Abstract
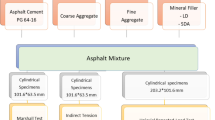
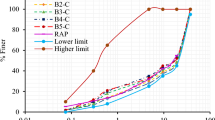
For determining the optimal percentage of RAP material in central plant hot recycling, binder was recovered from RAP by means of Abson recovery method, and properties tests of mixed binders consisting of recovered asphalt and fresh asphalt at different ratios were performed. In addition, the performances of mixture with different percentages of RAP such as rutting resistance, anti-cracking, moisture susceptibility and fatigue resistance were tested. The binder test results showed that the high temperature performance was improved with the increase of the percentage of the RAP, while the low temperature performance was declined. When the percentage of the recovered binder was less than 30%, the mixed binder could match the technical standards for fresh asphalt. Tests on the mixtures showed that rutting resistance increased gradually as RAP percentage increased, while thermal anti-cracking at low temperature and fatigue properties declined. The effect of the percentage of RAP on moisture susceptibility was limited. It is indicated that low temperature performance and fatigue properties are important for selecting the optimal percentage of RAP. Based on data obtained from binders and mixtures, it is concluded that the maximum percentage of RAP is approximately 30% without the addition of rejuvenating agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Richard R Davison. Basic Asphalt Recycling Manual[M]. US, Asphalt Recycling and Reclaiming Association, 2001: 33–45
Prithvi S Kandhal, Rajib B Mallick. FHWA-SA-98-042. Pavement Recycling Guidelines for State and Local Governments Participant’s Reference Book[S]. Washington, US Dept. of Transportation, 1997
Ren Shuan-zhe, Wang Yong-qi, Yin Ran. The Research on Recycled Asphalt Mixture Design[J]. Highway Traffic Science and Technology, 2007, (10): 35–39
Paul H R. Evaluation of Recycled Projects for Performance[M]. Baton Rouge: lLouisiana Transportation Research Center, 1998: 82–91
Xiong Chu-hua, Ling Tian-qing, Zhang Yong-xing, Wu Zhi-hui. The Use of Central Plant Hot Recycling Technology in Chengdu-Chongqing Highway Maintenance Project[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2008, (2): 193–197
Shen Jin-an, Li Fu-pu. JTG 052-2000. Standard Test Methods of bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering[S]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2000
Wu Zan-ping. The Performance Analysis and Evaluation Method Study of Huning Freeway Road Surface[R]. Nanjing, 2007: 93–97
Shen Jin-an, Li Fu-pu, Chen jing. JTG F40-2004. Technical Specifications For Construction Of Highway Asphalt Pavement[S]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2004
Yetkin Yildirim. Superpave Mix Design(SP-2)[M]. Kentucky, Asphalt Institute, 2001: 87–96
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Li, Y. Optimal percentage of reclaimed asphalt pavement in central plant hot recycling mixture. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 25, 659–662 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-010-0065-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-010-0065-4