Abstract
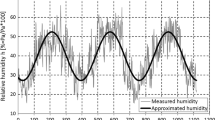
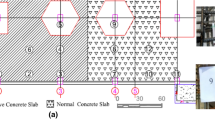
Shrinkage strain of concrete specimen with different reinforcement configuration was measured at various depths from the exposed surface by using several pairs of displacement sensors. Only one surface of the concrete specimen was exposed to dry condition during the experiment. The results show that differential shrinkage strain occurs in both plain and steel reinforced concrete specimens according to depths from the exposed surface. A higher reinforcement ratio results in a greater restraint against shrinkage of concrete nearby reinforcement rebar and a worse differential shrinkage strain distribution in the concrete specimen. The restraint against shrinkage of concrete becomes lower with the increasing distance from reinforcement rebar. Under the same reinforcement arrangement, a higher free shrinkage of concrete leads to a stronger restraint against shrinkage and a higher shrinkage stress formation in local concrete. The relationship between shrinkage strain and reduction of relative humidity in reinforced concrete structure is far different from that in plain concrete.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C M Aldea, S P Shah, A Karr. Permeability of Cracked Concrete[J]. Materials and Structures, 1999, 32(5): 370–376
A D Jensen, S Chatterji. State of the Art Report on Micro-cracking and Lifetime of Concrete-Part I [J]. Materials and Structures, 1996, 29(1): 3–8
H R Samaha, K C Hover. Influence of Microcracking on the Mass Transport Properties of Concrete[J]. ACI Materials Journal, 1992, 89(4): 416–424
R Bloom, A Bentur. Free and Restrained Shrinkage of Normal and High-performance Concretes[J]. ACI Materials Journal, 1995, 92(2): 211–217
S P Shah, C Ouyang, S Marikunte, et al. A Method to Predict Shrinkage Cracking of Concrete [J]. ACI Materials Journal, 1998, 95(4): 339–346
Z He, X Zhou, Z Li. New Experimental Method for Studying Early-age Cracking of Cement-based Materials[J]. ACI Materials Journal, 2004, 101(1): 50–56
B Persson. Eight-year Exploration of Shrinkage in High-performance Concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2002, 32(8): 1 229–1 237
M H Zhang, C T Tam, M P Leow. Effect of Water-to-cementitious Materials Ratio and Silica Fume on the Autogenous Shrinkage of Concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2003, 33(10): 1 687–1 694
C Andrade, J Sarría, C Alonso. Relative Humidity in the Interior of Concrete Exposed to Natural and Artificial Weathering[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1999, 29(8): 1 249–1 259
J H Moon, J Weiss. Estimating Residual Stress in the Restrained Ring Test under Circumferential Drying[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2006, 28(5): 486–496
J K Kim, C S Lee. Prediction of Differential Drying Shrinkage in Concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1998, 28(7): 985–994
M Sule, K V Breugel. The Effect of Reinforcement on Early-age Cracking due to Autogenous Shrinkage and Thermal Effects[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2004, 26(5): 581–587
X J Gao, X F Kan, Y Z Yang. Shrinkage Distribution of Concrete with One Surface Exposed to Dry Condition[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2009, 37(1):87–91(in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.50408016) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. HIT. NSRIF.201198)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, X., Qu, G. & Zhang, A. Influences of reinforcement on differential drying shrinkage of concrete. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 27, 576–580 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-012-0508-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-012-0508-1