Abstract
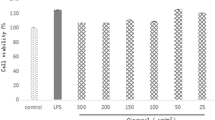
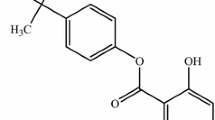
The anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of Usnic acid (UA) were explored on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cell line. The effects of UA on pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor-alfa (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), pro-inflammatory mediators such as nitric oxide (NO), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) were studied by sandwich ELISA, real-time PCR and western blot analyses. Similarly, the effect of UA on anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10) and anti-inflammatory mediator heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) were also studied following the same methods. Furthermore, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) was assayed by immunocytochemistry. The results showed that UA has anti-inflammatory effect by down-regulatinng iNOS, COX-2, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α, COX-2 gene expression through the suppression of NF-κB activation and increasing anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and anti-inflammatory mediator HO-1 production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cocchietto M N, Skert. A Review on Usnic Acid, an Interesting Natural Compound [J]. Naturwissenschaften, 2002,89(4): 137–146
Elo H, Matikainen J. Potent Activity of the Lichen Antibiotic (+)-Usnic Acid Against Clinical Isolates of Vancomycinresistant Enterococci and Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Aureus[J]. Naturwissenschaften, 2007, 94(6): 465–468
Dofferhoff A S, Vellenga E. Tumor Necrosis Factor (cachectin) and Other Cytokines in Septic Shock: A Review of the Literature [J]. Neth. J. Med., 1991, 39(1–2): 45–62
Kremer J P, Jarrar D. Interleukin-1, -6 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Release is Down-regulated in Whole Blood from Septic Patients [J]. Acta Haematol, 1996, 95(3–4): 268–273
Kamdar S J, Chapoval A I. Differential Sensitivity of Mouse Mononuclear Phagocytes to CSF-1 and LPS: the Potential in Vivo Relevance of Enhanced IL-6 Gene Expression [J]. Cell Immunol., 1996, 174(2): 165–172
Tanaka N, Hoshino Y. Interleukin-10 Induces Inhibitory C/EBPbeta through STAT-3 and Represses HIV-1Transcription in Macrophages[J]. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol., 2005, 33(4): 406–411
Rajakariar R, Yaqoob M M. COX-2 in Inflammation and Resolution [J]. Mol. Interv., 2006, 6(4): 199–207
Kulmatycki K M, Jamali F. Drug Disease Interactions: Role of Inflammatory Mediators in Disease and Variability in Drug Response [J]. J. Pharm. Pharm Sci., 2005, 8(3): 602–625
Hansson G K, Robertso A K. Inflammation and Atherosclerosis [J]. Annu. Rev. Pathol., 2006, 1: 297–329
Kwak H J, Song J S. The Inhibitory Effects of Roflumilast on Lipopolysaccharide-induced Nitric Oxide Production in RAW264.7 Cells Are Mediated by Heme Oxygenase-1 and Its Product Carbon Monoxide [J]. Inflamm. Res., 2005, 54(12): 508–513
Makarov S S. NF-kappa B as a Therapeutic Target in Chronic Inflammation: Recent Advances[J]. Mol. Med. Today, 2000, 6(11): 441–448
Lawrence T, Gilroy D W. Possible New Role for NF-kappa B in the Resolution of Inflammation [J]. Nat. Med., 2001, 7(12): 1 291–1 297
Tak P P, Firestein G S. NF-kappa B: a Key Role in Inflammatory Diseases [J]. J. Clin. Invest., 2001, 107(1): 7–11
Kim J S, Jobin C. Role of NF-kappa B in Inflammatory Disorders: Just When You Thought You Knew Everything [J]. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol Nutr., 2004, 38(1): 109–110
Kano Y M, Akutsu. In Vitro Cytotoxic Effects of Fludarabine (2-F-ara-A) in Combination with Commonly Used Anti Leukemic Agents by Isobologram Analysis [J]. Leukemia, 2000, 14(3): 379–388
Shaamash A H, Elsonosy E D. Placental Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) Activity and Nitric Oxide (NO) Production in Normal Pregnancy, Pre-eclampsia and Eclampsia[J]. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet., 2001, 72(2): 127–133
Specht K T, Richter. Quantitative Gene Expression Analysis in Micro Dissected Archival Tissue by Real-time RT-PCR [J]. J. Mol. Med., 2000, 78(7): B27–B30
Fuseler J W, Conner E M. Cytokine and Nitric Oxide Production in the Acute Phase of Bacterial Cell Wall-induced Arthritis [J]. Inflammation, 1997, 21(1): 113–131
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Zheng, G., Tao, J. et al. Anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of usnic acid. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 26, 955–959 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0344-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0344-8