Abstract
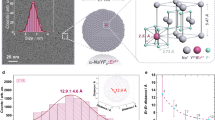
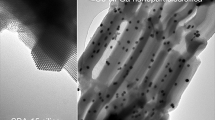
Memory effect has been studied in the system using magnetic nanoparticles with Ni nanocore encapsulated by non-magnetic and oxidation-resistant Ni2P nanoshell acquired through surface-phosphatizing Ni nanoparticles. The self-assembled array with interparticle spacing of about 6 nm shows memory effect up to 200 K below its average blocking temperature of 260 K. And reducing the interparticle spacing of the self-assembled array via annealing can further enlarge the temperature range of memory effect up to room-temperature. The memory effect can be understood based on the thermal relaxation theory of single-domain magnetic nanoparticles. Furthermore, the read-write magnetic coding is realized based on the temperature changes, using the memory effect up to room-temperature, which may be useful for future memory devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S D Bader. Colloquium: Opportunities in Nanomagnetism[J]. Rev. Mod. Phys., 2006, 78(1): 1–15
Y W Jun, J W Seo, J Cheon. Nanoscaling Laws of Magnetic Nanoparticles and Their Applicabilities in Biomedical Sciences[J]. Acc. Chem. Res., 2008, 41(2): 179–189
Y Sun, M B Salamon, K Garnier, et al. Memory Effects in an Interacting Magnetic Nanoparticle System[J]. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2003, 91(16): 167 206
S Chakraverty, M Bandyopadhyay, S Chatterjee, et al. Memory in a Magnetic Nanoparticle System: Polydispersity and Interaction Effects[J]. Phys. Rev. B, 2005, 71(5): 054 401
W Z Wang, J J Deng, J Lu, et al. Memory Effect in a System of Zincblende Mn-rich Mn(Ga)As Nanoclusters Embedded in GaAs[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, 91(20): 202 503
J Park, E Kang, S U Son, et al. Monodisperse Nanoparticles of Ni and NiO: Synthesis, Characterization, Self-Assembled Superlattices, and Catalytic Applications in the Suzuki Coupling Reaction[J]. Adv. Mater., 2005, 17(4): 429–434
H P Shao, Y Q Huang, H S Lee, et al. Cobalt Nanoparticles Synthesis from Co(CH3COO)2 by Thermal Decomposition[J]. J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2006, 304(1): e28–e30
P Li, J G Guan, Q J Zhang, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Monodisperse Nickel Nanoparticles by Polyol Process[J]. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2005, 20(4): 35–37
X F Zheng, S L Yuan, Z M Tian, et al. Nickel/Nickel Phosphide Core-Shell Structured Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Chemical, and Magnetic Architecture[J]. Chem. Mater., 2009, 21(20): 4 839–4 845
S J Jang, W J Kong, H Zeng. Magnetotransport in Fe3O4 Nanoparticle Arrays Dominated by Noncollinear Surface Spins[J]. Phys. Rev. B, 2007, 76(21): 212 403
H T Yang, D Hasegawa, M Takahashi, et al. Achieving a Noninteracting Magnetic Nanoparticle System Through Direct Control of Interparticle Spacing[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, 94(1): 013 103
L Néel. Théorie Du Traínage Magnétique Des Ferromagnétiques En grains Fins Avec Application Aux Terres Cuites[J]. Ann. Géophys., 1949, 5: 99–136
W F Brown. Thermal Fluctuations of a Single-Domain Particle[J]. Phys. Rev., 1963, 130(5): 1 677–1 686
C J Bae, S Angappane, J G Park, et al. Experimental Studies of Strong Dipolar Interparticle Interaction in Monodisperse Fe3O4 Nanoparticles[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, 91(10): 102 502
V Singh, M S Seehra, J Bonevich. Nickel-silica Nanocomposite: Variation of the Blocking Temperature with Magnetic Field and Measuring Frequency[J]. J. Appl. Phys., 2008, 103(7): 07D 524
F Wang, J Kim, Y J Kim, et al. Spin-glass Behavior in LuFe2O4[J]. Phys. Rev. B, 2009, 80(2): 024 419
W C Nunes, E D Biasi, C T Meneses, et al. Magnetic Behavior of Ni Nanoparticles with High Disordered Atomic Structure[J]. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 92(18): 183 113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11174092)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, H., Yuan, S., Zheng, X. et al. Memory effect up to room-temperature in Ni/Ni2P core-shell structured nanoparticles. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 28, 467–470 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-013-0714-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-013-0714-5