Abstract
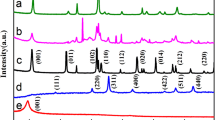
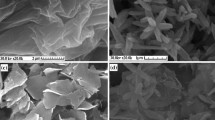
Novel visible light magnetically separable graphene-based BiOBr composite photocatalysts were prepared for the first time. The structures, morphologies and optical properties were characterized by field emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, respectively. The photocatalytic activity of the resulting samples was evaluated by degradation of tetracycline under visible light irradiation. An appropriate amount of introduced graphene can significantly enhance the photocatalytic activities. The enhanced activities were mainly attributed to the enhanced light absorption and the interfacial transfer of electrons. The corresponding photocatalytic mechanism was proposed based on the results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Y L, Liu Y M, Wang J S, et al. Titanium Alkoxide Induced BiOBr-Bi2WO6 Mesoporous Nanosheet Composites with Much Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(27): 7 949–7 956
Ao Y H, Xu J L, Wang P F, et al. Preparation of CdS Nanoparticle Loaded Flower-like Bi2O2CO3 Heterojunction Photocatalysts with Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity[J]. Dalton T, 2015, 44(25): 11 321–11 330
Cao M H, Wang P F, Ao Y H, et al. Visible Light Activated Photocatalytic Degradation of Tetracycline by a Magnetically Separable Composite Photocatalyst: Graphene Oxide/Magnetite/Cerium-doped Titania[J]. J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2016, 467: 129–139
Daimon T, Nosaka Y. Formation and Behavior of Singlet Molecular Oxygen in TiO2 Photocatalysis Studied by Detection of Near-infrared Phosphorescence[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111: 4 420–4 424
Nosaka Y, Daimon T, Nosaka A Y, et al. Singlet Oxygen Formation in Photocatalytic TiO2 Aqueous Suspension[J]. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2004, 6: 2 917–2 918
Zhang J, Shi F J, Lin J, et al. Self-Assembled 3-D Architectures of BiOBr as a Visible Light-Driven Photocatalyst[J]. Chem. Mater., 2008, 39: 2 937–2 941
Guo Y, Huang H, He Y, et al. In Situ Crystallization for Fabrication of Core-satellites Structured BiOBr-CdS Heterostructure with an Excellent Visible-Light-Responsive Photoreactivity[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(27): 11 702–11 711
Xia J X, Di J, Yin S, et al. Facile Fabrication of the Visible-light-driven Bi2WO6/BiOBr Composite with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity[J]. Rsc Adv., 2013, 4: 82–90
Cui W Q, An W J, Liu L, et al. Novel Cu2O Quantum Dots Coupled Flower-like BiOBr for Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Contaminant[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2014, 280: 417–427
Ye L Q, Liu J Y, Jiang Z, et al. Facets Coupling of BiOBr-g-C3N4 Composite Photocatalyst for Enhanced Visible-light-driven Photocatalytic Activity[J]. Appl. Cataly. B Environ., 2013, 142(10): 1–7
Wang X J, Yang W Y, Li F T, et al. Construction of Amorphous TiO2/BiOBr Heterojunctions via Facets Coupling for Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity [J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2015, 293: 126–136
Du Q Q, Wang W P, Wu Y Z, et al. Novel Carbon Dots/BiOBr Nanocomposites with Enhanced UV and Visible Light Driven Photocatalytic Activity[J]. Rsc Adv., 2015, 5: 31 057–31 063
Geim A K, Novoselov K S. The Rise of Graphene[J]. Nat. Mater., 2007, 6: 183–191
Wang Y J, Liu J C, Lei L, et al. High-quality Reduced Graphene Oxide-nanocrystalline Platinum Hybrid Materials Prepared by Simultaneous Co-reduction of Graphene Oxide and Chloroplatinic Acid[J]. Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2011, 6: 1–8
Neto A H C, Guinea F, Peres N M R, et al. The Electronic Properties of Graphene[J]. Rev. Mod. Phys., 2007, 81: 109–162
Watson S, Beydoun D, Amal R. Synthesis of a Novel Magnetic Photocatalyst by Direct Deposition of Nanosized TiO2 Crystals onto a Magnetic Core[J]. J. Photoch. Photobio. A, 2002, 148: 303–313
