Induction Healing Effect of Porous Asphalt Concrete Through Four Point Bending Fatigue Test[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2012, 29(4): 403–409
LIU Q, SCHLANGEN E, VEN M. Induction Healing of Porous Asphalt Concrete Beams on an Elastic Foundation[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2013, 25(7): 880–885
LIU Q, WU S, SCHLANGEN E. Induction Heating of Asphalt Mastic for Crack Control[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2013, 41(41): 345–351
TANG J, LIU Q, WU S, et al. Investigation of the Optimal Self-healing Temperatures and Healing Time of Asphalt Binders[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2016, 113: 1 029–1 033
ZHOU X X, Wu S, LIU G, et al. Molecular Simulations and Experimental Evaluation on the Curing of Epoxy Bitumen[J]. Materials & Structures., 2016, 49(1–2): 241–247
ZHOU X X, ZHANG X, XU S, et al. Evaluation of Thermo-mechanical Properties of Graphene/carbon- Nanotubes Modified Asphalt with Molecular Simulation[J]. Molecular Simulation, 2017, 43(4): 312–319
DU Y, LI F, WANG S, et al. Inhibition and Removal of Thin Ice on the Surface of Asphalt Pavements by Hydrophobic Method[J]. Journal of Testing & Evaluation, 2016, 44(2): 20 150 106
MEDEIROS M, HELENE P. Efficacy of Surface Hydrophobic Agents in Reducing Water and Chloride Ion Penetration in Concrete[J]. Materials and Structures, 2008, 41(1): 59–71
KAELBLE D H, MOACANIN J. A Surface Energy Analysis of Bio-adhesion[J]. Polymer, 1977, 18(5): 475–482
YANG J M, LIN H T. Wettability and Protein Adsorption on HT-PB-based Polyurethane Films[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2001, 187(1–2): 159–169
LIU Z, HANSEN W. Effect of Hydrophobic Surface Treatment on Freeze-thaw Durability of Concrete[J]. Cement & Concrete Composites, 2016, 69: 49–60
VRIES I J D, POLDER R B. Hydrophobic Treatment of Concrete[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 1997, 11(4): 259–265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51808329) and Science and Technology Department of Shanxi Province International Cooperation (No. 201603D421027) and the Special Project of Commercialization of Shanxi Province Research Foundation (No.201804D131034)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Sun, B., Wu, S. et al. Evaluation on Self-healing Mechanism and Hydrophobic Performance of Asphalt Modified by Siloxane and Polyurethane. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 34, 630–637 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2097-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2097-8