Abstract
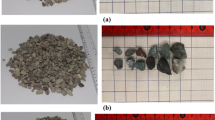
A new form of foam cement was produced by mixing alkali-activated slag, clay, a small amount of polypropylene fibers with prepared foam during stirring. The preparation of the material is quite different from the normal one, which is produced just at room temperature and without baking. The fabrication of this energy-saving and low-price material can be favorable for lowering carbon emission by using recycled industrial wastes. Thermal conductivity of 0.116 W/(m·k), compressive strength of 3.30 MPa, flexural strength of 0.8 MPa and density of 453 kg/m3 can be achieved after 28 days aging. The hydration product is C-S-H with less Ca(OH)2, calcium aluminum and zeolite, which was characterized by X-ray diffraction(XRD) measurement. This prospective foam cement may be expected to be an excellent economical energy-saving building material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F K Akthar, J R G Evans. High Porosity(>90%) Cementitious Foams[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2010, 40(2): 352–358
Guoqiang Li, Venkata D, Muthyala. A Cement Based Syntactic Foam[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 478(1–2): 77–86
Rongxi Shen, Qi Cui, Qinghai Li. New Type Fibre Reinforced Cement-Based Composites[M]. Beijing: China Building Material Industry Publishing House, 2004
Chaosheng Tang, Bin Shi, Wei Gao, et al. Stength and Mechanical Behavior of Short Polypropylene Fiber Reinforced and Cement Stabilized Clayey Soil[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembrances, 2007, 25: 194–202
F. Puertas, T Amat, A Fernandez-Jimenez, et al. Mechanical and Durable Behaviour of Alkaline Cement Mortars Reinforced with Polypropylene Fibres[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2003, 33(12): 2 031–2 036
Nangru Yang. Basement of Physical and Chemical for the Formation of Alkali-Activated Cementious MaterialI[J]. Journal of Chiness Ceramic Society, 1996, 24(2): 209–215
P I A Malek, D M Roy. Alkali Activated Geopolymer[C]. Tenth International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement, 1997
A JUST, B Middendorf. Microstructure of High-Strength Foam Concrete[J]. Materials Characterization, 2009, 60(7): 741–748
E K Kunhanandan Nambiar, K Ramamurthy. Influence of Filler Type on the Properties of Foam Concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2006, 28(5): 475–480
Wang Lijiu. Building Material[M]. Beijing: China Waterpower Press, 2008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the Ministry of Science & Technology of China(No.2006BAJ04A04)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Tan, X. Preparation and properties of alkali activated foam cement reinforced with polypropylene fibers. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 26, 960–964 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0345-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0345-7