Ao Y H, Xu J J, Fu D, et al. Photocatalytic Degradation of X-3B by Titania-coated Magnetic Activated Carbon under UV and Visible Irradiation[J]. J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 471: 33–38
Cao C H, Xiao L, Chen C H, et al. Magnetically Separable Cu2O/Chitosan-Fe3O4 Nanocomposites: Preparation, Characterization and Visible-light Photocatalytic Performance[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 333: 110–118
Wang C, Cao M H, Wang P F, et al. Preparation of a Magnetic Graphene Oxide-Ag3PO4 Composite Photocatalyst with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity under Visible Light Irradiation[J]. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E, 2013, 45: 1 080–1 086
Wang L, Wei H G, Fan Y J, et al. One-Dimensional CdS/α-Fe2O3 and CdS/Fe3O4 Heterostructures: Epitaxial and Nonepitaxial Growth and Photocatalytic Activity[J]. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113: 14 119–14 125
Kong L, Jiang Z, Xiao T C, et al. Exceptional Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Activity over BiOBr-ZnFe2O4 Heterojunctions[J]. Chem. Commun., 2011, 47: 5 512–5 514
Wang P F, Ao Y H, Wang C, et al. A One-pot Method for the Preparation of Graphene-Bi2MoO6 Hybrid Photocatalysts that Are Responsive to Visible-Light and Have Excellent Photocatalytic Activity in the Degradation of Organic Pollutants[J]. Carbon, 2012, 50: 5 256–5 264
Ai L H, Zhang C Y, Chen Z L. Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution by a Solvothermal-Synthesized Graphene/Magnetite Composite[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 192: 1515–1524
Yang Z P, Gong X Y, Zhang C J. Recyclable Fe3O4/Hydroxyapatite Composite Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic Applications[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2010, 165: 117–121
Shang M, Wang W Z, Zhang L. Preparation of BiOBr Lamellar Structure with High Photocatalytic Activity by CTAB as Br Source and Template[J]. J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 167: 803–809
Ng Y H, Iwase A, Bell N J, et al. Semiconductor/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites Derived from Photocatalytic Reactions[J]. Catal. Today, 2011, 164: 353–357
Zhou F, Shi R, Zhu Y F. Significant Enhancement of the Visible Photocatalytic Degradation Performances of γ-Bi2MoO6 Nanoplate by Graphene Hybridization[J]. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2011, 340: 77–82
Nguyen-Phan T D, Pham V H, Shin E W, et al. The Role of Graphene Oxide Content on the Adsorption-Enhanced Photocatalysis of Titanium Dioxide/Graphene Oxide Composites[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2011, 170: 226–232
Wang X W, Tian H W, Yang Y, et al. Reduced Craphene Oxide/CdS for Efficiently Photocatalystic Degradation of Methylene Blue[J]. J. Alloys Compd., 2012, 524: 5–12
Ao Y H, Wang D D, Wang P F, et al. A BiOBr/Co-Ni Layered Double Hydroxide Nanocomposite with Excellent Adsorption and Photocatalytic Properties[J]. Rsc Adv., 2015, 5: 54 613–54 621
Marschall, Roland. Semiconductor Composites: Strategies for Enhancing Charge Carrier Separation to Improve Photocatalytic Activity[J]. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24: 2 421–2 440
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Funded by National Science Funds for Creative Research Groups of China (No.51421006), Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (No. IRT13061), the National Science Fundation of China for Excellent Young Scholars (No. 51422902), the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41430751), National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 51225901), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51579073), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No.BK20141417), Fundamental Research Funds (No. 2016B43814), and PAPD
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, T., Wang, P. & Ao, Y. Novel Visible Light Driven Magnetically Separable Graphene/BiOBr Composite Photocatalysts with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 34, 521–526 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2082-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2082-2