Abstract
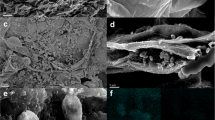
Bio-ceramsite technology is one of the most effective technologies in the pretreatment of drinking water. In this work, bio-ceramsite was fabricated by Citrobacter freundii (C. freundii) immobilization on the ceramsite. The findings of the current study suggest that the bio-ceramites showed biosorption abilities for Cd(II) and Pb(II) and the removal efficiency for Pb(II) is lower than Cd(II). The adsorption mechanism can be attributed to electrostatic attraction and covalent bond. The morphology of the cells changed after the adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) due to the dissociation of the assembly of peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide. The fluorescence polarization has shown a significant decrease in membrane fluidity and an increase of permeability of cell membrane. The spectral profile of C. freundii suggests the alteration of carbonyl, amide and phosphonic groups on the cell membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mulligan C N, Yong R N, Gibbs B F. Remediation Technologies for Metal-contaminated Soils and Groundwater: an Evaluation [J]. Engineering Geology, 2001, 60(1–4): 193–207
Chen Y D, Zhang W G, Ma H L. A Magnetic Record of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Yangtze River Subaqueous Delta[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 476–477: 368–377
Stanislav V, Tomas R K. Biosorption of Cd2+ and Zn2+ by Cell Surface-engineered Saccharomyces Cerevisiae[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2006, 60(2): 96–102
Veronica L C, Liliana B V, Carlos M A. Indigenous Microorganisms as Potential Bioremediators for Environments Contaminated with Heavy Metals [J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2012, 69: 28–37
Hussein H, Farag S, Moawad H. Isolation and Characterization of Pseudomonas Resistant to Heavy Metals Contaminants[J]. Arab J. Biotechnol, 2004, 7(1): 13–22
Hussein H, Farag S, Kandeel K. Biosorption of Heavy Metals from Waste Water Using Pseudomonas Sp [J]. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 7(1): 38–46
Meunier N, Laroulandie J, Blais J F. Cocoa Shells for Heavy Metal Removal from Acidic Solutions[J]. Bioresour. Technol, 2003, 90(3): 255–263
Volesky B, Holan Z R. Biosorption of Heavy Metals[J]. Biotechnol. Prog., 1995, 11(3): 235–250
Li H D, Liu T, Li Z. Low-cost Supports Used to Immobilize Fungi and Reliable Technique for Removal Hexavalent Chromium in Wastewater[J]. Bioresour. Technol., 2008, 99(7): 2 234–2 241
Cheng J, Jia L Y, Zhang B. Comparison of Quartz sand, Anthracite, Shale and Biological Ceramsite for Adsorptive Removal of Phosphorus from Aqueous Solution[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 26(2): 466–477
Ahlberg G, Gustafsson O, Wedel P. Leaching of Metals from Sewage Sludge During One Year and Their Relationship to Particle Size [J]. Environ. Pollut., 2006, 144(2): 545–553
Fuliana A, Conesa J A, Font R. Formation and Destruction of Chlorinated Pollutants During Sewage Sludge Incineration[J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2004, 38(10): 2 953–2 958
David A A, Juliet S S, Jennifer E S. The Effect of High Ionic Strength on Neptunium (V) Adsorption to a Halophilic Bacterium[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta., 2013, 110(1): 45–57
Liu J Y, Duan C, Zhou J Z. Adsorption of Bacteria onto Layered Double Hydroxide Particles to Form Biogranule-like Aggregates[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2013, 75–76: 39–45
Chen L S, Colemen W G. Cloning and Characterization of the Escherichia coli K-12 rfa-2 (rfaC) Gene, a Gene Required for Lipopolysaccharide Inner Core Synthesis[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 1993, 175(9): 2 534–2 540
Sharma P K, Rao K H. Analysis of Different Approaches for Evaluation of Surface Energy of Microbial Cells by Contact Angle Goniometry[J]. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2002, 98(3,5): 341–463
Trevors J T. Fluorescent Probes for Bacterial Cytoplasmic Membrane Research[J]. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods, 2003, 57(2): 87–103
Denich T J, Beaudette L A, Cassidy M B. Membrane Fluidity of the Pentachlorophenol-mineralizing Sphingomonas Sp [J]. J. Eluor., 2003, 13(5): 385–391
Naumann D, Shultz C, Sabisch A. New Insights into the Phase Behaviour of a Complex Anionic Amphiphile: architecture and Dynamics of Bacterial Deep Rough Lipopolysaccharide Membranes as Seen by FTIR, X-ray, and Molecular Modelling Techniques [J]. J. Mol. Struct., 1989, 214: 213–246
Kacurakova M, Mathlouthi M. FTIR and Laser-Raman Spectra of Oligosaccharides in Water: Characterization of the Glycosidic Bond [J]. Carbohydr. Res., 1996, 284(2): 145–157
Kinder R, Ziegler C, Wessels J M. Gamma-irradiation and UV-C Lightinduced Lipid Peroxidation: a Fourier Transform-infrared Absorption Spectroscopic Study [J]. Int. J. Radiat. Biol., 1997, 71(5): 561–571
Naumann D. FT-Infrared and FT-Raman Spectroscopy in Biomedical Research[J]. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev., 2001, 36(2–3): 239–298
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2012AA100604)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Sun, K., Qi, X. et al. The fabrication of bio-ceramsite for the removal of heavy metals and its toxicity to bacteria. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 30, 649–654 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-015-1205-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-015-1205-7