Abstract
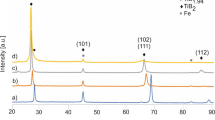
A stainless steel/10wt%TiC nanocomposite particles were prepared by high-energy ball-milling method using stainless steel, carbon and titanium as raw materials. The evolution of phase composition, microstructure and specific surface area of the stainless steel/TiC nanocomposite particles with increasing ball-milling time in the range of 0–100 h were investigated by XRD, SEM, TEM and BET techniques. The results showed that the stainless steel/TiC nanocomposite particles were fabricated when the ball-milling time was longer than 20 h. However, the nanocomposite particles were soldered and agglomerated again when the ball-milling time was longer than 60 h. The microstructure of the composite particles transformed from lamellar structure to nanostructure during the repeated process of the cold welding and cracking. TEM image reveals clearly that the in-situ TiC nanoparticles with grain size of 3–8 nm are in the interior of the stainless steel/TiC nanocomposite particles obtained by ball-milling 100 h.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang H M, Hei Z K, Liu G, et al. Formation of Nano-Structureed Surface Layer on AISI 304 Stainless Steel by Means of Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment[J]. Acta Mater., 2003, 51(7): 1 871
Wang Li. Tensile and Wear Properties of TiC Reinforced 420 Stainless Steel Fabricated by in situ Synthesis[J]. Journal of Southeast University, 2004, 20(4): 846–491
C T Kwok, F T Cheng, H C Man, et al. Corrosion Characteristics of Nanostructured Layer on 316L Stainless Steel Fabricated by Cavitation-annealing[J]. Materials Letters, 2006, 60: 2 419–2 422
C L Yeh, H J Wang. Comparative Study on Combustion Synthesis of Ta-Si Compounds[J]. Intermetallics, 2007, 15(10): 1 277–1 284
Masahiro Kubota. Properties of Nano-structured Pure A1 Produced by Mechanical Grinding and Spark Plasma Sintering[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 434–435: 294–297
L J Yang. The Effect of Solidification Time in Squeeze Casting of Aluminium and Zinc Alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 192: 114–120
Masafumi Chiba, Hideki Hotta, Tohru Nobuki. Microstructure Dependence of the Magnetic Properties in Fine Mg-Tm (Tm: Co, Fe) Particles by Using a Mechanical Alloying Technique[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2007, 316(2): 454–457
Chen L F, Liu Y, Tang H P, et al. The Study of in situ TiC Reinforced Ti Matrix Composites[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005, 34(10): 1 609–1 612 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (No. 2006ABA304)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Zhou, J. Preparation and characterization of stainless steel/TiC nanocomposite particles by ball-milling method. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 24, 38–41 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-009-1038-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-009-1038-3